User login
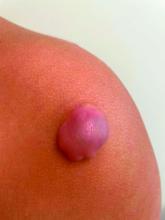
Given the characteristic clinical presentation, the most likely diagnosis is pilomatrixoma.
Pilomatrixomas are benign adnexal tumors that arise from immature matrix cells of the hair follicles located on dermal or subcutaneous tissue.
The cause of pilomatrixoma remains unclear. Recent studies have suggested that the development of pilomatrixoma are related to mutations in the Wnt signaling pathway, where beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1) mutation is the most frequently reported.1-4
Pilomatrixomas are more common in children and often present before 10 years of age.1,2,5 They commonly appear in head and neck, as well as upper extremities, trunk, and lower extremities.2,6
The clinical manifestations of pilomatrixomas are diverse and according to their appearance five classic clinical types are described: mass, pigmented, mixed, ulcerated, and keloid-like.2,3 The mass type is the predominant form, where it generally presents as a hard and freely mobile nodule covered by skin that may present a firm calcified protruding nodule. Other less common types include: lymphangiectasic, anetodermic, perforating, and bullous.2,6,7
Pilomatrixomas are mostly solitary, whereas multiple forms are reported to be associated with familial inheritance or syndromic conditions, such as myotonic dystrophy, Gardner syndrome, Turner’s syndrome, and Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.2-4 However, children and adolescents occasionally present with multiple pilomatricomas with no associated syndrome.
On physical exam a helpful features for the diagnosis is the “teeter-totter sign,” which can be illustrated by pressing on one edge of the lesion that will cause the opposite edge to protrude from the skin. Another helpful tool is to use a light to transilluminate and the calcification produces a bluish opaque hue,8 as light cannot transmit through the calcification, often differentiating it from epidermal inclusion cysts or other noncalcified lesions.
What is the differential diagnosis?
Because of the diverse clinical presentations, pilomatrixomas are frequently misdiagnosed. The percentage of correct preoperative diagnosis reported is low, varying from 16% to 43% in different series.1,9-11 They most frequently are misdiagnosed as other types of cysts such as epidermal, dermoid, or sebaceous.2,3,5,12,13 Rapidly growing pilomatrixomas can be also be misdiagnosed as malignant soft-tissue tumors, cutaneous lymphoma, or sarcomas.5,13
When presenting with a classic history and physical features, diagnosis is clinical, and no further studies are recommended.14 To improve diagnostic accuracy when encountering unusual subtypes, imaging is recommended, including ultrasound. Ultrasound adds a high positive predictive value (95.56%).2 Generally, on ultrasound a pilomatrixoma is described as an oval, well-defined, heterogeneous, hyperechoic subcutaneous mass with or without posterior shadowing.2 The definitive diagnosis is, however, made by histopathologic examination.
Pilomatrixomas do not spontaneously regress, therefore complete surgical resection is the standard treatment. During the follow-up period, very low recurrence rates have been reported, varying from 1.5% to 2% which generally occurs because of incomplete resection.2,3
Plexiform neurofibromas are usually congenital tumors of peripheral nerve sheath associated with neurofibromatosis type 1, often with a “bag of worms” feel on palpation. Epidermoid cysts generally present as dermal nodules often with a visible puncture, mobile on soft and mobile on palpation. Dermatofibromas present as firm, usually hyperpigmented papule or nodules that are fixed to subcutaneous tissue, thus often “dimpling” when pitched. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare soft-tissue sarcoma which presents as a firm, slow growing indurated plaques growing over months to years.
Conclusion
Pilomatrixomas are a benign adnexal tumor that sometimes can present as atypical forms such as this case. Diagnosis is usually based on clinical diagnosis, and transillumination can be a bedside clue. When the clinical diagnosis remains obscure an ultrasound can be helpful. The main aim of this case is to improve awareness of the variable presentations of pilomatrixomas and the importance of high level of suspicion supported by careful clinical evaluation.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Al-Nabti is a clinical fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego. Dr. Guelfand is a visiting dermatology resident in the division of pediaric and adolescent dermatology, University of Califonia, San Diego.
References
1. Jones CD et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:631-41.
2. Hu JL et al. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2020;21(5):288-93.
3. Adhikari G and Jadhav GS. Cureus. 2022;14(2):22228.
4. Cóbar JP et al. J Surg Case Rep. 2023;2023(4):rjad182.
5. Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;85:148-53.
6. Kose D et al. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014;10(3):549-51.
7. Sabater-Abad J et al. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26(8):13030/qt4h16s45w.
8. Alkatan HM et al. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021;84:106068.
9. Pant I et al. Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:390-2.
10. Kaddu S et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 1996;18(4):333-8
11. Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;85:148-53.
12. Wang YN et al. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(16):2011-2.
13. Yannoutsos A et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40(9):690-3.
14. Zhao A et al. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021;1455613211044778.
Given the characteristic clinical presentation, the most likely diagnosis is pilomatrixoma.
Pilomatrixomas are benign adnexal tumors that arise from immature matrix cells of the hair follicles located on dermal or subcutaneous tissue.
The cause of pilomatrixoma remains unclear. Recent studies have suggested that the development of pilomatrixoma are related to mutations in the Wnt signaling pathway, where beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1) mutation is the most frequently reported.1-4
Pilomatrixomas are more common in children and often present before 10 years of age.1,2,5 They commonly appear in head and neck, as well as upper extremities, trunk, and lower extremities.2,6
The clinical manifestations of pilomatrixomas are diverse and according to their appearance five classic clinical types are described: mass, pigmented, mixed, ulcerated, and keloid-like.2,3 The mass type is the predominant form, where it generally presents as a hard and freely mobile nodule covered by skin that may present a firm calcified protruding nodule. Other less common types include: lymphangiectasic, anetodermic, perforating, and bullous.2,6,7
Pilomatrixomas are mostly solitary, whereas multiple forms are reported to be associated with familial inheritance or syndromic conditions, such as myotonic dystrophy, Gardner syndrome, Turner’s syndrome, and Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.2-4 However, children and adolescents occasionally present with multiple pilomatricomas with no associated syndrome.
On physical exam a helpful features for the diagnosis is the “teeter-totter sign,” which can be illustrated by pressing on one edge of the lesion that will cause the opposite edge to protrude from the skin. Another helpful tool is to use a light to transilluminate and the calcification produces a bluish opaque hue,8 as light cannot transmit through the calcification, often differentiating it from epidermal inclusion cysts or other noncalcified lesions.
What is the differential diagnosis?
Because of the diverse clinical presentations, pilomatrixomas are frequently misdiagnosed. The percentage of correct preoperative diagnosis reported is low, varying from 16% to 43% in different series.1,9-11 They most frequently are misdiagnosed as other types of cysts such as epidermal, dermoid, or sebaceous.2,3,5,12,13 Rapidly growing pilomatrixomas can be also be misdiagnosed as malignant soft-tissue tumors, cutaneous lymphoma, or sarcomas.5,13
When presenting with a classic history and physical features, diagnosis is clinical, and no further studies are recommended.14 To improve diagnostic accuracy when encountering unusual subtypes, imaging is recommended, including ultrasound. Ultrasound adds a high positive predictive value (95.56%).2 Generally, on ultrasound a pilomatrixoma is described as an oval, well-defined, heterogeneous, hyperechoic subcutaneous mass with or without posterior shadowing.2 The definitive diagnosis is, however, made by histopathologic examination.
Pilomatrixomas do not spontaneously regress, therefore complete surgical resection is the standard treatment. During the follow-up period, very low recurrence rates have been reported, varying from 1.5% to 2% which generally occurs because of incomplete resection.2,3
Plexiform neurofibromas are usually congenital tumors of peripheral nerve sheath associated with neurofibromatosis type 1, often with a “bag of worms” feel on palpation. Epidermoid cysts generally present as dermal nodules often with a visible puncture, mobile on soft and mobile on palpation. Dermatofibromas present as firm, usually hyperpigmented papule or nodules that are fixed to subcutaneous tissue, thus often “dimpling” when pitched. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare soft-tissue sarcoma which presents as a firm, slow growing indurated plaques growing over months to years.
Conclusion
Pilomatrixomas are a benign adnexal tumor that sometimes can present as atypical forms such as this case. Diagnosis is usually based on clinical diagnosis, and transillumination can be a bedside clue. When the clinical diagnosis remains obscure an ultrasound can be helpful. The main aim of this case is to improve awareness of the variable presentations of pilomatrixomas and the importance of high level of suspicion supported by careful clinical evaluation.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Al-Nabti is a clinical fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego. Dr. Guelfand is a visiting dermatology resident in the division of pediaric and adolescent dermatology, University of Califonia, San Diego.
References
1. Jones CD et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:631-41.
2. Hu JL et al. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2020;21(5):288-93.
3. Adhikari G and Jadhav GS. Cureus. 2022;14(2):22228.
4. Cóbar JP et al. J Surg Case Rep. 2023;2023(4):rjad182.
5. Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;85:148-53.
6. Kose D et al. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014;10(3):549-51.
7. Sabater-Abad J et al. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26(8):13030/qt4h16s45w.
8. Alkatan HM et al. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021;84:106068.
9. Pant I et al. Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:390-2.
10. Kaddu S et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 1996;18(4):333-8
11. Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;85:148-53.
12. Wang YN et al. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(16):2011-2.
13. Yannoutsos A et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40(9):690-3.
14. Zhao A et al. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021;1455613211044778.
Given the characteristic clinical presentation, the most likely diagnosis is pilomatrixoma.
Pilomatrixomas are benign adnexal tumors that arise from immature matrix cells of the hair follicles located on dermal or subcutaneous tissue.
The cause of pilomatrixoma remains unclear. Recent studies have suggested that the development of pilomatrixoma are related to mutations in the Wnt signaling pathway, where beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1) mutation is the most frequently reported.1-4
Pilomatrixomas are more common in children and often present before 10 years of age.1,2,5 They commonly appear in head and neck, as well as upper extremities, trunk, and lower extremities.2,6
The clinical manifestations of pilomatrixomas are diverse and according to their appearance five classic clinical types are described: mass, pigmented, mixed, ulcerated, and keloid-like.2,3 The mass type is the predominant form, where it generally presents as a hard and freely mobile nodule covered by skin that may present a firm calcified protruding nodule. Other less common types include: lymphangiectasic, anetodermic, perforating, and bullous.2,6,7
Pilomatrixomas are mostly solitary, whereas multiple forms are reported to be associated with familial inheritance or syndromic conditions, such as myotonic dystrophy, Gardner syndrome, Turner’s syndrome, and Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.2-4 However, children and adolescents occasionally present with multiple pilomatricomas with no associated syndrome.
On physical exam a helpful features for the diagnosis is the “teeter-totter sign,” which can be illustrated by pressing on one edge of the lesion that will cause the opposite edge to protrude from the skin. Another helpful tool is to use a light to transilluminate and the calcification produces a bluish opaque hue,8 as light cannot transmit through the calcification, often differentiating it from epidermal inclusion cysts or other noncalcified lesions.
What is the differential diagnosis?
Because of the diverse clinical presentations, pilomatrixomas are frequently misdiagnosed. The percentage of correct preoperative diagnosis reported is low, varying from 16% to 43% in different series.1,9-11 They most frequently are misdiagnosed as other types of cysts such as epidermal, dermoid, or sebaceous.2,3,5,12,13 Rapidly growing pilomatrixomas can be also be misdiagnosed as malignant soft-tissue tumors, cutaneous lymphoma, or sarcomas.5,13
When presenting with a classic history and physical features, diagnosis is clinical, and no further studies are recommended.14 To improve diagnostic accuracy when encountering unusual subtypes, imaging is recommended, including ultrasound. Ultrasound adds a high positive predictive value (95.56%).2 Generally, on ultrasound a pilomatrixoma is described as an oval, well-defined, heterogeneous, hyperechoic subcutaneous mass with or without posterior shadowing.2 The definitive diagnosis is, however, made by histopathologic examination.
Pilomatrixomas do not spontaneously regress, therefore complete surgical resection is the standard treatment. During the follow-up period, very low recurrence rates have been reported, varying from 1.5% to 2% which generally occurs because of incomplete resection.2,3
Plexiform neurofibromas are usually congenital tumors of peripheral nerve sheath associated with neurofibromatosis type 1, often with a “bag of worms” feel on palpation. Epidermoid cysts generally present as dermal nodules often with a visible puncture, mobile on soft and mobile on palpation. Dermatofibromas present as firm, usually hyperpigmented papule or nodules that are fixed to subcutaneous tissue, thus often “dimpling” when pitched. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans is a rare soft-tissue sarcoma which presents as a firm, slow growing indurated plaques growing over months to years.
Conclusion
Pilomatrixomas are a benign adnexal tumor that sometimes can present as atypical forms such as this case. Diagnosis is usually based on clinical diagnosis, and transillumination can be a bedside clue. When the clinical diagnosis remains obscure an ultrasound can be helpful. The main aim of this case is to improve awareness of the variable presentations of pilomatrixomas and the importance of high level of suspicion supported by careful clinical evaluation.
Dr. Eichenfield is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, and Rady Children’s Hospital, San Diego. Dr. Al-Nabti is a clinical fellow in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology, University of California, San Diego. Dr. Guelfand is a visiting dermatology resident in the division of pediaric and adolescent dermatology, University of Califonia, San Diego.
References
1. Jones CD et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40:631-41.
2. Hu JL et al. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2020;21(5):288-93.
3. Adhikari G and Jadhav GS. Cureus. 2022;14(2):22228.
4. Cóbar JP et al. J Surg Case Rep. 2023;2023(4):rjad182.
5. Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;85:148-53.
6. Kose D et al. J Cancer Res Ther. 2014;10(3):549-51.
7. Sabater-Abad J et al. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26(8):13030/qt4h16s45w.
8. Alkatan HM et al. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2021;84:106068.
9. Pant I et al. Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55:390-2.
10. Kaddu S et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 1996;18(4):333-8
11. Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016;85:148-53.
12. Wang YN et al. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(16):2011-2.
13. Yannoutsos A et al. Am J Dermatopathol. 2018;40(9):690-3.
14. Zhao A et al. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021;1455613211044778.
On physical exam there was a well-circumscribed skin-colored nodule measuring 3.1 x 3 cm that was tender on palpation. The nodule was mobile, with a firm, stony feel, and no punctum was visualized. Transillumination revealed a subtle bluish hue within the nodule.