Dermpath Diagnosis
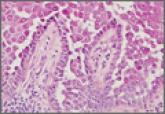
Hailey-Hailey Disease
Hailey-Hailey disease typically presents as suprabasal blisters with a perivascular and interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate. The differential...
Katherine S. Redding, MD, MSPH; Emily H. Jones, MD; Tejesh Patel, MD; Robert B. Skinner, MD
From the Department of Dermatology, University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Emily H. Jones, MD, 930 Madison Ave, Ste 840, Memphis, TN 38163 (emjones25@gmail.com).

Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is a superficial blistering disorder mediated by Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxins. It is rare in adults, but when diagnosed, it often is associated with renal failure, immunodeficiency, or overwhelming staphylococcal infection. A unique case of a pregnant woman with chronic atopic dermatitis who developed SSSS is presented.
To the Editor:
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) is a superficial blistering disorder mediated by Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxins (ETs).1 It is rare in adults, but when diagnosed, it is often associated with renal failure, immunodeficiency, or overwhelming staphylococcal infection.2 We present a unique case of a pregnant woman with chronic atopic dermatitis (AD) who developed SSSS.
A 21-year-old gravida 3, para 2, aborta 0pregnant woman (29 weeks’ gestation) with a history of chronic AD who was hospitalized with facial edema, purulent ocular discharge, and substantial worsening of AD presented for a dermatology consultation. Her AD was previously managed with topical steroids but had been complicated by multiple methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections. On physical examination, she had substantial periorbital edema with purulent discharge from both eyes (Figure 1A), perioral crust with radial fissures (Figure 2A), and mild generalized facial swelling and desquamation (Figure 3). However, the oral cavity was not involved. She had diffuse desquamation in addition to chronic lichenified plaques of the arms, legs, and trunk and SSSS was clinically diagnosed. Cultures of conjunctival discharge were positive for MRSA. The patient was treated with intravenous vancomycin and had a full recovery (Figures 1B and 2B). She delivered a healthy newborn with Apgar scores of 9 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively, at 36 weeks and 6 days’ gestation by cesarean delivery; however, her postoperative care was complicated by preeclampsia, which was treated with magnesium sulfate. The newborn showed no evidence of infection or blistering at birth or during the hospital stay.
Figure 1. Periorbital edema with purulent ocular discharge before (A) and after (B) treatment. | Figure 2. Perioral desquamation and radial fissuring before (A) and after (B) treatment. |
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is a superficial blistering disorder that ranges in severity from localized blisters to generalized exfoliation.1 Exfoliative toxin is the major virulence factor responsible for SSSS. Exfoliative toxin is a serine protease that targets desmoglein 1, resulting in intraepidermal separation of keratinocytes.3 Two serologically distinct exfoliative toxins—ETA and ETB—have been associated with human disease.4 Although ETA is encoded on a phage genome, ETB is encoded on a large plasmid.3 Initially it was thought that only strains of S aureus carrying lytic group II phages were responsible for ET production; however, it is now accepted that all phage groups are capable of producing ET and causing SSSS.1
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome is most common in infants and children and rare in adults. Although it has been occasionally described in otherwise healthy adults,5 it is most often diagnosed in patients with renal failure (decreased toxin excretion), immunodeficiency (lack of antibodies against toxins), and overwhelming staphylococcal infection (excessive toxin).2 Mortality in treated children is low, but it can reach almost 60% in adults1; therefore, defining risk factors that may aid in early diagnosis are exceedingly important.
We believe that both our patient’s history of AD and her pregnancy contributed to the development of SSSS. The patient had a history of multiple MRSA infections prior to this hospitalization, suggesting MRSA colonization, which is a common complication of AD with more than 75% of AD patients colonized with S aureus.6 Additionally, S aureus superantigen stimulation can result in the loss of regulatory T cells’ natural immunosuppression. Regulatory T cells are remarkably increased in patients with AD; therefore, the inflammatory response to S aureus is likely amplified in an atopic patient, as there is more native immunosuppressive capacity to be affected.4 Furthermore, we believe that pregnancy and its associated immunomodulation is a risk for SSSS. Immune changes in pregnancy are still not well understood; however, it is known that there are alterations to allow symbiosis between the mother and fetus. Anti-ET IgG antibodies are thought to play an important role in protecting against SSSS. Historically, studies on serum immunoglobulin levels during pregnancy have had conflicting findings. They have shown that IgG is either unchanged or decreased, while IgA, IgE, and IgM can be increased, decreased, or unchanged.7 In a study of immunoglobulins in pregnancy, Bahna et al7 showed that IgE is unchanged over the course of pregnancy, but their analysis did not address IgG levels. If IgG levels in fact decrease during pregnancy, the mother could be at risk for SSSS due to her inability to neutralize toxins. Even if total IgG levels remain unchanged, it is possible that specific antitoxin antibodies are decreased. Additionally, there is a documented suppression and alteration in T-cell response to prevent fetal rejection during pregnancy.8 Adult SSSS has been documented several times in human immunodeficiency virus–positive patients, suggesting there may be some association between T-cell suppression and SSSS susceptibility.9 Interestingly, pregnancy, similar to AD, results in an increase in immunosuppressive T cells,10 which, if deactivated by superantigens, could potentially contribute to an increased inflammatory response. All of these immune system alterations likely leave the mother vulnerable to toxin-mediated events such as SSSS.

Hailey-Hailey disease typically presents as suprabasal blisters with a perivascular and interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate. The differential...
No abstract available.
