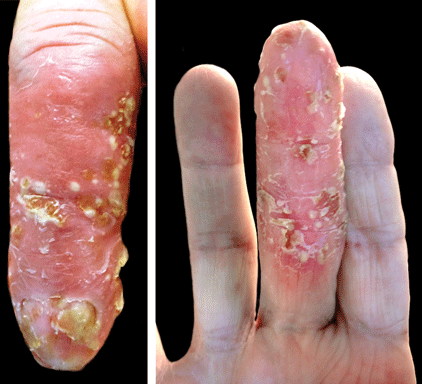
The Diagnosis: Acrodermatitis Continua of Hallopeau
Acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau (ACH) is considered to be a form of acropustular psoriasis that presents as a sterile, pustular eruption initially affecting the fingertips and/or toes.1 The slow-growing pustules typically progress locally and can lead to onychodystrophy and/or osteolysis of the underlying bone.2,3 Most commonly affecting adult women, ACH often begins following local trauma to or infection of a single digit.4 As the disease progresses proximally, the small pustules burst, leaving a shiny, erythematous surface on which new pustules can develop. These pustules have a tendency to amalgamate, leading to the characteristic clinical finding of lakes of pus. Pustules frequently appear on the nail matrix and nail bed presenting as severe onychodystrophy and ultimately anonychia.5,6 Rarely, ACH can be associated with generalized pustular psoriasis as well as conjunctivitis, balanitis, and fissuring or annulus migrans of the tongue.2,7
Diagnosis can be established based on clinical findings, biopsy, and bacterial and fungal cultures revealing sterile pustules.8,9 Histologic findings are similar to those seen in pustular psoriasis, demonstrating subcorneal neutrophilic pustules, Munro microabscesses, and dilated blood vessels with lymphocytic infiltrate in the papillary dermis.10
Due to the refractory nature of the disease, there are no recommended guidelines for treatment of ACH. Most successful treatment regimens consist of topical psoriasis medications combined with systemic psoriatic therapies such as cyclosporine, methotrexate, acitretin, or biologic therapy.8,11-16 Our patient achieved satisfactory clinical improvement with clobetasol propionate ointment 0.05% twice daily alternating with calcipotriene cream 0.005% twice daily.