To the Editor:
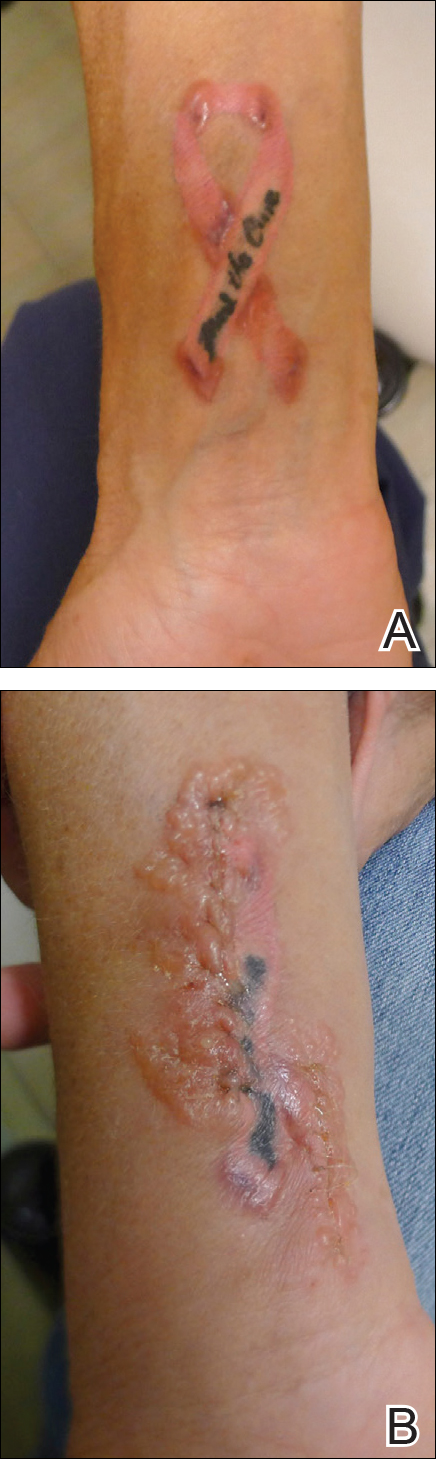
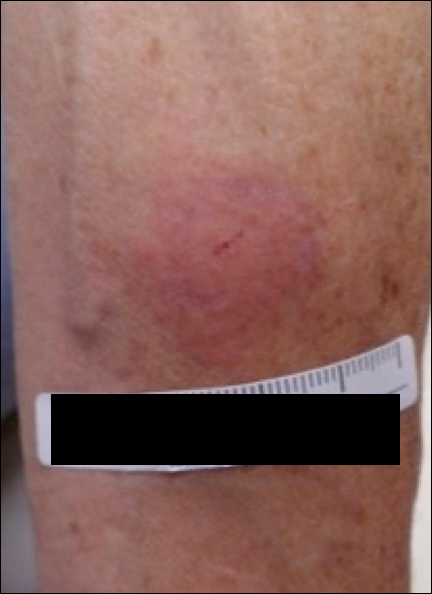
A 42-year-old woman who had a tattoo on the right wrist surgically removed 2 days prior developed severe erythema and swelling at the incision site (Figure 1). Exposure at the incision site was limited to bacitracin, poliglecaprone 25 suture, and plain cotton gauze. Patch testing of bacitracin was performed, which was ++ (moderately positive reaction) at the 96-hour reading, indicating that part of the reaction was due to the topical antibiotic. Testing of the suture was performed by tying the suture to the skin of the forearm and removing it at 48 hours. There was a ++ reaction to the suture prior to removal at 48 hours, which increased to +++ (severely positive reaction) after suture removal at 96 hours (Figure 2). Therefore, it appears that allergy to the suture also was partially responsible for the postsurgical reaction.
Poliglecaprone 25 suture is a monofilament synthetic absorbable material that is a copolymer of glycolide and ε-caprolactone. One case report of oral contact allergy to this suture material resulted in failure of an oral graft; however, no testing was performed to verify the contact allergy.1 Caprolactam ([CH2]5C[O]NH) is a related chemical that can be synthesized by treating caprolactone ([CH2]5CO2) with ammonia at elevated temperatures.2 Contact allergy has been reported to polyamide 6 suture, which is obtained by polymerizing ε-caprolactam. This report stated that contact allergy to ε-caprolactam also has been reported occupationally during manufacture and from its use in fishing nets, socks, gloves, and stockings.3
The package insert for the poliglecaprone 25 suture states that the material is “nonantigenic, nonpyrogenic and elicits only a slight tissue reaction during absorption.”4 We present a case of contact allergy to poliglecaprone 25 suture that was confirmed by allergy testing.