Case Letter
From the University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Michelle Bardack, MD, 2400 Tucker Ave NE, Albuquerque, NM 87131 (MiBardack@salud.unm.edu).

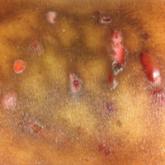
A 1-day-old Hispanic female infant was born via uncomplicated vaginal delivery at 41 weeks' gestation after a normal pregnancy. Linear plaques containing multiple ruptured vesicles and bullae following Blaschko lines were noted on the right medial thigh and anterior arm. The infant was afebrile and generally well-appearing.
The infant's mother was noted to have diffuse hypopigmented patches over the trunk, arms, and legs (present since adolescence) with whorled cicatricial alopecia of the vertex scalp and peg-shaped teeth (Figure). Together, these findings suggested incontinentia pigmenti (IP), which the mother revealed she had been diagnosed with in childhood. The infant's characteristic lesions in the setting of her mother's diagnosed genodermatosis confirmed the diagnosis of IP.
Incontinentia pigmenti is an X-linked dominant disorder that presents with many classic dermatologic, dental, neurologic, and ophthalmologic findings. The causative mutation occurs in IKBKG/NEMO (inhibitor of κ polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, kinase γ/nuclear factor-κB essential modulator) gene on Xq28, disabling the resultant protein that normally protects cells from tumor necrosis factor family-induced apoptosis.1 Incontinentia pigmenti usually is lethal in males and causes an unbalanced X-inactivation in surviving female IP patients. Occurring at a rate of 1.2 per 100,000 births,2 IP typically presents in female infants with skin lesions patterned along Blaschko lines that evolve in 4 stages over a lifetime.3 Stage I, presenting in the neonatal period, manifests as vesiculobullous eruptions on the limbs and scalp. Stages II to IV vary in duration from months to years and are comprised of a verrucous stage, a hyperpigmented stage, and a hypopigmented stage, respectively.3 All stages of IP can overlap and coexist.
The vesiculobullous findings in infants with IP may be mistakenly attributed to other diseases with prominent vesicular or bullous components including herpes simplex virus, epidermolysis bullosa, and infantile acropustulosis. With neonatal herpes simplex virus infection, vesicular skin or mucocutaneous lesions occur 9 to 11 days after birth and can be confirmed by specimen culture or qualitative polymerase chain reaction, while stage I of IP appears within the first 6 to 8 weeks of life and can be present at birth.4 The hallmark of epidermolysis bullosa, caused by mutations in keratins 5 and 14, is blistering erosions of the skin in response to frictional stress,1 thus these lesions do not follow Blaschko lines. Infantile acropustulosis, a nonheritable vesiculopustular eruption of the hands and feet, rarely occurs in the immediate newborn period; it most often appears in the 3- to 6-month age range with recurrent eruptions at 3- to 4-week intervals.5 Focal dermal hypoplasia is another X-linked dominant disorder with blaschkolinear findings at birth that presents with pink or red, angular, atrophic macules, in contrast to the bullous lesions of IP.6
Incontinentia pigmenti may encompass a wide range of systemic symptoms in addition to the classic dermatologic findings. Notably, central nervous system defects are concurrent in up to 40% of IP cases, with seizures, mental retardation, and spastic paresis being the most common sequelae.7 Teeth defects, seen in 35% of patients, include delayed primary dentition and peg-shaped teeth. Many patients will experience ophthalmologic defects including vision problems (16%) and retinopathy (15%).7
The cutaneous eruptions of IP may be treated with topical corticosteroids or topical tacrolimus, and vesicles should be left intact and monitored for signs of infection.8,9 Seizures, if present, should be treated with anticonvulsants, and regular neuropsychiatric monitoring and physical rehabilitation may be warranted. Patients should be regularly monitored for retinopathy beginning at the time of diagnosis. Retinal fibrovascular proliferation is treated with xenon laser photocoagulation to reduce the high risk for retinal detachment in this population.10,11 Older and younger at-risk relatives must be evaluated by genetic testing or thorough physical examination to clarify their disease status and determine the need for additional genetic counseling.

Annular atrophic lichen planus (AALP) is a rare variant of lichen planus. The clinical presentation of AALP shows distinct atrophic plaques with...
Granuloma faciale (GF) is an uncommon cutaneous disease of uncertain etiology that predominantly affects the face. Extrafacial lesions are rare....
