Nevus sebaceus (NS) is a benign hair follicle neoplasm present in approximately 1.3% of the population, typically involving the scalp, neck, or face.1 These lesions usually are present at birth or identified soon after, during the first year. They present as a yellowish hairless patch or plaque but can develop a more papillomatous appearance, especially after puberty. Historically, the concern with NS was its tendency to transform into basal cell carcinoma (BCC), which prompted surgical excision of the lesion during childhood. This theory has been discounted more recently, as further research has suggested that what was once thought to be BCC may have been confused with the similarly appearing trichoblastoma; however, malignant transformation of NS does still occur, with BCC still being the most common.2 We present the case of a long-standing NS with rare transformation to apocrine carcinoma.
Case Report
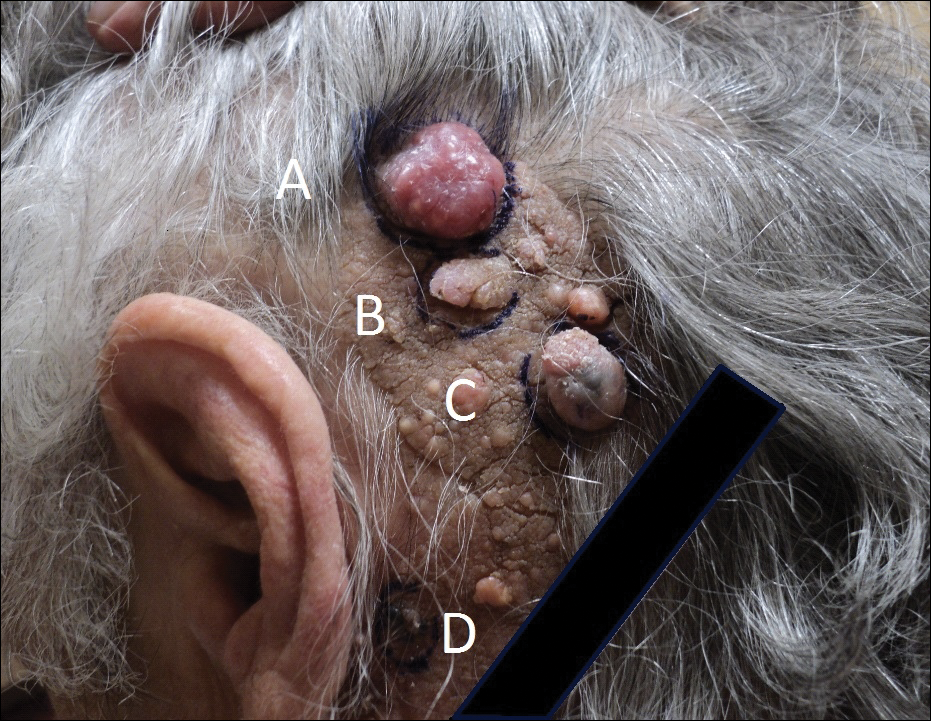
A 76-year-old woman presented with several new lesions within a previously diagnosed NS. She reported having the large plaque for as long as she could recall but reported that several new growths developed within the plaque over the last 2 months, slowly increasing in size. She reported a prior biopsy within the growth several years prior, which she described as an irritated seborrheic keratosis.
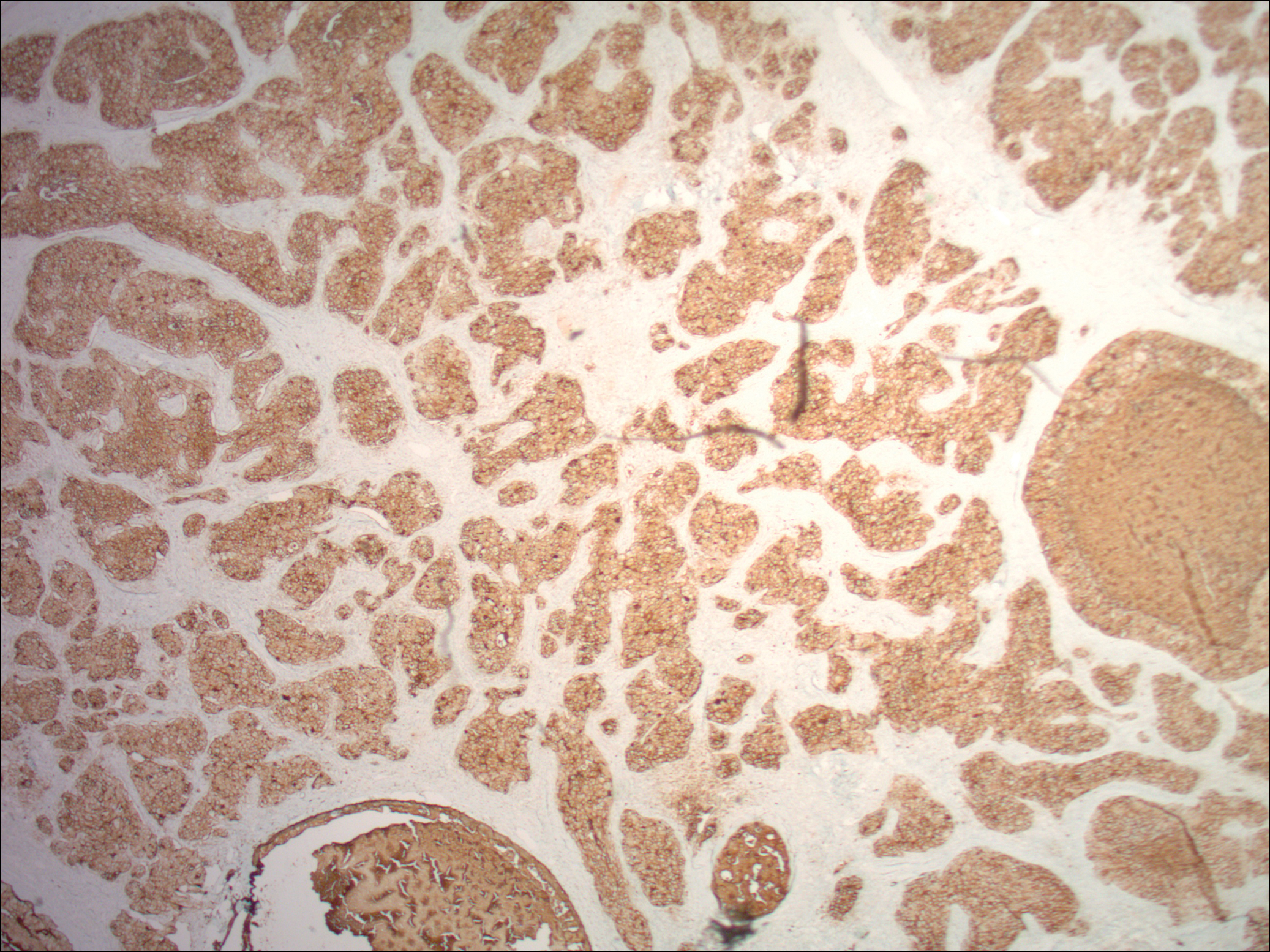
Physical examination demonstrated 4 distinct lesions within the flesh-colored, verrucous plaque located on the left side of the temporal scalp (Figure 1). The first lesion was a 2.5-cm pearly, pink, exophytic tumor (labeled as A in Figure 1). The next 2 lesions were brown, pedunculated, verrucous papules (labeled as B and C in Figure 1). The last lesion was a purple papule (labeled as D in Figure 1). Four shave biopsies were performed for histologic analysis of the lesions. Lesions B, C, and D were consistent with trichoblastomas, as pathology showed basaloid epithelial tumors that displayed primitive follicular structures, areas of stromal induction, and some pigmentation. Lesion A, originally thought to be suspicious for a BCC, was determined to be a primary cutaneous apocrine adenocarcinoma upon pathologic review. The pathology showed a dermal tumor displaying solid and tubular areas with decapitation secretion. Nuclear pleomorphism and mitoses were present (Figure 2), and staining for carcinoembryonic antigen was positive (Figure 3). Immunoreactivity with epithelial membrane antigen and cytokeratin 7 was noted as well as focal positivity for mammaglobin. Primary apocrine carcinoma was favored over metastatic carcinoma due to the location of the lesion within an NS along with a negative history of internal malignancy. Dermatopathology recommended complete removal of all lesions within the NS.
Upon discussing biopsy results and recommendations with our patient, she agreed to undergo excision with intraoperative pathology by a plastic surgeon within our practice to ensure clear margins. The surgical defect following excision was sizeable and closed utilizing a rhomboid flap, full-thickness skin graft, and a split-thickness skin graft. At surgical follow-up, she was doing well and there have been no signs of local recurrence for 10 months since excision.