The Diagnosis: Pediculosis Pubis
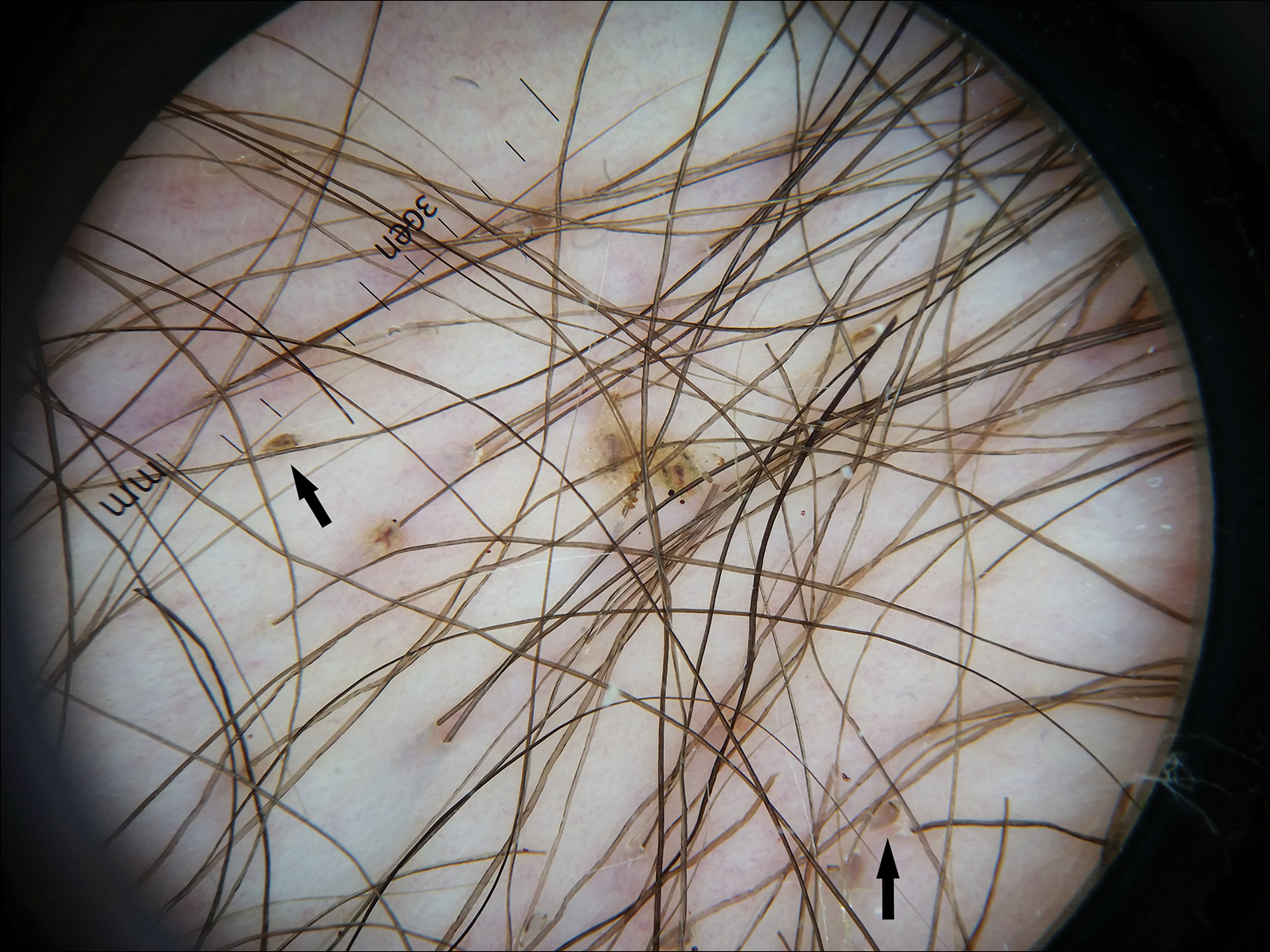
Dermoscopy of the pubic hair demonstrated a louse clutching multiple shafts of hairs (Figure) as well as scattered nits, confirming the presence of Phthirus pubis and diagnosis of pediculosis pubis. The key clinical diagnostic feature in this case was severe itching of the pubic area, with visible nits present on pubic hairs. Itching and infestation also can involve other hair-bearing areas such as the chest, legs, and axillae. The patient was treated with permethrin cream 5% applied to the pubic area and chest. Symptoms and infestation were resolved at 1-week follow-up.
Pediculosis pubis is an infestation of pubic hairs by the pubic (crab) louse P pubis, which feeds on host blood. Other body areas covered with dense hair also may be involved; 60% of patients are infested in at least 2 different sites.1 Pediculosis pubis is most commonly sexually transmitted through direct contact.2 Worldwide prevalence has been estimated at approximately 2% of the adult population, and a survey of 817 US college students in 2009 indicated a lifetime prevalence of 1.3%.3 The prevalence is slightly higher in men, highest in men who have sex with men, and rare in individuals with shaved pubic hair.1 The most common symptom is pruritus of the genital area. Infested patients also may develop asymptomatic bluish gray macules (maculae ceruleae) secondary to hemosiderin deposition from louse bites.4
The diagnosis of pediculosis pubis is made by identification of P pubis, either by examination with the naked eye or confirmation with dermoscopy or microscopy. Although the 0.8- to 1.2-mm lice are visible to the naked eye, they can be difficult to see if not filled with blood, and nits on the hairs can be mistaken for white piedra (fungal infection of the hair shafts) or trichomycosis pubis (bacterial infection of the hair shafts).4 Scabies and tinea cruris do not present with attachments to the hairs. Scabies may present with papules and burrows and tinea cruris with scaly erythematous plaques. Small numbers of lice and nits may be missed by the naked eye or a traditional magnifying glass.5 The use of dermoscopy allows for fast and accurate identification of the characteristic lice and nits, even in these more challenging cases.5 Accurate diagnosis is important, as approximately 31% of infested patients have other concurrent sexually transmitted infections that warrant screening.6
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends first-line treatment with permethrin cream (1% or 5%) or pyrethrin with piperonyl butoxide applied to all affected areas and washed off after 10 minutes.7 Patients should be reevaluated after 1 week if symptoms persist and re-treated if lice are found on examination.7,8 Malathion lotion 0.5% (applied and washed off after 8-12 hours) or oral ivermectin (250 µg/kg, repeated after 2 weeks) may be used for alternative therapies or cases of permethrin or pyrethrin resistance.7 Ivermectin also is effective for involvement of eyelashes where topical insecticides should not be used.9 Sexual partners should be treated to prevent repeat transmission.7,8 Bedding and clothing can be decontaminated by machine wash on hot cycle or isolating from body contact for 72 hours.7 Patients also should be screened for other sexually transmitted infections, including human immunodeficiency virus.6