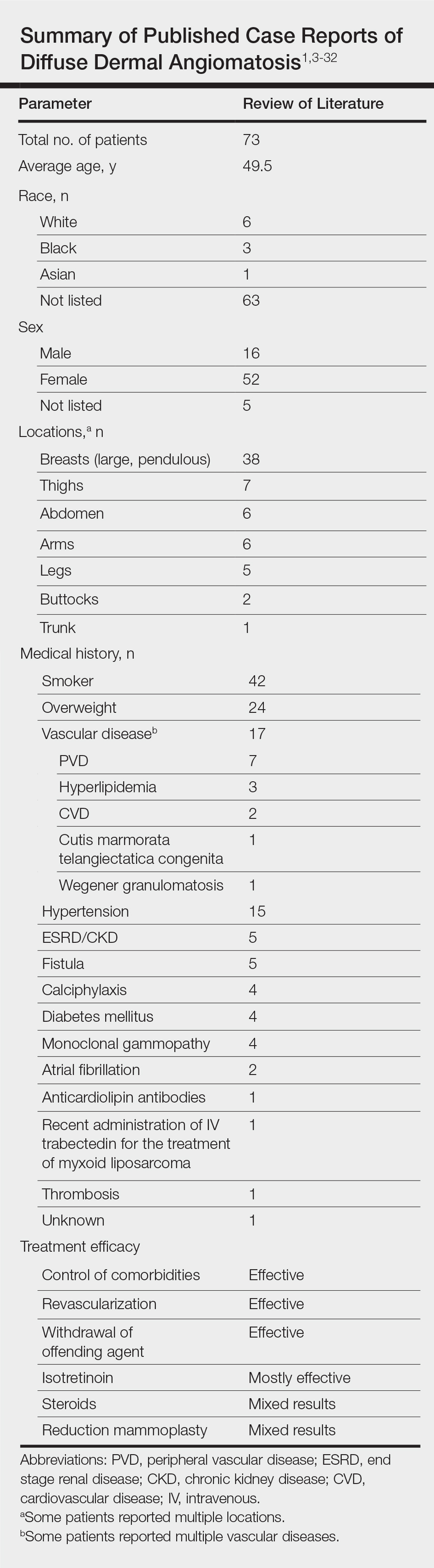
Vascular proliferation in DDA is hypothesized to stem from ischemia or inflammation.5 Peripheral vascular atherosclerosis has been associated with DDA.6 The epidemiology of DDA is not well known because of the rarity of the disease. We performed a more specific review of the literature by limiting the PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE to the term diffuse dermal angiomatosis rather than a broader search including all reactive angioendotheliomatoses. Only 31 case reports have been published1,3-32; of them, only adults were affected. Most reported cases were in middle-aged females. A summary of the demographics of DDA is provided in the Table.1,3-32
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of DDA remains unclear. It has been hypothesized that ischemia or inflammation creates local hypoxia, leading to an increase in vascular endothelial growth factor with subsequent endothelial proliferation and neovascularization.5 Rongioletti and Robora2 supported this hypothesis, proposing that occlusion or inflammation of the vasculature creates microthrombi and thus hypoxia. Afterward, histiocytes are recruited to reabsorb the microthrombi while hyperplasia of endothelial cells and pericytes ensues.7 Complete resolution of skin lesions following revascularization provides support for this theory.8
Etiology
Diffuse dermal angiomatosis is a rare complication of ischemia that may be secondary to atherosclerosis, arteriovenous fistula, or macromastia.9-11 In DDA of the breasts, ulcerations of fatty tissue occur due to trauma in these patients who have large pendulous breasts, causing angiogenesis resembling DDA histologically.2 One case of DDA was reported secondary to relative ischemia from cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita,12 whereas another case highlighted Wegener granulomatosis as the cause of ischemia.7 There also have been reported cases associated with calciphylaxis and anticardiolipin antibiodies.13 In general, any medical condition that can lead to ischemia can cause DDA. Comorbid conditions for DDA include cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and most often severe peripheral vascular disease. Many patients also have a history of smoking.14 Diffuse dermal angiomatosis rarely presents without underlying comorbidity, with only 1 case report of unknown cause (Table).
Presentation, Histopathology, and Differential Diagnosis
Cutaneous reactive angiomatosis disorders present the same clinically, with multiple erythematous to violaceous purpuric patches and plaques that can progress to necrosis and ulceration. Lesions are widely distributed but are predisposed to the upper and lower extremities.2 The differential diagnosis of DDA includes CREA, acroangiodermatitis (pseudo–Kaposi sarcoma), or vascular malignancies such as Kaposi sarcoma and low-grade angiosarcoma.7
In DDA, lesions may be painful and sometimes have a central ulceration.15 They often are associated with notable peripheral vascular atherosclerotic disease and are mainly found on the lower extremities.12,16 Histologically, DDA presents as a diffuse proliferation of endothelial cells between collagen bundles. The endothelial cells are distributed throughout the papillary and reticular dermis and develop into vascular lumina.17 Furthermore, the proliferating endothelial cells are spindle shaped and contain vacuolated cytoplasm.14