Photo Challenge
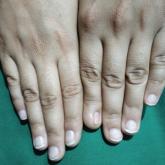
Micronychia of the Index Finger
A 21-year-old woman who was initially seeking dermatology consultation for acne also was noted to have micronychia of the nail of the left index...
From the Department of Dermatology and Key Laboratory of Immunodermatology, First Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyan.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81803148) and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0901504).
Correspondence: Song Zheng, MD, First Hospital of China Medical University, Nanjing N St, Heping District, Shenyang 110001, China (zhengsongcmu@163.com).

A 67-year-old man presented with pink nodules on the scalp that were enlarging and increasing over the course of 2 months. The patient was otherwise healthy, had no constitutional symptoms such as fever or weight loss, and did not note pruritus or pain. His medications included telmisartan and Salvia miltiorrhiza for hypertension and coronary heart disease, respectively. He had been a heavy smoker for 44 years. Physical examination revealed several dome-shaped, pink nodules with smooth surfaces distributed in an agminated appearance on the scalp. The lesions were indurated and ranged from 1 to 5 cm in diameter.
Biopsy revealed a cellular neoplasm consisting of atypical polygonal cells with a hobnailed appearance, vasoformative characteristics, and rare extravasated erythrocytes. The tumor had an infiltrative growth pattern as demonstrated by dissecting dermal collagen and a poorly defined border with adjacent normal tissue (Figure 1). Immunohistochemistry revealed that the lesion was positive for CD31 and D2-40 (Figure 2) but negative for cytokeratin, CD10, CD68, human herpesvirus 8, CD34, and Melan A, thus confirming the endothelial origin of the tumor cells and the diagnosis of cutaneous angiosarcoma (CAS). The patient was treated with extended surgical excision and radiation therapy. No recurrence or metastasis was found throughout 2 years of follow-up.
Radical resection with a negative margin is considered the first-line treatment of choice. Although there is a paucity of studies assessing the specific width of surgical margins, application of no less than a 3-cm peripheral margin as well as a clear deep margin is recommended.5 Adjuvant radiation therapy also is essential to prevent local recurrence. Patients receiving combination therapy have a superior overall survival rate when compared to those undergoing surgery or radiation therapy alone.4
Cutaneous follicle center lymphoma also may present as 1 or more localized erythematous papules, plaques, and/or nodules, commonly arising on the scalp/forehead or trunk of middle-aged men. Despite being a low-grade lymphoma with a favorable prognosis, it may have a relatively fast growth and locally aggressive course if left untreated. The distinguishing histologic feature is a dense proliferation of neoplastic infiltrates in the dermis, which is separated from the epidermis by the grenz zone.6
The clinical presentation of cutaneous metastatic carcinomas varies greatly, with 1 or multiple localized or widespread lesions commonly involving the abdominal wall, scalp, and face. The lesions also may mimic benign dermatologic conditions, thus potentially resulting in erroneous clinical diagnosis and delayed therapy of the primary malignancy. Obtaining clinical history is crucial; however, a precise diagnosis may require histologic examination.7
Atypical fibroxanthoma is a rare superficial cutaneous sarcoma that typically occurs on the head and neck in sun-damaged elderly individuals. Clinically, AFX presents as well-circumscribed red or pink nodules or plaques with or without ulceration, crust, or scale.8 Atypical fibroxanthoma lesions usually are small, with a median diameter of 1 cm, while those greater than 2 cm reportedly account for less than 5% of cases.9 Atypical fibroxanthoma typically grows rapidly with no pain or discomfort. Histologically, AFX is characterized by a well-circumscribed dermal nodule consisting of pleomorphic spindle cells and multinucleated giant cells that can stain positively for CD10 and procollagen 1.10
Cutaneous pseudolymphoma is a benign inflammatory response process that stimulates polyclonal T- or B-cell lymphoproliferation. The clinical presentation may appear as localized or disseminated flesh-colored or red papules, infiltrated plaques, and nodules.11 Histopathology will show mixtures of B and T cells along with dendritic cells and macrophages, but irregular vascular structure and dissecting dermal collagen are not involved.
We present an unusual case of CAS with multiple pink nodules on the scalp. Early biopsy of these lesions is important to reach a correct diagnosis and to initiate appropriate treatment.

A 21-year-old woman who was initially seeking dermatology consultation for acne also was noted to have micronychia of the nail of the left index...
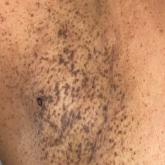
A 50-year-old Hispanic woman presented with asymptomatic, progressive, brown hyperpigmentation involving the axillae, neck, upper back, and...
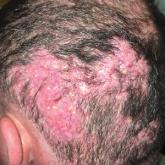
A 35-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with a slow-growing plaque on the scalp of 10 years’ duration. The lesion was mildly...
