Treatment of Recurrent Cases—For the 5 patients with recurrence, surgical margins were not reported in all the cases but ranged from 0.5 to 2 cm (4/5 [80%] reported). On average, follow-up for this group of patients was 29 months, with a range of 12 to 60 months (Table 3).
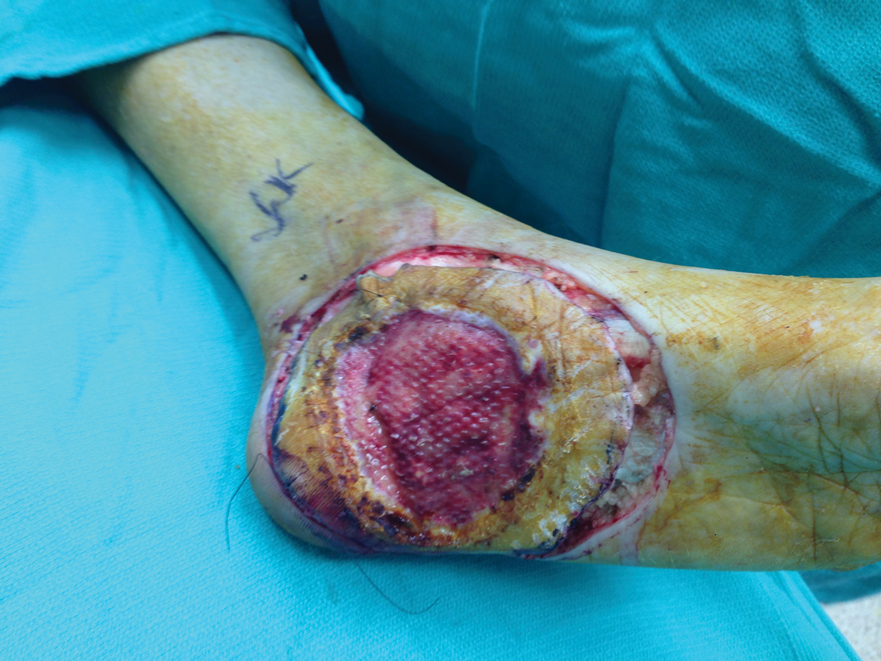
The first case with a recurrence (patient 12) initially presented with a chronic calluslike growth of the medial ankle. The lesion initially was treated with wide local excision with negative margins. Reconstruction was performed in a staged fashion with use of a dermal regenerative template followed later by split-thickness skin grafting. Tumor recurrence with negative margins occurred 3 times over the next 2 years despite re-resections with negative pathologic margins. Each recurrence presented as graft breakdown and surrounding hyperkeratosis (Figure 3). After the third graft placement failed, the patient elected for a BKA. There has not been recurrence since the BKA after 5 years total follow-up from the time of primary tumor resection. Of note, this was the only patient in our cohort who was immunosuppressed and evaluated for regional nodal involvement by positron emission tomography.
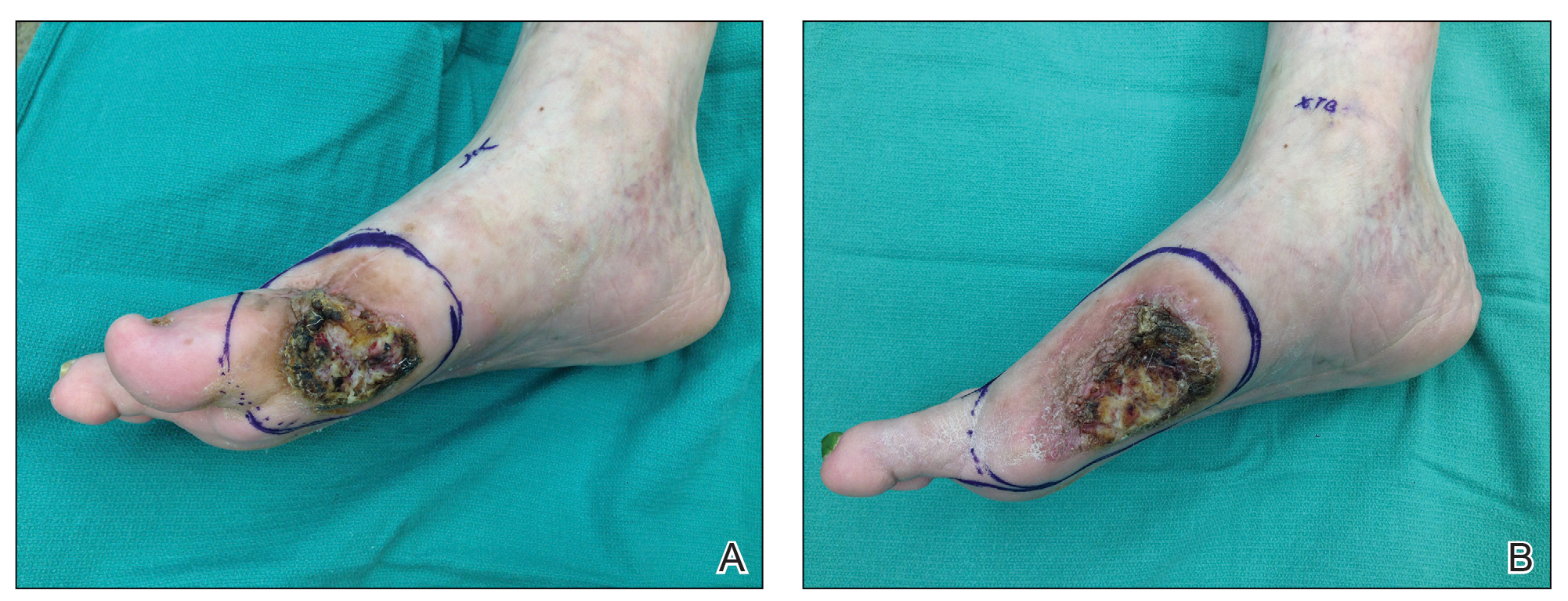
Another patient with recurrence (patient 13) presented with a chronic great toe ulcer of 5 years’ duration that formed on the dorsal aspect of the great toe after a previously excised wart (Figure 4A). This patient underwent mid-proximal metatarsal amputation with 2-cm margins and subsequent skin graft. Pathologic margins were negative. Within 6 months, there was hyperkeratosis and a draining wound (Figure 4B). Biopsy results confirmed recurrent disease that was treated with re-resection, including complete metatarsal amputation with negative margins and skin graft placement. Verrucous carcinoma recurred at the edges of the graft within 8 months, and the patient elected for a BKA. In addition, this patient also presented with a verrucous carcinoma of the contralateral great toe. The tumor presented as a warty ulcer of 4 months’ duration in the setting of osteomyelitis and was resected by great toe amputation that was performed concurrently with the opposite leg BKA; there has been no recurrence. Of note, this was the only patient to have right inguinal sentinel lymph node tissue sampled and HPV testing conducted, which were negative for verrucous carcinoma and high or low strains of HPV.
Another recurrent case (patient 14) presented with a large warty lesion on the dorsal great toe positive for verrucous carcinoma. He underwent a complete great toe amputation with skin graft placement. Verrucous carcinoma recurred on the edges of the graft within 6 months, and the patient was lost to follow-up when a BKA was suggested.
The fourth recurrent case (patient 15) initially had been treated for 1 year as a viral verruca of the dorsal aspect of the great toe. He had an exophytic mass positive for verrucous carcinoma growing on the dorsal aspect of the great toe around the prior excision site. After primary wide excision with negative 1-cm margins and graft placement, the tumor was re-excised twice within the next 2 years with pathologic negative margins. The patient underwent a foot amputation due to a severe osteomyelitis infection at the reconstruction site.
The final recurrent case (patient 16) presented with a mass on the lateral great toe that initially was treated as a viral verruca (for unknown duration) that had begun to ulcerate. The patient underwent wide excision with 1-cm margins and graft placement. Final pathology was consistent with verrucous carcinoma with negative margins. Recurrence occurred within 11 months on the edge of the graft, and a great toe amputation through the metatarsal phalangeal joint was performed.
Comment
Our series of 19 cases of verrucous carcinoma adds to the limited number of reported cases in the literature. We sought to evaluate the potential risk factors for early recurrence. Consistent with prior studies, our series found verrucous carcinoma of the foot to occur most frequently in patients aged 50 to 70 years, predominantly in White men.1 These tumors grew in the setting of chronic inflammation, tissue regeneration, multiple comorbidities, and poor wound hygiene. Misdiagnosis of verrucous carcinoma often leads to ineffective treatments and local invasion of nerves, muscle, and bone tissue.9,15,16 Our case series also clearly demonstrated the diagnostic challenge verrucous carcinoma presents, with an average delay in diagnosis of 5 years; correct diagnosis often did not occur until the tumor was 4 cm in size (average) and more than 50% had chronic ulceration. Tissue collection of the raised ulcer borders and the deep dermis layer of warty lesions is imperative for diagnosis. Clinicians should have a high suspicion for verrucous carcinoma in the setting of a chronic ulceration or warty lesion that is resistant to traditional treatment.