Methods
A retrospective chart review was conducted with approval from our institutional review board at the University of Texas Medical Branch (Galveston, Texas). Included in the chart review were all cutaneous malignancies treated by MMS at our outpatient, office-based surgical center from March 15, 2020, to April 30, 2020; this period corresponded to the peak of the COVID-19–related government-mandated medical and business shutdowns in our geographic region (southeast Texas). All cases performed were in compliance with national- and state-level guidance. Data were also collected for all cutaneous malignancies treated by MMS at our office from March 15, 2019, to April 30, 2019, as well as March 15, 2018, to April 30, 2018; these periods represented prepandemic control periods.
Data were collected for 516 surgeries performed on 458 patients and included patient age, preoperative clinical size, postoperative defect size, number of Mohs stages to achieve clearance, MMS appropriate use criteria (AUC) location (categorized as high-, medium-, or low-risk tumor location),13 and tumor type (categorized as BCC, SCC, or MIS). All variables were examined for unusual or missing values. Five patients with rare tumor types were observed and removed from the data set.
Statistical Analysis—An a priori power analysis for a power set at 0.85 determined sample sizes of 105 per group. Bivariate analyses were performed to compare variables for patients undergoing MMS during the pandemic vs prepandemic periods. Continuous outcome variables—Mohs stages, preoperative size, postoperative size, and patient age—were categorized for the analysis. Preoperative tumor size was dichotomized, with less than 2 cm2 as the referent category vs 2 cm2 or greater, and postoperative defect size was dichotomized with less than 3.6 cm2 as the referent category vs 3.6 cm2 or greater. Mohs stage was dichotomized as 1 stage (referent) vs more than 1 stage, and patient age was dichotomized as younger than 65 years (referent) vs 65 years or older.
Multivariate analyses were also performed to compare preoperative and postoperative sizes for patients undergoing MMS during the pandemic vs prepandemic periods, controlling for Mohs AUC location. Bivariate unadjusted and multivariate analyses were performed using a GENMOD logistic regression procedure in SAS (SAS Institute) to account for correlation in clustered data because a patient could be included for more than 1 surgery in the data set. Data were analyzed using SAS 9.4 for Windows. Because outcome variables tended to be skewed and not distributed normally, outcome variables were recorded as medians with interquartile ranges where possible to give a more accurate representation of the data than could be demonstrated with means with standard deviations.
Results
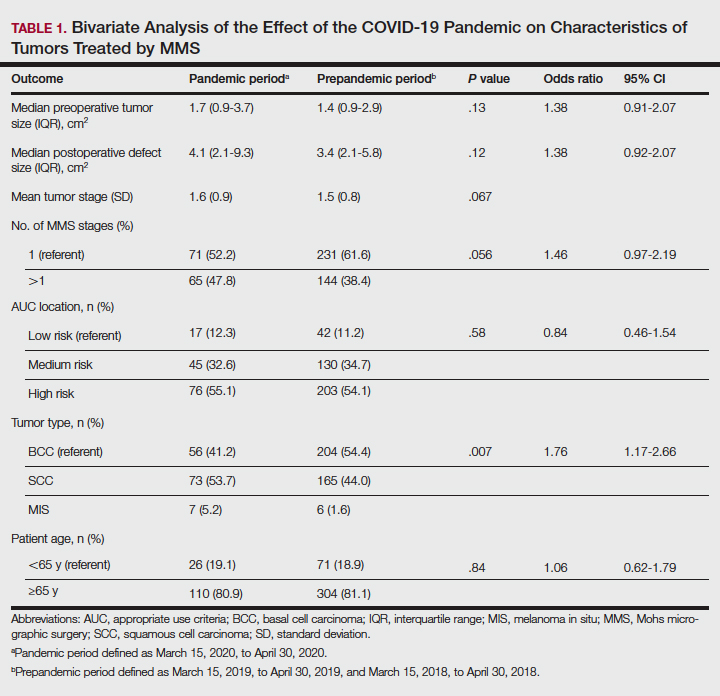
One hundred thirty-eight skin cancers were treated during the COVID-19 pandemic from March 15, 2020, to April 30, 2020, and 378 skin cancers were treated during the prepandemic control periods of March 15, 2019, to April 30, 2019, and March 15, 2018, to April 30, 2018. Tumor type treated during the pandemic period was more likely to be SCC or MIS (representing generally more severe tumor types) vs BCC when compared with the prepandemic periods, with an odds ratio (OR) of 1.763 (95% CI, 1.17-2.66). This outcome was statistically significant (P=.01).
Tumors treated during the pandemic period were more likely to have necessitated more than one Mohs stage for clearance compared to the prepandemic periods, though this difference was not statistically significant (OR, 1.461; 95% CI, 0.97-2.19; P=.056). Neither AUC location of treated tumors nor age were significantly different between prepandemic and pandemic periods (P=.58 and P=.84, respectively). Table 1 includes all bivariate analysis results.
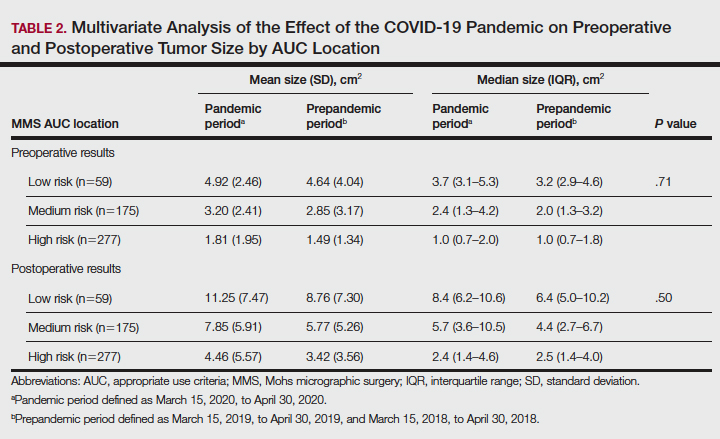
Additionally, although mean preoperative and postoperative sizes were larger for each AUC location during the pandemic vs prepandemic periods, these differences did not reach statistical significance on multivariate analysis (P=.71 and P=.50, respectively)(Table 2).