Angiolymphoid hyperplasia with eosinophilia (ALHE) is a rare nodular unencapsulated mass that is characterized by benign anomalous vascular hyperplasia of epithelioidlike endothelial cells attached to dilated blood vessels. The mass is surrounded by lymphocytes and eosinophils that can present clinically as papules, plaques, or nodules.1 The etiology of ALHE is unknown; it is hypothesized that it is a vascular neoplasm or a lymphoproliferative disorder.
Coccidioidomycosis (CM) is a prevalent deep fungal infection endemic to the southwestern United States caused by Coccidioides immitis and Coccidioides posadasii. Infection can occur from direct inoculation through abrasions or direct trauma but usually occurs through the inhalation of spores and can result in a reactive rash (eg, Sweet syndrome, erythema nodosum, interstitial granulomatous dermatitis).2 Coccidioidomycosis also can result in respiratory pneumonia and dissemination from pulmonary infection of the skin. As such, it is important to distinguish CM and its immunologically mediated eruptions for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
We report a novel case of ALHE as a reactive dermatologic presentation in a patient with CM.
Case Report
A 72-year-old woman presented to the dermatology clinic with itchy papules and plaques on the arms and legs of 17 years’ duration. Her medical history included coronary artery disease and hypercholesterolemia as well as a remote history of cutaneous marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the nose, which was confirmed by histology and treated more than 10 years prior and has remained in remission for 6 years. Her current medications included aspirin, atorvastatin, lisinopril, and metoprolol succinate.
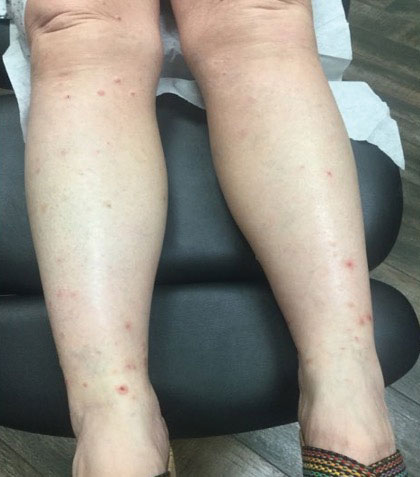
Our patient first presented to our dermatology clinic for itchy nodules and papules on the legs and arms. The patient previously had been seen by another dermatologist 2 months prior for the same condition. At that time, biopsies of the lesions were reported as prurigo nodules. Physical examination at the current presentation revealed round, pink to flesh-colored, raised papules and plaques scattered on the arms and legs (Figure 1). The differential diagnosis included lymphomatoid papulosis, cutaneous B-cell lymphoma, pseudolymphoma, cutaneous CM, and papular mucinosis.
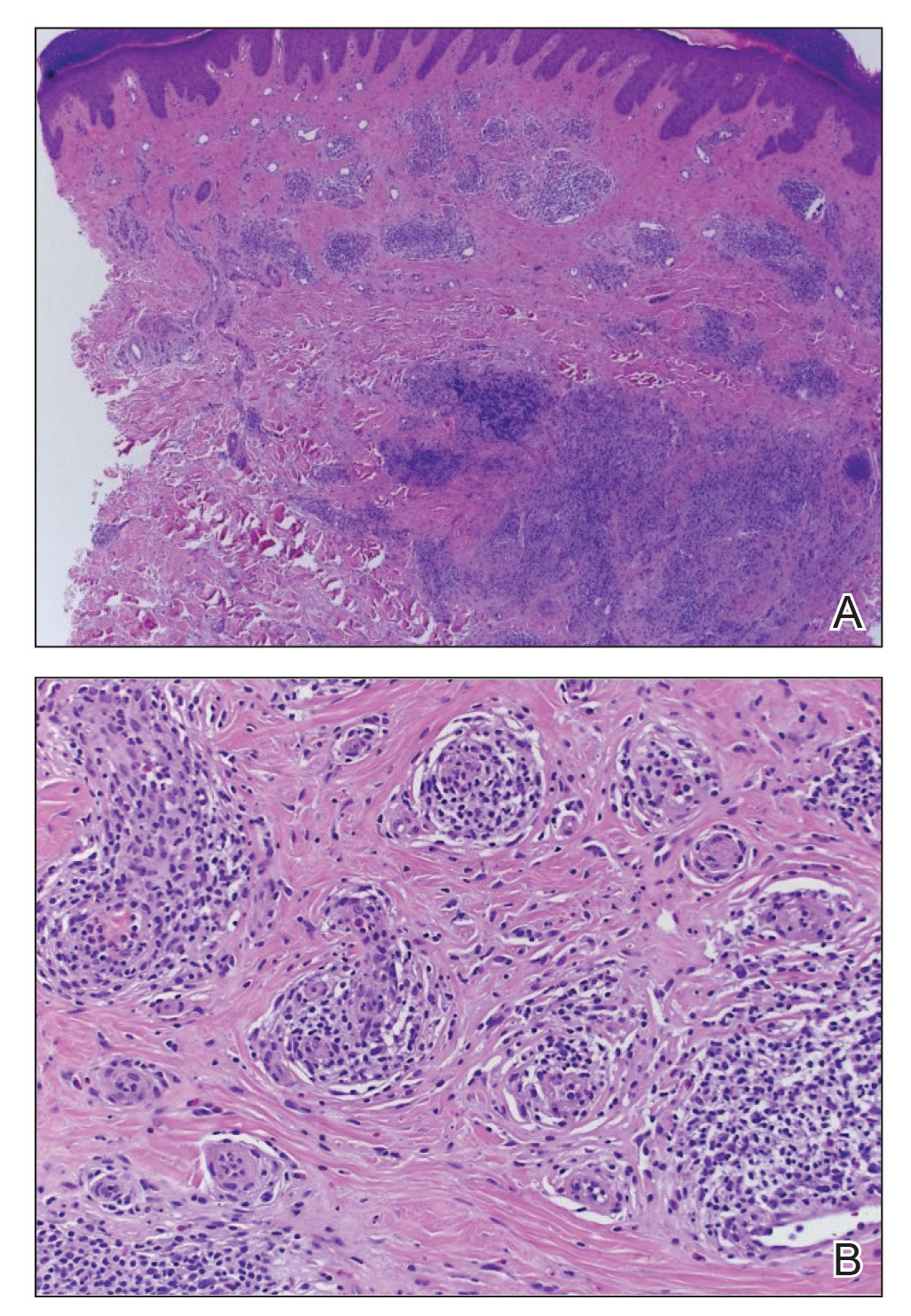
Four-mm punch biopsies of the right proximal pretibial region and left knee region were taken and sent for histologic analysis, direct immunofluorescence testing, and tissue culture. Testing for atypical mycobacteria and deep fungal infection was negative; bacterial cultures and sensitivity testing were negative. Direct immunofluorescence testing was negative. Microscopic examination of material from the right proximal pretibial region showed widely dilated, variously shaped, large blood vessels in a multinodular pattern; the vessels also were surrounded by an inflammatory cell infiltrate containing eosinophils. Histologic findings were consistent with ALHE.
Subsequent biopsies were completed 2 weeks and 1 month from the initial presentation. Both histology reports—from 2 different histopathology laboratories—were consistent with ALHE (Figure 2). Additional work-up during the patient’s initial visit to our clinic for the rash included CM serologic testing, which demonstrated IgM and IgG antibodies. Subsequently, chest radiography revealed a 2.2×2.3-cm mass in the right lower lobe of the lung. Follow-up computed tomography 1 month later confirmed the nodule in the same area to be 2.3×2.1×1.8 cm.