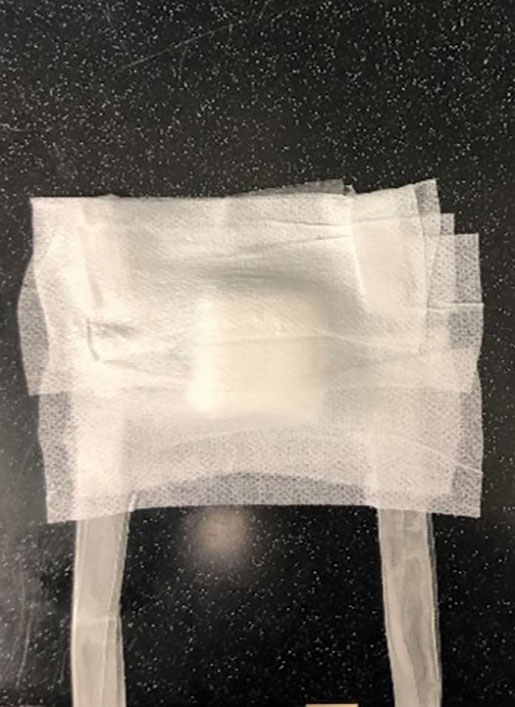
Prototype #1—We created 2 tabs—each 2-feet long—using bandaging tape that was folded on itself once horizontally (Figure 2). The tabs were aligned on either side of the wound, the tops of which sat approximately 2 inches above the top of the first layer of adhesive bandage. An initial layer of adhesive surgical dressing was applied to cover the wound; 1 inch of the dressing was left exposed on the top of each tab. In addition, there were 2 “feet” running on the bottom.
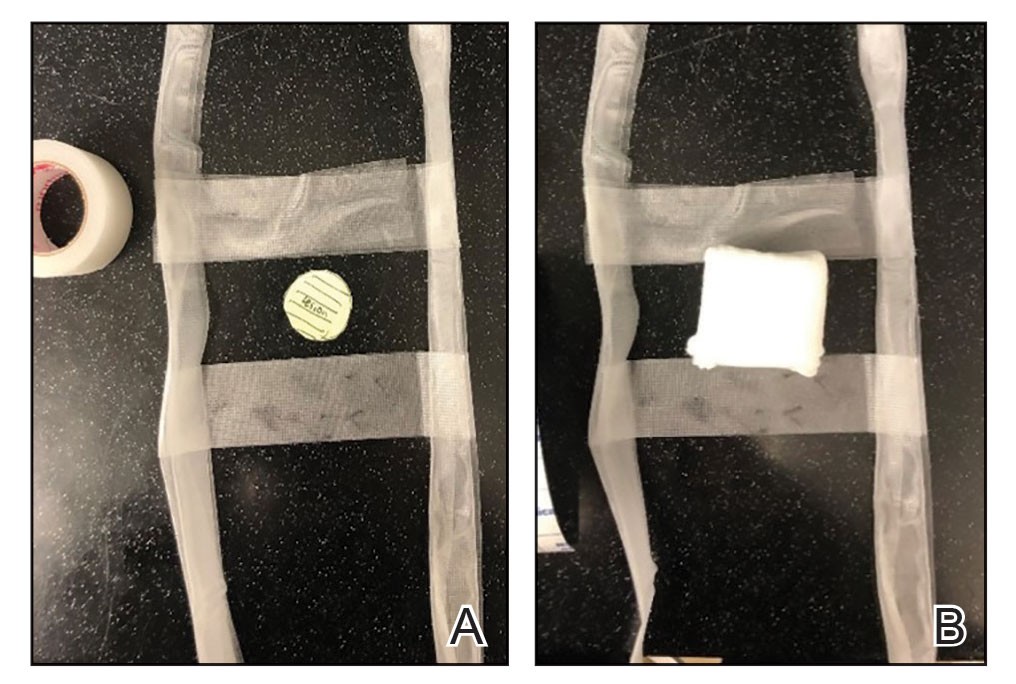
FIGURE 2. A, Step 1 in preparing prototype #1 bandage: create 2 pull tabs, each 2-feet long, using bandaging tape folded on itself once horizontally. Place these tabs on either side of the lesion, then secure to the patient with adhesive gauze. Include any necessary wound packing underneath. B, Step 2: fold the tops of the pull tabs over the top side of the adhesive tape and tape down with more adhesive bandage.
The tops of the tabs were folded back over the adhesive tape, creating a type of “hook.” An additional final layer of adhesive tape was applied to ensure adequate pressure on the surgical site.
The patient was instructed to remove the bandage 2 days after the procedure. The outcome was qualified through a 3-day postoperative telephone call. The patient was asked about postoperative pain and his level of satisfaction with treatment. He was asked if he had any changes such as bleeding, swelling, signs of infection, or increased pain in the days after surgery or perceived postoperative complications, such as irritation. We asked the patient about the relative ease of removing the bandage and if removal was painful. He reported that the bandage was easy to remove, and that doing so was not painful; furthermore, he did not have problems with the bandage or healing and did not experience any medical changes. He found the bandage to be comfortable. The patient stated that the hanging feet of the prototype #1 bandage were not bothersome and were sturdy for the time that the bandage was on.
Prototype #2—We prepared a bandage using surgical packing as the tab (Figure 3). The packing was slowly placed around the site, which was already covered with nonadhesive gauze and fenestrated surgical gauze, with adequate spacing between each loop (for a total of 3 loops), 1 of which crossed over the third loop so that the adhesive bandaging tape could be removed easily. This allowed for a single tab that could be removed by a single pull. A final layer of adhesive tape was applied to ensure adequate pressure, similar to prototype #1. The same postoperative protocol was employed to provide a consistent standard of care. We recommend use of this prototype when surgical tape is not available, and surgical packing can be used as a substitute.
Practice Implications
Patients have a better appreciation for avoiding excess visits to medical offices due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The risk for exposure to SARS-CoV-2 infection is greater when patients who lack a support system must return to the office for aftercare or to have a bandage removed. Although protection offered by the COVID-19 vaccine alleviates concern, many patients have realized the benefits of only visiting medical offices in person when necessary.
The concept of pull tab bandages that can be removed by the patient at home has other applications. For example, patients who travel a long distance to see their physician will benefit from easier aftercare and avoid additional follow-up visits when provided with a self-removable bandage.


