Dermatologic disparities disproportionately affect patients with skin of color (SOC). Two studies assessing the diagnostic accuracy of medical students have shown disparities in diagnosing common skin conditions presenting in darker skin compared to lighter skin at early stages of training.1,2 This knowledge gap could be attributed to the underrepresentation of SOC in dermatologic textbooks, journals, and educational curricula.3-6 It is important for dermatologists as well as physicians in other specialties and ancillary health care workers involved in treating or triaging dermatologic diseases to recognize common skin conditions presenting in SOC. We sought to evaluate the effectiveness of a focused educational module for improving diagnostic accuracy and confidence in treating SOC among interprofessional health care providers.
Methods
Interprofessional health care providers—medical students, residents/fellows, attending physicians, advanced practice providers (APPs), and nurses practicing across various medical specialties—at The University of Texas at Austin Dell Medical School and Ascension Medical Group (both in Austin, Texas) were invited to participate in an institutional review board–exempt study involving a virtual SOC educational module from February through May 2021. The 1-hour module involved a pretest, a 15-minute lecture, an immediate posttest, and a 3-month posttest. All tests included the same 40 multiple-choice questions of 20 dermatologic conditions portrayed in lighter and darker skin types from VisualDx.com, and participants were asked to identify the condition in each photograph. Questions appeared one at a time in a randomized order, and answers could not be changed once submitted.
For analysis, the dermatologic conditions were categorized into 4 groups: cancerous, infectious, inflammatory, and SOC-associated conditions. Cancerous conditions included basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Infectious conditions included herpes zoster, tinea corporis, tinea versicolor, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome, and verruca vulgaris. Inflammatory conditions included acne, atopic dermatitis, pityriasis rosea, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, lichen planus, and urticaria. Skin of color–associated conditions included hidradenitis suppurativa, acanthosis nigricans, keloid, and melasma. Two questions utilizing a 5-point Likert scale assessing confidence in diagnosing light and dark skin also were included.
The pre-recorded 15-minute video lecture was given by 2 dermatology residents (P.L.K. and C.P.), and the learning objectives covered morphologic differences in lighter skin and darker skin, comparisons of common dermatologic diseases in lighter skin and darker skin, diseases more commonly affecting patients with SOC, and treatment considerations for conditions affecting skin and hair in patients with SOC. Photographs from the diagnostic accuracy assessment were not reused in the lecture. Detailed explanations on morphology, diagnostic pearls, and treatment options for all conditions tested were provided to participants upon completion of the 3-month posttest.
Statistical Analysis—Test scores were compared between conditions shown in lighter and darker skin types and from the pretest to the immediate posttest and 3-month posttest. Multiple linear regression was used to assess for intervention effects on lighter and darker skin scores controlling for provider type and specialty. All tests were 2-sided with significance at P<.05. Analyses were conducted using Stata 17.
Results
One hundred participants completed the pretest and immediate posttest, 36 of whom also completed the 3-month posttest (Table). There was no significant difference in baseline characteristics between the pretest and 3-month posttest groups.
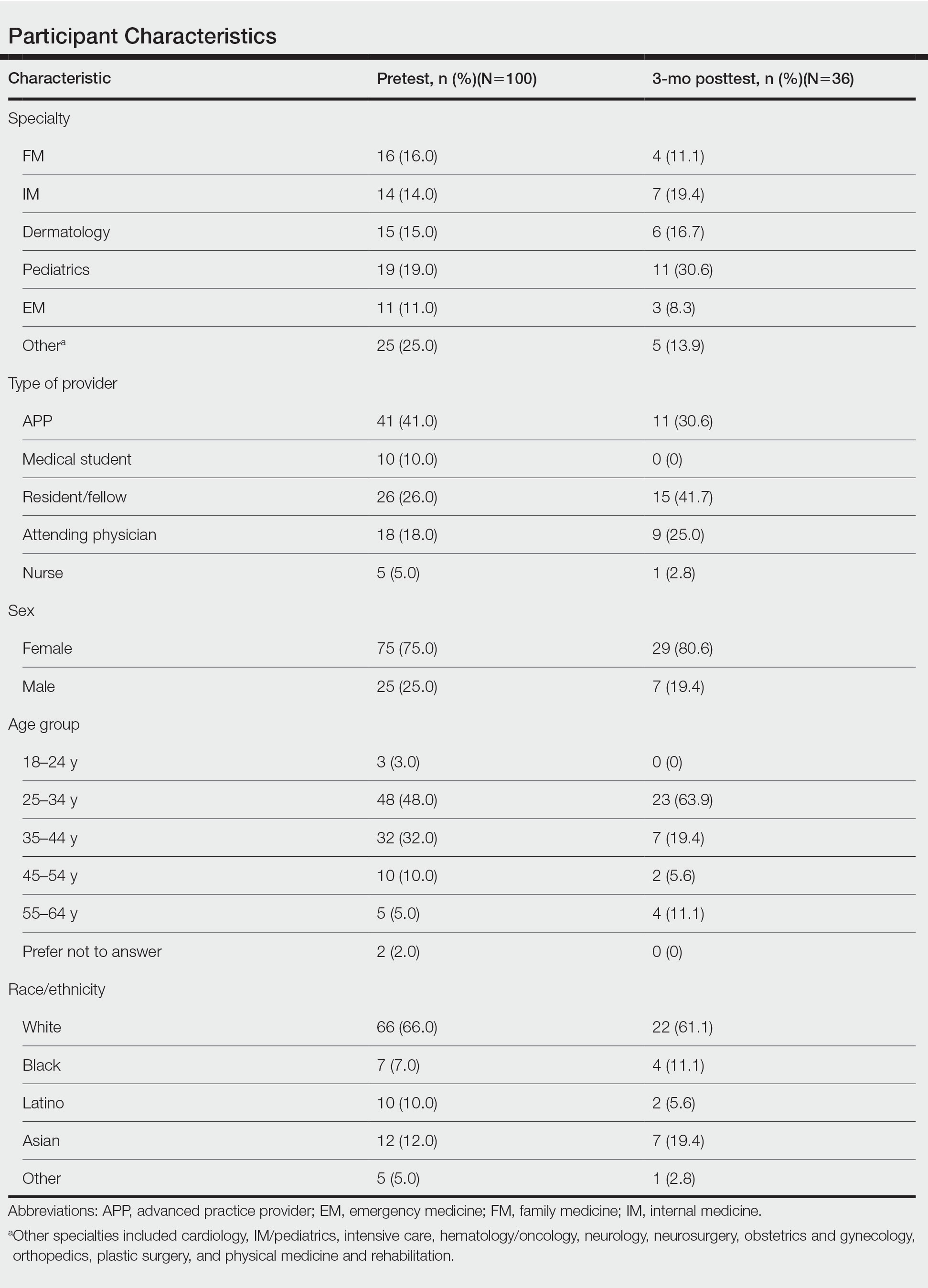
Test scores were correlated with provider type and specialty but not age, sex, or race/ethnicity. Specializing in dermatology and being a resident or attending physician were independently associated with higher test scores. Mean pretest diagnostic accuracy and confidence scores were higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with those shown in darker skin (13.6 vs 11.3 and 2.7 vs 1.9, respectively; both P<.001). Pretest diagnostic accuracy was significantly higher for skin conditions shown in lighter skin compared with darker skin for cancerous, inflammatory, and infectious conditions (72% vs 50%, 68% vs 55%, and 57% vs 47%, respectively; P<.001 for all)(Figure 1). Skin of color–associated conditions were not associated with significantly different scores for lighter skin compared with darker skin (79% vs 75%; P=.059).