Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)—a chronic, relapsing, inflammatory disorder involving terminal hair follicles in apocrine gland–rich skin—manifests as tender inflamed nodules that transform into abscesses, sinus tracts, and scarring.1,2 The etiology of HS is multifactorial, encompassing lifestyle, microbiota, hormonal status, and genetic and environmental factors. These factors activate the immune system around the terminal hair follicles and lead to hyperkeratosis of the infundibulum of the hair follicles in intertriginous regions. This progresses to follicular occlusion, stasis, and eventual rupture. Bacterial multiplication within the plugged pilosebaceous units further boosts immune activation. Resident and migrated cells of the innate and adaptive immune system then release proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor, IL-1β, and IL-17, which further enhance immune cell influx and inflammation.3,4 This aberrant immune response propagates the production of deep-seated inflammatory nodules and abscesses.3-8
The estimated prevalence of HS is 1% worldwide.9 It is more prevalent in female and Black patients (0.30%) than White patients (0.09%) and is intermediate in prevalence in the biracial population (0.22%).10 Hidradenitis suppurativa is thought to be associated with lower socioeconomic status (SES). In a retrospective analysis of HS patients (N=375), approximately one-third of patients were Black, had advanced disease, and had a notably lower SES.11 Furthermore, HS has been reported to be associated with systemic inflammation and comorbidities such as morbid obesity (38.3%) and hypertension (39.6%) as well as other metabolic syndrome–related disorders and depression (48.1%).1
Hidradenitis suppurativa may contribute to the risk for depression through its substantial impact on health-related quality of life, which culminates in social withdrawal, unemployment, and suicidal thoughts.12 The high prevalence of depression in individuals with HS1 and its association with systemic inflammation13 increases the likelihood that a common genetic predisposition also may exist between both conditions. Because depression frequently has been discovered as a concomitant diagnosis in patients with HS, we hypothesize that a shared genetic susceptibility also may exist between the 2 disorders. Our study sought to explore data on the co-occurrence of depression with HS, including its demographics and racial data.
Methods
We conducted a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE as well as Google Scholar using the terms depression and hidradenitis suppurativa to obtain all research articles published from 2000 to 2022. Articles were selected based on relevance to the topic of exploration. English-language articles that directly addressed the epidemiology, etiology, pathophysiology, and co-occurrence of both depression and HS with numerical data were included. Articles were excluded if they did not explore the information of interest on these 2 disorders or did not contain clear statistical data of patients with the 2 concurrent medical conditions.
Results
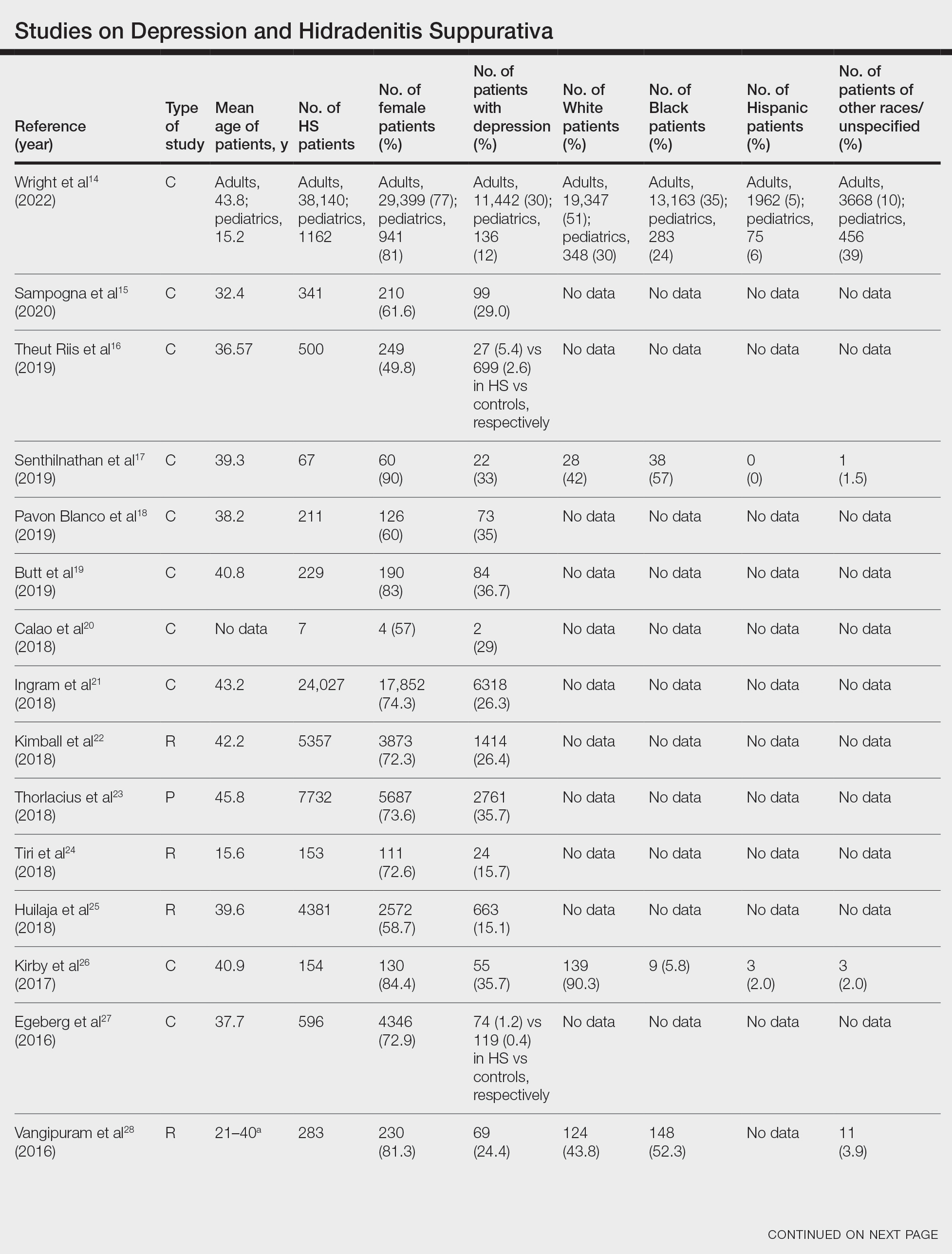
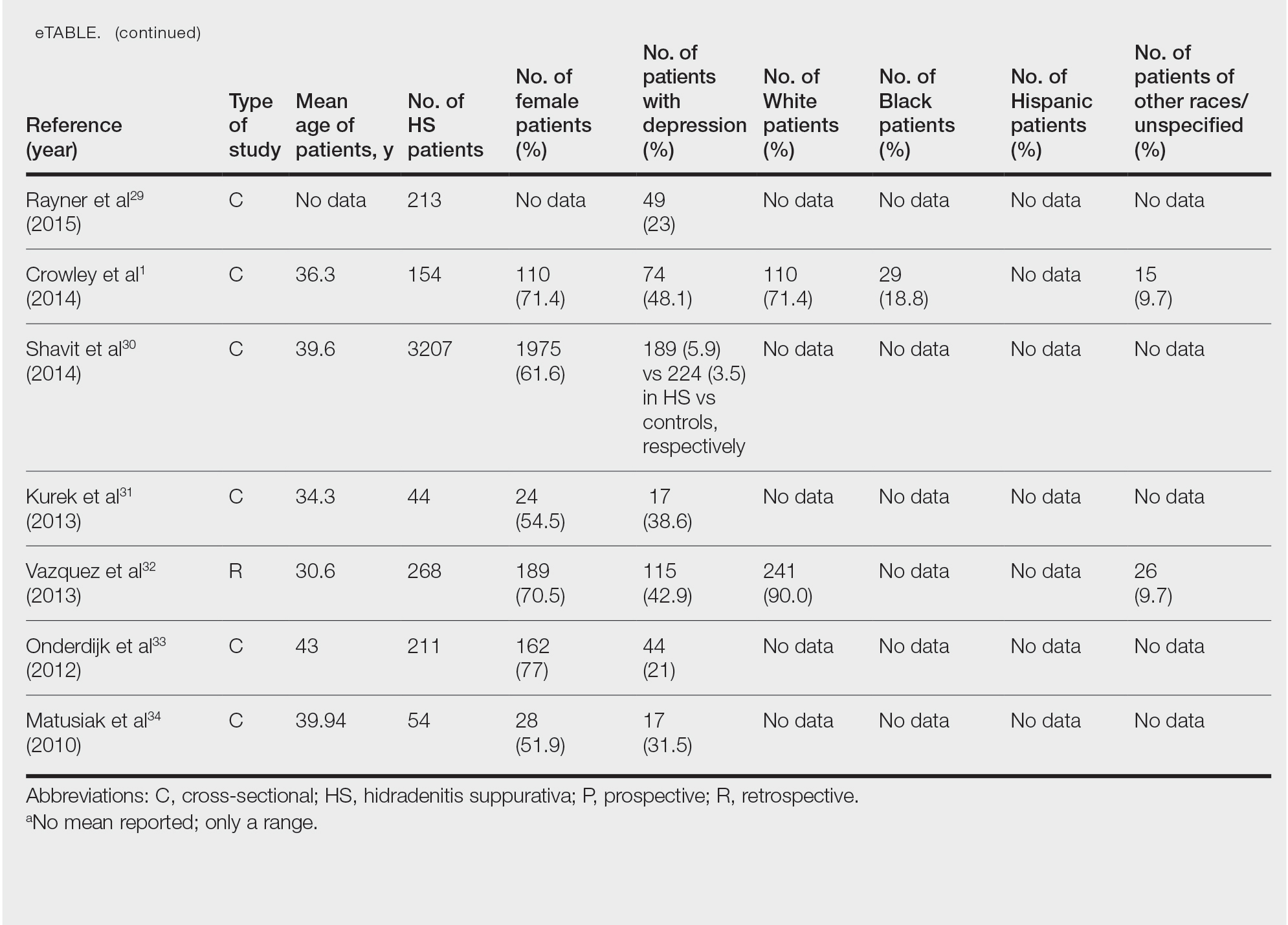
Twenty-two cross-sectional, prospective, and retrospective studies that fit the search criteria were identified and included in the analysis (eTable).1,14-34 Sixteen (72.7%) studies were cross-sectional, 5 (22.7%) were retrospective, and only 1 (4.5%) was a prospective study. Only 6 of the studies provided racial data,1,14,17,26,28,32 and of them, 4 had predominately White patients,1,14,26,32 whereas the other 2 had predominantly Black patients.17,28
Hidradenitis suppurativa was found to coexist with depression in all the studies, with a prevalence of 1.2% to 48.1%. There also was a higher prevalence of depression in HS patients than in the control patients without HS. Furthermore, a recent study by Wright and colleagues14 stratified the depression prevalence data by age and found a higher prevalence of depression in adults vs children with HS (30% vs 12%).
Comment
Major depression—a chronic and debilitating illness—is the chief cause of disability globally and in the United States alone and has a global lifetime prevalence of 17%.35 In a study of 388 patients diagnosed with depression and 404 community-matched controls who were observed for 10 years, depressed patients had a two-thirds higher likelihood of developing a serious physical illness than controls. The depression-associated elevated risk for serious physical illness persisted after controlling for confounding variables such as alcohol abuse, smoking, and level of physical activity.36 Studies also have demonstrated that HS is more prevalent in Black individuals10 and in individuals of low SES,37 who are mostly the Black and Hispanic populations that experience the highest burden of racial microaggression38 and disparities in health access and outcomes.39,40 The severity and chronicity of major depressive disorder also is higher in Black patients compared with White patients (57% vs 39%).41 Because major depression and HS are most common among Black patients who experience the highest-burden negative financial and health disparities, there may be a shared genetic disposition to both medical conditions.