Multifaceted Treatment
For an older adult, “there is never a wrong time to start sun-protective measures” to prevent or try to halt the progression of dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman said, noting that “UV radiation is an immunosuppressant, so there are many good reasons to start” if the adult is not already taking measures on a regular basis.
Potential treatments for the syndrome of dermatoporosis are backed by few clinical studies, but dermatologists are skilled at translating the use of products from one disease state to another based on understandings of pathophysiology and mechanistic pathways, Dr. Friedman commented in an interview after the meeting.
For instance, “from decades of research, we know what retinoids will do to the skin,” he said in the interview. “We know they will turn on collagen-1 and -3 genes in the skin, and that they will increase the production of glycosaminoglycans ... By understanding the biology, we can translate this to dermatoporosis.” These changes were demonstrated, for instance, in a small study of topical retinol in older adults.
Studies of topical alpha hydroxy acid (AHA), moreover, have demonstrated epidermal thickening and firmness, and “some studies show they can limit steroid-induced atrophy,” Dr. Friedman said at the meeting. “And things like lactic acid and urea are super accessible.”
Topical dehydroepiandrosterone is backed by even less data than retinoids or AHAs are, “but it’s still something to consider” as part of a multimechanistic approach to dermatoporosis, Dr. Friedman shared, noting that a small study demonstrated beneficial effects on epidermal atrophy in aging skin.
The use of vitamin D analogues such as calcipotriene, which is approved for the treatment of psoriasis, may also be promising. “One concept is that [vitamin D analogues] increase calcium concentrations in the epidermis, and calcium is so central to keratinocyte differentiation” and epidermal function that calcipotriene in combination with topical steroid therapy has been shown to limit skin atrophy, he noted.
Nutritionally, low protein intake is a known problem in the older population and is associated with increased skin fragility and poorer healing. From a prevention and treatment standpoint, therefore, patients can be counseled to be attentive to their diets, Dr. Friedman said. Experts have recommended a higher protein intake for older adults than for younger adults; in 2013, an international group recommended a protein intake of 1-1.5 g/kg/d for healthy older adults and more for those with acute or chronic illness.
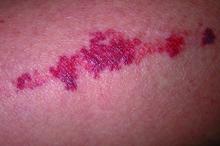
“Patients love talking about diet and skin disease ... and they love over-the-counter nutraceuticals as well because they want something natural,” Dr. Friedman said. “I like using bioflavonoids in combination with vitamin C, which can be effective especially for solar purpura.”
A 6-week randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial involving 67 patients with purpura associated with aging found a 50% reduction in purpura lesions among those took a particular citrus bioflavonoid blend twice daily. “I thought this was a pretty well-done study,” he said, noting that patient self-assessment and investigator global assessment were utilized.