Article
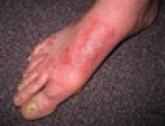
Interstitial Granulomatous Dermatitis Associated With Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
A 44-year-old man presented with an eruption of pruritic erythematous plaques on his lower extremities of 6 months’ duration that were...

