Article
Cutaneous Adenosquamous Carcinoma: A Rare Neoplasm With Biphasic Differentiation
Cutaneous adenosquamous carcinoma (cASC) is an extremely rare malignant neoplasm. Due to its disputed pathophysiology, ambiguity of presentation,...
From the Centre Hospitalier Marne la Vallée Hospital, Jossigny, France. Dr. Gallais Sérézal was from and Dr. Hillion is from the Dermatology Clinic, and Drs. Dumitru and Le Foll are from the Oncology Department. Dr. Gallais Sérézal currently is from Karolinska University Hospital, Solna, Sweden.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Irène Gallais Sérézal, MD, Dermatology Clinic, B2 00, Karolinska University Hospital, 17164 Solna, Sweden (gs.irene@gmail.com).

Iatrogenic dissemination of cancer cells has been described often on scars of tumor surgery, and in malignant melanoma, bruises and hematoma revealing preexisting metastases have been reported. This case illustrates the abilities of tumor cells to colonize the skin under favorable conditions and emphasizes the importance of minimizing bleeding events and iatrogenic seeding of internal neoplasms in daily practice.
To the Editor:
In a recent Cutis® article, Cesaretti et al1 reported a case of cutaneous metastasis from primary gastric cancer that appeared on a resection scar 6 years after remission and without any relapse of the primary tumor. We report a case of a 68-year-old man who was referred to the dermatology clinic with a 15×20-cm nonpruritic, nonscaly, bruiselike lesion on the right forearm of 1 month’s duration. Approximately 1.5 years prior to presentation, the patient was diagnosed with gastric adenocarcinoma (stage IV: T4N3M1) with hepatic and lung metastasis. Following 6 months of chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil, a positron emission tomography–computed tomography scan was performed and showed a reduction in metastasis but growth of the primitive tumor. After 1 year of chemotherapy, the new positron emission tomography–computed tomography scan showed no metastases. However, the primitive tumor had increased in size.
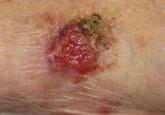
One month prior to presentation to the dermatology department, a traumatic blood sample on the right forearm left the patient with a persistent ecchymosis. The lesion was thought to be a healing ecchymosis and no biopsy was performed. One month later, the skin lesion had become much thicker and more erythematous (Figure) but not larger. A skin biopsy of this well-defined plaque was performed. Histologic examination showed neovascularization, proliferative epithelial cells, and cytokeratin markers AE1/AE3 and CK20, leading to the diagnosis of skin metastasis of the gastric adenocarcinoma. Chemotherapy was discontinued because of the patient’s altered general status and palliative care was given until he died the following month (2 months after presentation).
Iatrogenic dissemination of cancer cells has been described often on scars of tumor surgery,2 and in malignant melanoma, bruises and hematoma revealing preexisting metastases have been reported.3,4 Our report of secondary metastasis on an ecchymosis suggests that the traumatic blood sample performed before the development of the metastasis caused circulating tumor cells in the skin, which led to their local proliferation. The skin metastasis was the first sign of relapse and was followed by alteration of the general status and death.
Our patient is an example of the “soil and seed”5 hypothesis. Our case illustrates the abilities of tumor cells to colonize the skin under favorable conditions and emphasizes the importance of minimizing bleeding events and iatrogenic seeding of internal neoplasms in daily practice.

Cutaneous adenosquamous carcinoma (cASC) is an extremely rare malignant neoplasm. Due to its disputed pathophysiology, ambiguity of presentation,...

Leser-Trélat sign is a rare skin condition characterized by the sudden appearance of seborrheic keratoses that rapidly increase in number and size...

Cutaneous metastases of internal neoplasms are uncommon. They can be metachronous or synchronous to the primary tumor and typically appear late in...
