The annual number of medical malpractice payment reports fell 28% from 2004 to 2014, according to the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality.
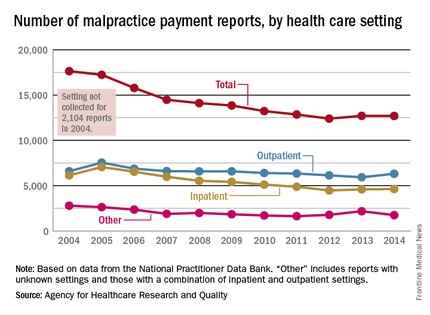
The total number of medical malpractice payment reports (MMPRs) for 2014 was 12,699, a decrease of 28% since 2004, when there were 17,641. The total had gone down every year until a slight increase in 2013, but the number held steady in 2014, the AHRQ reported in the Chartbook on Patient Safety.
Since 2004, MMPRs related to inpatient settings have been dropping slightly faster than outpatient-related MMPRs, with the exception, again, of 2013, when the number of inpatient MMPRs went up while the outpatient total dropped. Both types went up in 2014, but the category of “other” – reports related to unknown settings and those from a combination of the two – dropped in 2014 to keep the overall number from going up again, data from the National Practitioner Data Bank show.
Looking at the types of allegation leading to MMPRs, treatment was highest, accounting for 27.4% of the total from 2004 to 2014, with diagnosis right behind at 27.1%, followed by surgery at 23.5% and obstetrics at 6.7%. Medication-related cases represented 5.3% of all MMPRs over that period, the AHRQ noted.