“I disapprove of what you say, but I will defend to the death your right to say it.” The choice of the secretary general of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery to open with this quote was the first hint that the next presentation at the 2019 annual meeting would be anything but dull. The session chair followed with a reminder to keep the discussion polite and civil.
Presenter David Taggart, MD, PhD, did not disappoint. The professor of cardiovascular surgery at the University of Oxford (England) began with the announcement that he had withdrawn his name from a recent paper in the New England Journal of Medicine. He then proceeded to accuse his coinvestigators of misrepresenting the findings of a major clinical trial.
Dr. Taggart was chair of the surgical committee for the Abbott-sponsored EXCEL trial, which compared two procedures for patients who had blockages in their left main coronary artery: percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using coronary stents, and coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG). The investigators designed the trial to compare outcomes for the two treatments using a composite endpoint of death, stroke, and MI. The 3-year follow-up data had been published in NEJM without controversy – or, at least, without public controversy.
But when it came time to publish the 5-year follow-up, there was a significantly higher rate of death in the stent group, and both Dr. Taggart and the journal editors were concerned that this finding was being downplayed in the manuscript.
In their comments to the authors, the journal editors had recommended including the mortality difference (unless clearly trivial) ‘”in the concluding statement in the final paragraph.” Yet, the concluding statement of the published paper read that there “was no significant difference between PCI and CABG.”
In Dr. Taggart’s view, that claim was dangerous for patients, and so he was left with no choice but to remove himself as an author, a first for the academic with over 300 scientific papers to his name.
Earlier publications from the EXCEL trial had influenced European treatment guidelines. But subsequent allegations of misconduct and hidden data spurred the EACTS to repudiate those guidelines out of concern “that some results in the EXCEL trial appear to have been concealed and that some patients may therefore have received the wrong clinical advice.”
The controversy pitted cardiothoracic surgeons against interventional cardiologists, who were seen as increasingly encroaching on the surgeons’ turf. Dr. Taggart was a long-time critic of the subspecialty.
Surgeons demanded an independent analysis of the EXCEL trial data – a demand that the investigators have yet to satisfy. Dr. Taggart was the first to speak publicly, but others had major reservations about the trial reporting and conduct years earlier.
Mortality data held back
One such person was Lars Wallentin, MD, a professor of cardiology at Uppsala (Sweden) University Hospital, who chaired the independent committee that monitored the safety and scientific validity of the EXCEL trial.
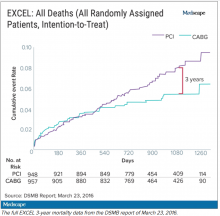
The committee, known as the data and safety monitoring board (DSMB), received a report on March 23, 2016, that showed that increasingly more patients who had received stents were dying, compared with the group of patients that had undergone CABG. A graph of the survival curves showed the gap between the two groups widening after 3 years (Figure 1).
By September of that year, Dr. Wallentin and other members of the DSMB were anxious to share the concerning mortality difference with the broader medical community.
They were aware that EACTS and the European Society of Cardiology had started the process of updating their guidelines on myocardial revascularization, and were keen for the guideline writing committee to see all of the data.
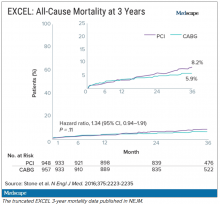
Meanwhile, the trial investigators, led by principal investigator Gregg Stone, MD, then at New York–Presbyterian Hospital and Columbia University Medical Center, were preparing to publish a report of the 3-year outcomes. Recruitment for EXCEL started in September 2010, so at the time of the 3-year analysis in 2016, some patients had been followed up for over 5 years. But the data, published in NEJM in October 2016, were capped at 3 years (Figure 2). It didn’t show the widening gap in late mortality that Dr. Wallentin and the rest of the DSMB had seen.
When asked about this, the investigators said they were transparent about their plans to cap the data at 3 years in an amendment to the study protocol. Stone’s coprincipal investigators were interventional cardiologist Patrick Serruys, MD, then of Imperial College London; and two surgeons: Joseph Sabik, MD, then of the Cleveland Clinic Foundation, and A. Pieter Kappetein, MD, PhD, then at Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam. The four principal investigators all declared financial payments from stent manufacturers either to themselves or their institutions.
Study sponsor Abbott has distanced itself from the decisions made and has referred all questions about the trial to the EXCEL investigators. Charles Simonton, chief medical officer at Abbott (now at Abiomed) was a coauthor on both the 3- and 5-year papers. Dr. Wallentin believes that the sponsor must have been aware of the DSMB’s concerns.