‘Subclinical’ CS
Ben-Shlomo highlighted a condition called minimal autonomous cortisol secretion (formerly “subclinical CS”). “This condition is found when a person has an adrenal nodule that produces cortisol in excess, however not to levels observed in CS. An abnormal finding on the overnight 1-mg low-dose dexamethasone suppression test (LDDST) will identify this disorder, showing mildly unsuppressed morning cortisol level, while all other tests will be within normal range.”
She described minimal autonomous cortisol secretion as a form of “smoldering CS,” which has become more commonly diagnosed. “The condition needs to be treated because the patient can develop insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and osteoporosis over time.”
Once a cause has been determined, the optimal course of action is to take a multidisciplinary approach because CS affects multiple systems.
‘Pseudo-Cushing Syndrome’
A variety of abnormalities of the hypothalamus-pituitary adrenal (HPA) axis can be associated with hypercortisolemia and a rounder facial appearance but aren’t actually CS, Ben-Shlomo said.
Often called “pseudo-Cushing syndrome,” these conditions have recently been renamed “non-neoplastic hypercortisolism” or “physiologic non-neoplastic endogenous hypercortisolism.” They share some clinical and biochemical features of CS, but the hypercortisolemia is usually secondary to other factors. They increase the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone, which stimulates adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and adrenal cortisol secretion.
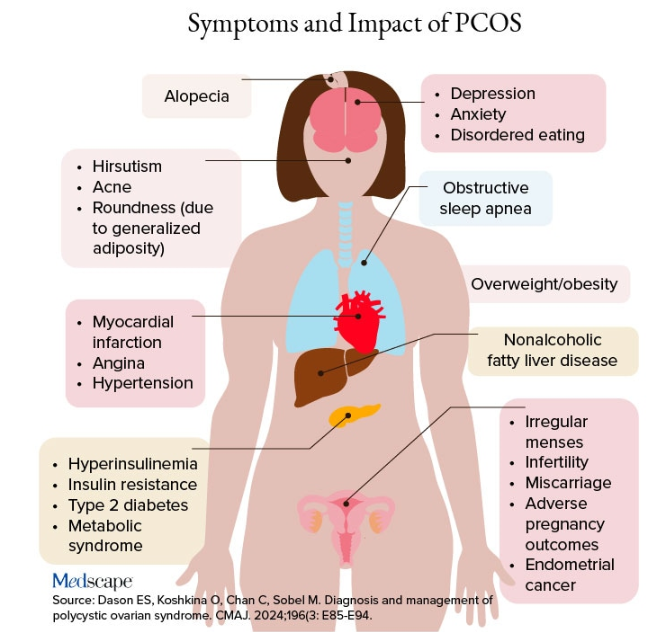
Identifying PCOS
PCOS is often associated with central obesity, Sherif noted, but not all women with PCOS have overweight or a central distribution of fat.
“Ask about menstrual periods and whether they come monthly,” Sherif advised. “If women using hormonal contraception say they have a regular cycle, ask if their cycle was regular prior to starting contraception. So many women with PCOS are undiagnosed because they started contraception in their teens to ‘regulate their periods’ and never realized they had PCOS.”
Additional symptoms of PCOS and its impact are found in the figure below.
PCOS is diagnosed when two of the following three Rotterdam criteria are met, and other diagnoses are excluded:
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Clinical hyperandrogenism or biochemical hyperandrogenism
- Polycystic ovarian morphology on transvaginal ultrasonography or high anti-mullerian hormone (applicable only if patient is ≥ 8 years from menarche)
If PCOS is suspected, further tests can be conducted to confirm or rule out the diagnosis.
Alcohol Abuse: Alcohol abuse stimulates hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone, leading to increased ACTH levels. It’s associated with a higher fasting cortisol level, particularly at 8:30 AM or so, and attributable to impaired cortisol clearance due to alcohol-related hepatic dysfunction. The LDDST will show abnormal cortisol suppression.
Sherif advised asking patients about alcohol use, recommending treatment for alcohol use disorder, and repeating clinical and biochemical workup after patients have discontinued alcohol consumption for ≥ 1 month.
Eating Disorders Mimicking CS: Eating disorders, particularly anorexia nervosa, are associated with endocrine abnormalities, amenorrhea, impaired body temperature regulation, and hypercortisolism, likely due to chronic fasting-related stress. Dysregulation of the HPA axis may linger, even after weight recovery.
It’s unlikely that patients with anorexia will display the “rounded face” associated with hypercortisolism, but some research suggests that anorexia can result in a disproportionate accumulation of central adiposity after recovery from the illness.