CHICAGO – A joint American College of Rheumatology and European League Against Rheumatism panel has written the first-ever classification criteria for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD), and the draft version of the criteria identified the disorder with 99.2% specificity and 85.5% sensitivity when compared with expert case opinions.
“We’ve come a long way” to write these criteria 17 years after the first case report, and about a decade after IgG4-RD first became part of routine rheumatology practice, John H. Stone, MD, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. He cited one estimate that about 185,000 Americans currently have IgG4-RD.
Approval of the draft criteria by both the ACR and EULAR remains pending.
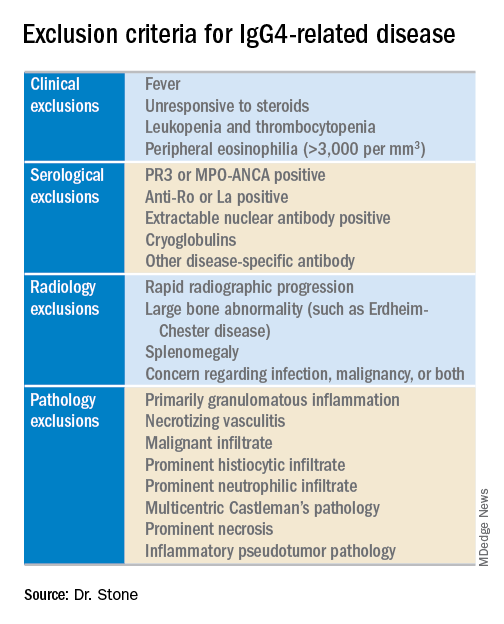
The working group assembled by the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism to write the classification criteria included 89 members, and the draft document they produced combined inclusion and exclusion criteria, “the first ACR and EULAR classification criteria to include specific exclusions, to my knowledge,” said Dr. Stone professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of clinical rheumatology at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. The exclusions reflect the many other disorders that can mimic IgG4-RD, including cancers and several rheumatologic diseases, especially granulomatosis with polyangiitis and Sjögren’s syndrome.
The writing panel used 487 case reports from 272 patients diagnosed with IgG4-RD and 215 patients diagnosed with a different, mimic disease to derive the classification criteria, and then used 908 case reports – 493 from IgG4-RD patients and 415 reports from mimic cases – to test and validate the criteria.
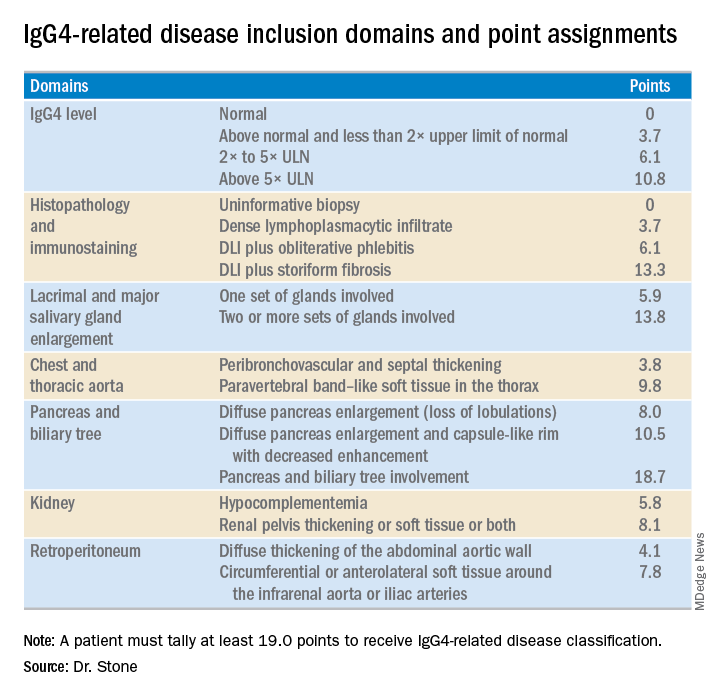
The first step in classifying a patient with IgG4-RD is to identify involvement of at least one organ from the list the panel compiled of 10 organs where involvement typifies the disease: pancreas, bile ducts, orbits, lacrimal glands, major salivary glands, retroperitoneum, kidney, aorta, pachymeninges, and thyroid gland (Riedel’s thyroiditis, but not Hashimoto’s disease). Patients who do not have disease involvement in at least one of these organs don’t qualify as having IgG4-RD.
The next step is to rule out patients who have at least one exclusion criterion from a list of 21 exclusions the panel cited, divided into four categories based on the test that finds each exclusion: clinical examination, serology, radiology, or pathology.
The last step is to identify enough individual classification hallmarks in the patient so that collectively they definitively identify IgG4-RD. The writing panel endorsed seven inclusion-criteria domains that each contain at least two different disease manifestations that confer points if fulfilled. To qualify for IgG4-RD classification, a patient needs to have enough manifestations to tally at least 19 points.
Fulfilling the inclusion criteria is the key step in classification, but the exclusion criteria also play a role in helping to rule the disease in or out, Dr. Stone noted. Without the exclusion criteria, the remaining classification criteria identified the 1,395 total cases and mimics studied with an increased sensitivity of 90% (compared with 85.5% when the exclusion criteria also apply), but with reduced specificity of 88.5% (compared with 99.2%). High specificity is a key aim. The criteria are supposed to give greater uniformity to patient selection for studies and ensure that enrolled patients actually have IgG4-RD. “Our goal was criteria that would prevent enrollment of patients without IgG4-RD,” he said.
Although IgG4 level is one of the seven inclusion domains and can give a patient as many as 10.8 points toward classification when the level exceeds five times the upper limit of normal, the criteria solidify the notion that “we have greatly overemphasized IgG4” in past considerations of the disease, said Dr. Stone. Elevation of IgG4 is one of several disease markers in most patients, but it’s not essential to classification and is missing in nearly a third of patients. While the cause of IgG4-RD remains unknown, it appears to involve an abnormal interaction between B cells and a CD4+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte, an understanding that has led to testing investigational therapies that target B cells including rituximab (Rituxan) and an agent called XmAb5871. “Rituximab works very well,” Dr. Stone said. The absence of a known cause is a reason why classification is so complex.
Dr. Stone also reminded his audience that IgG4-RD is an indolent disease that can produce symptoms for months or years before getting diagnosed. It often is accompanied by significant weight loss of 20 or more pounds, but without fever, and often features a dissociation between a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate but a relatively low level of C-reactive protein. “It’s astonishing how much weight patients lose,” he said.
Though barely more than a decade on the scene, awareness of IgG4-RD among rheumatologists has become widespread, though awareness has probably lagged among many primary care physicians, Dr. Stone said in an interview. The estimated prevalence of about 185,000 U.S. residents with IgG4-RD is probably an underestimate, he added. His group at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston averages 3-5 patients evaluated each week as possibly having IgG4-RD, and this one group is now following more than 350 patients who have been diagnosed with the disease. “It’s probably more common than a lot of other conditions that rheumatologists treat, more common than scleroderma or ANCA-associated vasculitis,” Dr. Stone said. “The new criteria will help further raise awareness.”
Dr. Stone has been a consultant to and has received research funding from Genentech, Roche, and Xencor.