Roughly 79% of adults aged 65-75 years were up to date with their colorectal cancer (CRC) screening in 2018, compared with a significantly lower 63% of those aged 50-64, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That works out to almost 69% of Americans aged 50-75 years with up-to-date CRC screening, which was defined as a blood stool test in the past year, sigmoidoscopy in the past 5 years, and/or colonoscopy in the past 10 years, Djenaba A. Joseph, MD, and associates at the CDC’s National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion wrote in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
“CRC screening has increased steadily among adults over the past 20 years,” the authors noted. However, they observed a lower rate of screening in the 50-64 age group (vs. the 65-75 age group) that was consistent and significant across all demographic groups studied: sex, race/ethnicity, education, annual income, residence location, health insurance status, and regular health care provider status.
The range of screening rates in those groups went from a low of 32.6% (in 50- to 64-year-olds who had no health insurance) to a high of 87.1% (in 65- to 75-year-olds who had annual household incomes of $75,000 and over).
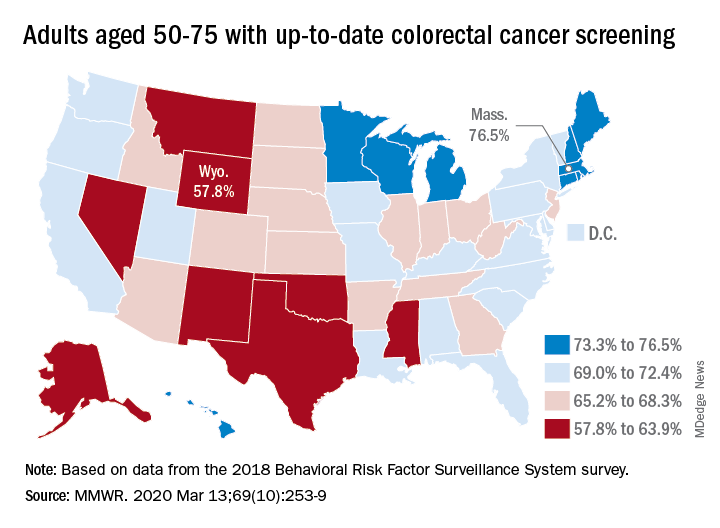
Up-to-date CRC screening rates were higher for the 65-75 age group in every state. The highest screening rate was observed in Rhode Island, at 84.9% in the 65-75 age group. Massachusetts had the highest rate for 50- to 64-year-olds, at 72.1%, and the highest rate for all ages studied (50-75 years), at 76.5%. Wyoming was lowest in all three categories: 51.5% in the 50-64 age group, 68.5% in the 65-75 age group, and 57.8% in the 50-75 age group.
“To achieve further increases in CRC screening to maximize benefit, specific efforts to increase screening in persons aged 50-64 years are needed,” Dr. Joseph and colleagues wrote. They added that efforts might include “providing education about insurance coverage for preventive services, providing clear communication about test options, and conducting research to identify and understand barriers and facilitators to CRC screening specific to this younger age group to inform effective interventions to increase screening.”
SOURCE: Joseph DA et al. MMWR. 2020 Mar 13;69(10):253-9.