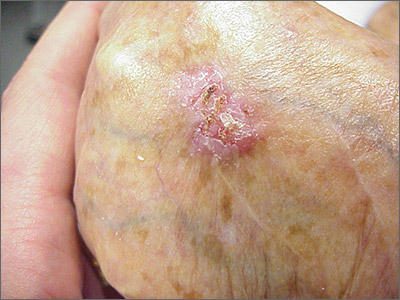
While the eroded scabbed area in a raised lesion with pearly borders raised the suspicion of basal cell carcinoma (BCC), a superficial shave biopsy revealed that this was sclerosing basosquamous carcinoma.
Basosquamous carcinoma is an uncommon form of BCC. It features nests/clusters of basaloid cells arising from the basal layer of the epidermis (a hallmark of BCC), as well as keratinization, which is seen in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Basosquamous carcinoma occurs in the same areas as more common types of nonmelanoma skin cancers (NMSCs)—that is, sun-exposed areas. Not surprisingly, then, the highest risk areas for basosquamous carcinoma are the face, hands, arms, scalp (in those without hair), and back. People with occupational or intentional sun exposure through tanning have even higher rates of NMSC than the average population; patients using tanning booths exposing their entire bodies warrant more extensive physical exams.
Basosquamous carcinoma is one of the subtypes of BCC that is associated with a higher risk of local invasion, recurrence, and metastasis. Treatment with Mohs micrographic surgery (MMS) reduces the risk of recurrence to 4% (from 12% to 51%). Even with MMS, basosquamous carcinoma can be particularly challenging. It may require additional excision stages, as well as a larger than anticipated excision size at the time of surgery.
In this case, the patient was referred for MMS due to the high-risk nature of this lesion.
Photo and text courtesy of Daniel Stulberg, MD, FAAFP, Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque.