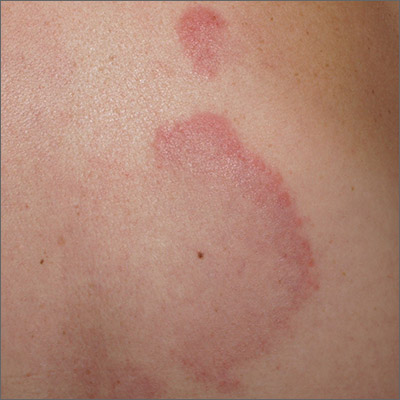
A punch biopsy of the markedly erythematous lateral edge helped to confirm this as tumid lupus erythematosus (TLE), a rare subtype of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus. TLE occurs in men and women of all ages. Annular or arcuate patches and plaques most often arise on the face, trunk, extremities, and V of the neck after sun exposure. However, as in this case, plaques may appear in areas covered by clothing. Plaques generally do not itch or hurt, but their presence can be alarming.
Annular and arcuate plaques raise a complex differential diagnosis including common conditions such as urticaria and tinea corporis, as well as more uncommon disorders such as erythema annulare centrifugum and lymphoma cutis. Unlike tinea corporis and erythema annulare centrifugum, there is very little, if any, scaling of the superficial epidermis. Plaques heal without scarring or changes to skin pigmentation.
Multiple punch biopsies of affected areas are key to a proper diagnosis. Patients with confirmed TLE should undergo antinuclear antibody testing to rule out systemic lupus erythematosus, although the vast majority will have normal results.
Treatment includes potent or ultrapotent topical steroids for the trunk and extremities, and mid- to low-potency steroids for intertriginous areas or the face. Systemic immunomodulators with hydroxychloroquine are used as first-line treatment for more extensive disease.
In this case, the patient had a normal antinuclear antibody titer and was treated with topical betamethasone dipropionate augmented 0.05% cream bid for 2 weeks, which led to complete clearance. She experienced a flare-up a year later and was retreated with the same results.
Text and photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. (Photo copyright retained.)