1. Numbers of insects (species and individuals). Smithsonian BugInfo Web site. www.si.edu/spotlight/buginfo/bugnos. Accessed November 25, 2020.
2. Antonicelli L, Bilò MB, Bonifazi F. Epidemiology of Hymenoptera allergy. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002;2:341-346.
3. Jack jumper ant allergy. Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA) Web site. Updated October 19, 2019. www.allergy.org.au/patients/insect-allergy-bites-and-stings/jack-jumper-ant-allergy. Accessed November 25, 2020.
4. Kemp SF, deShazo RD, Moffit JE, et al. Expanding habitat of the imported fire ant (Solenopsis invicta ): a public health concern. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2000;105:683-691.
5. Goodnight ML. Arachnid. In: Encyclopædia Britannica . 2012. www.britannica.com/animal/arachnid. Accessed November 25, 2020.
6. Despommier DD, Gwadz RW, Hotez PJ. Arachnids. In: Despommier DD, Gwadz RW, Hotez PJ. Parasitic Diseases . 3rd ed. Springer-Verlag; 1995:268-283.
7. Diaz JH, Leblanc KE. Common spider bites. Am Fam Physician . 2007;75:869-873.
8. Mowry JB, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR Jr, McMillan N, Ford M. 2013 Annual report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 31st Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila) . 2014;52:1032-1283.
9. Pucci S, Antonicelli L, Bilò MB, et al. Shortness of interval between two stings as risk factor for developing Hymenoptera venom allergy. Allergy. 1994;49:894-896.
10. Müller UR. Bee venom allergy in beekeepers and their family members. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol . 2005;5:343-347.
11. Müller UR. Cardiovascular disease and anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol . 2007;7:337-341.
12. Golden DBK. Stinging insect allergy. Am Fam Physician. 2003;67:2541-2546.
13. Golden DBK, Demain T, Freeman T, et al. Stinging insect hypersensitivity: a practice parameter update 2016. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017;118:28-54.
14. Bilò BM, Rueff F, Mosbech H, et al; EAACI Interest Group on Insect Venom Hypersensitivity. Diagnosis of Hymenoptera venom allergy. Allergy. 2005;60:1339-1349.
15. Reisman RE. Insect stings. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:523-527.
16. Pucci S, D’Alò S, De Pasquale T, et al. Risk of anaphylaxis in patients with large local reactions to hymenoptera stings: a retrospective and prospective study. Clin Mol Allergy. 2015;13:21.
17. Golden DBK. Large local reactions to insect stings. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract . 2015;3:331-334." class="smart-paging drupal-content" src="/sites/all/modules/contrib/smart_paging/plugins/wysiwyg/smart_paging/images/spacer.gif" title="<--pagebreak-->">
18. Clark S, Camargo CA Jr. Emergency treatment and prevention of insect-sting anaphylaxis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;6:279-283.
19. Stinging insect allergy. In: Volcheck GW. Clinical Allergy: Diagnosis and Management . Humana Press; 2009:465-479.
20. Järvinen KM, Celestin J. Anaphylaxis avoidance and management: educating patients and their caregivers. J Asthma Allergy. 2014;7:95-104.
21. Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) . Insect venom allergies: overview. InformedHealth.org. Updated May 7, 2020. www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0096282/. Accessed November 25, 2020.
22. Casale TB, Burks AW. Clinical practice. Hymenoptera-sting hypersensitivity. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1432-1439.
23. Shelley RM. Centipedes and millipedes with emphasis on North American fauna. Kansas School Naturalist . 1999;45:1-16. https://sites.google.com/g.emporia.edu/ksn/ksn-home/vol-45-no-3-centipedes-and-millipedes-with-emphasis-on-n-america-fauna#h.p_JEf3uDlTg0jw . Accessed November 25, 2020.
24. Ogg B. Centipedes and millipedes. Nebraska Extension in Lancaster County Web site. https://lancaster.unl.edu/pest/resources/CentipedeMillipede012.shtml. Accessed November 25, 2020.
25. Cushing PE. Spiders (Arachnida: Araneae). In: Capinera JL, ed. Encyclopedia of Entomology . Springer, Dordrecht; 2008:226.
26. Diaz JH, Leblanc KE. Common spider bites. Am Fam Physician. 2007;75:869-873.
27. The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) , Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Venomous spiders. www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/spiders/. Accessed November 25, 2020.
28. Starr S. What you need to know to prevent a poisonous spider bite. AAP News . 2013;34:42. www.aappublications.org/content/aapnews/34/9/42.5.full.pdf. Accessed November 25, 2020.
29. Spider bites. Mayo Clinic Web site. www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/spider-bites/symptoms-causes/syc-20352371 . Accessed November 25, 2020.
30. Barish RA, Arnold T. Spider bites. In: Merck Manual (Professional Version). Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp.; 2016. www.merckmanuals.com/professional/injuries-poisoning/bites-and-stings/spider-bites. Accessed November 25, 2020.
31. Juckett G. Arthropod bites. Am Fam Physician. 2013;88:841-847.
32. Clark RF, Wethern-Kestner S, Vance MV, et al. Clinical presentation and treatment of black widow spider envenomation: a review of 163 cases. Ann Emerg Med . 1992;21:782-787.
33. Koehler PG, Pereira RM, Diclaro JW II. Fleas. Publication ENY-025. University of Florida IFAS Extension. Revised January 2012. https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/ig087. Accessed November 25, 2020.
34. Bitam I, Dittmar K, Parola P, et al. Fleas and flea-borne diseases. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:e667-e676.
35. Leulmi H, Socolovschi C, Laudisoit A, et al. Detection of Rickettsia felis , Rickettsia typhi , Bartonella species and Yersinia pestis in fleas (Siphonaptera) from Africa. PLoS Negl Trop Dis . 2014;8:e3152.
36. Naimer SA, Cohen AD, Mumcuoglu KY, et al. Household papular urticaria. Isr Med Assoc J. 2002;4(11 suppl):911-913.
37. Golomb MR, Golomb HS. What’s eating you? Cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis ). Cutis. 2010;85:10-11.
38. Dryden MW. Flea and tick control in the 21st century: challenges and opportunities. Vet Dermatol . 2009;20:435-440.
39. Dryden MW. Fleas in dogs and cats. Merck Sharp & Dohme Corporation: Merck Manual Veterinary Manual . Updated December 2014. www.merckvetmanual.com/integumentary-system/fleas-and-flea-allergy-dermatitis/fleas-in-dogs-and-cats . Accessed November 25, 2020.
40. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Getting rid of fleas. www.cdc.gov/fleas/getting_rid.html . Accessed November 25, 2020.
41. Chattopadhyay P, Goyary D, Dhiman S, et al. Immunomodulating effects and hypersensitivity reactions caused by Northeast Indian black fly salivary gland extract. J Immunotoxicol . 2014;11:126-132.
42. Hrabak TM, Dice JP. Use of immunotherapy in the management of presumed anaphylaxis to the deer fly. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2003;90:351-354.
43. Royden A, Wedley A, Merga JY, et al. A role for flies (Diptera) in the transmission of Campylobacter to broilers? Epidemiol Infect. 2016;144:3326-3334.
44. Fradin MS, Day JF. Comparative efficacy of insect repellents against mosquito bites. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:13-18.
" class="smart-paging drupal-content" src="/sites/all/modules/contrib/smart_paging/plugins/wysiwyg/smart_paging/images/spacer.gif" title="<--pagebreak-->">
45. Carpenter S, Groschup MH, Garros C, et al. Culicoides biting midges, arboviruses and public health in Europe. Antiviral Res. 2013;100:102-113.
46. Peng Z, Yang M, Simons FE. Immunologic mechanisms in mosquito allergy: correlation of skin reactions with specific IgE and IgG anti-bodies and lymphocyte proliferation response to mosquito antigens. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1996;77:238-244.
47. Simons FE, Peng Z. Skeeter syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999;104:705-707.
48. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Travelers’ health. Clinician resources. wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/clinician-information-center. Accessed November 25, 2020.
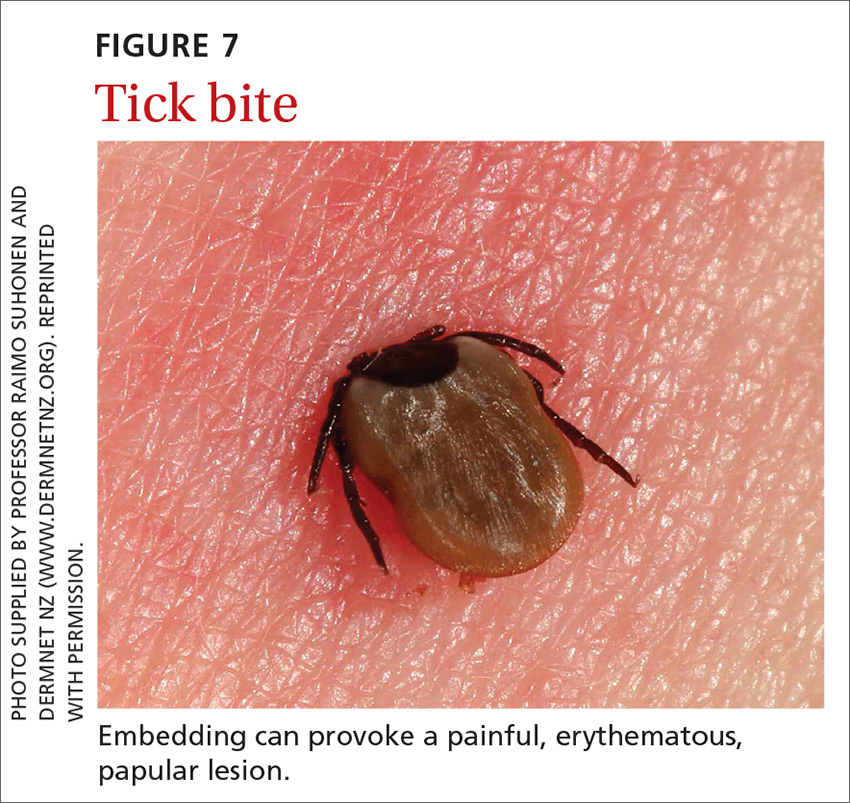
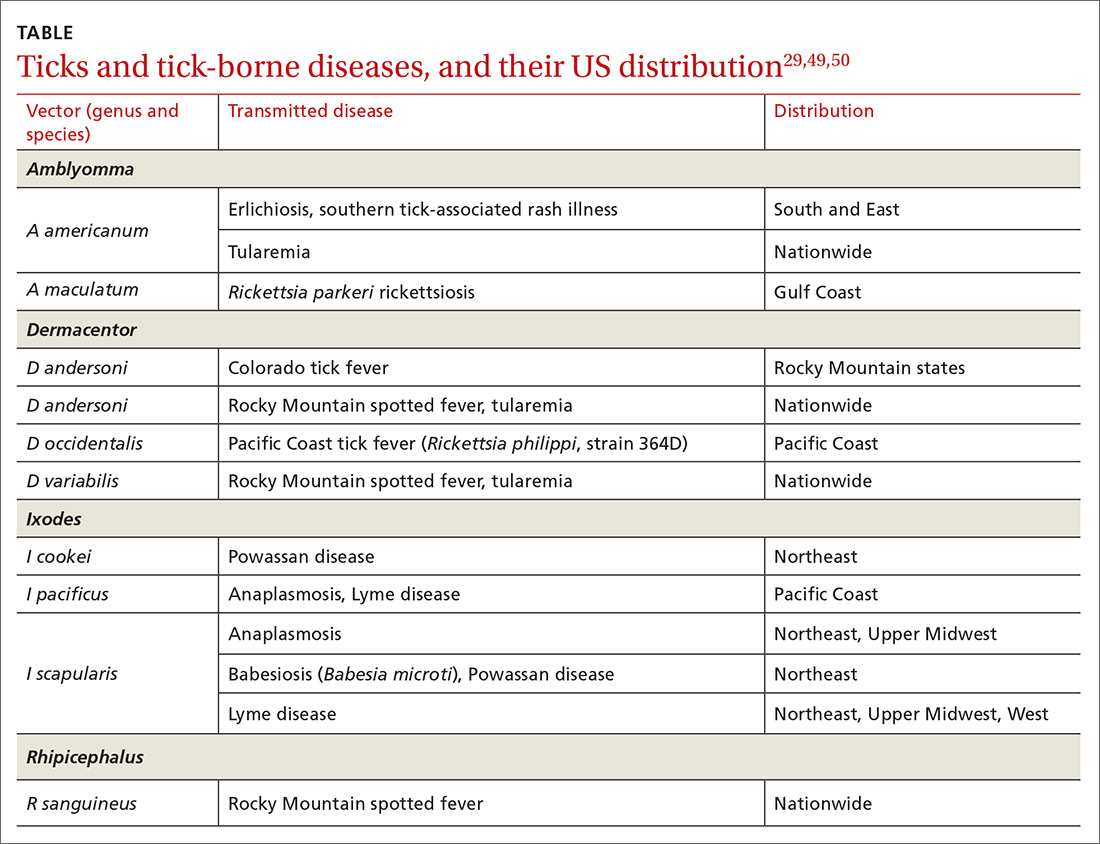
49. Gauci M, Loh RK, Stone BF, et al. Allergic reactions to the Australian paralysis tick, Ixodes holocyclus : diagnostic evaluation by skin test and radioimmunoassay. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989;19:279-283.
50. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ticks. Removing a tick. www.cdc.gov/ticks/removing_a_tick.html. Accessed November 25, 2020.
51. Golden DB, Kagey-Sobotka A, Norman PS, et al. Insect sting allergy with negative venom skin test responses. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2001;107:897-901.
52. Arzt L, Bokanovic D, Schrautzer C, et al. Immunological differences between insect venom-allergic patients with and without immunotherapy and asymptomatically sensitized subjects. Allergy. 2018;73:1223-1231.
53. Heddle R, Golden DBK. Allergy to insect stings and bites. World Allergy Organization Web site. Updated August 2015. www.worldallergy.org/education-and-programs/education/allergic-disease-resource-center/professionals/allergy-to-insect-stings-and-bites. Accessed November 25, 2020.
54. RuëffF, Przybilla B, Müller U, et al. The sting challenge test in Hymenoptera venom allergy. Position paper of the Subcommittee on Insect Venom Allergy of the European Academy of Allergology and Clinical Immunology. Allergy. 1996;51:216-225.
55. Management of simple insect bites: where’s the evidence? Drug Ther Bull . 2012;50:45-48.
56. Tracy JM. Insect allergy. Mt Sinai J Med . 2011;78:773-783.
57. Golden DBK. Insect sting allergy and venom immunotherapy: a model and a mystery. J Allergy Clin Immunol . 2005;115:439-447.
58. Winther L, Arnved J, Malling H-J, et al. Side-effects of allergen-specific immunotherapy: a prospective multi-centre study. Clin Exp Allergy . 2006;36:254-260.
59. Mellerup MT, Hahn GW, Poulsen LK, et al. Safety of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Relation between dosage regimen, allergen extract, disease and systemic side-effects during induction treatment. Clin Exp Allergy . 2000;30:1423-1429.
60. Anaphylaxis and insect stings and bites. Med Lett Drugs Ther . 2017;59:e79-e82.
61. Sampson HA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL, et al. Second symposium on the definition and management of anaphylaxis: summary report—second National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Network symposium. Ann Emerg Med . 2006;47:373-380.
62. Pflipsen MC, Vega Colon KM. Anaphylaxis: recognition and management. Am Fam Physician . 2020;102:355-362. Accessed November 25, 2020.