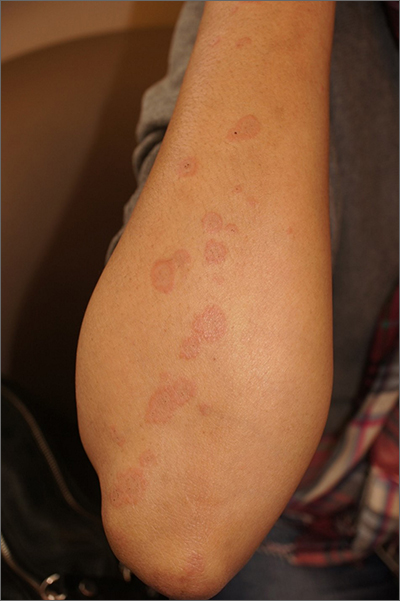
The clinical features of targetoid lesions occurring soon after herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection points to a diagnosis of erythema multiforme (EM), which was confirmed by punch biopsy. The differential diagnosis for targetoid small lesions includes granuloma annulare, pityriasis rosea, and linear IgA bullous dermatosis. Larger targetoid lesions would be more concerning for erythema migrans (Lyme disease), tumid lupus, and severe tinea corporis.
Erythema multiforme represents an immune reaction triggered most often by HSV. About 10% of cases are triggered by exposure to various other viruses, drugs, and bacteria—notably, Mycoplasma pneumonia.1 Symptoms vary from mildly uncomfortable crops of annular and targetoid plaques to widespread annular plaques and bullae.
In the past, EM was considered a clinical variant along a continuum with Stevens Johnson Syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). Although mucosal involvement may occur with EM, it never progresses to SJS or TEN. The latter 2 diagnoses are associated with significant skin pain, dusky confluent patches, and a positive Nikolsky sign—wherein skin pressure causes superficial separation of the epidermis. Additionally, SJS and TEN tend to involve the trunk, whereas EM typically involves acral surfaces.
EM is self-limited but may recur in patients with additional HSV flares. Patients with frequent recurrences benefit from long-term suppression of HSV with valacyclovir 500 mg bid. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cool compresses control mild pain. Itching may be relieved with topical, medium-potency steroids or oral antihistamines. Oral ulcers or lesions may be treated with lidocaine oral suspension. Systemic steroids are contraindicated for mild disease, but they have a somewhat controversial role in alleviating severe symptoms.
This patient had mild symptoms and tolerated topical triamcinolone 0.1% cream bid without recurrence at 6 months.
Text courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD, medical director, MDFMR Dermatology Services, Augusta, ME. Photos courtesy of Jonathan Karnes, MD (copyright retained).