Intimate partner violence (IPV) includes physical, sexual, or psychological aggression or stalking perpetrated by a current or former relationship partner.1 IPV affects more than 12 million men and women living in the United States each year.2 According to a national survey of IPV, approximately one-third (35.6%) of women and one-quarter (28.5%) of men living in the United States experience rape, physical violence, or stalking by an intimate partner during their lifetime.2 Lifetime exposure to psychological IPV is even more prevalent, affecting nearly half of women and men (48.4% and 48.8%, respectively).2
Lifetime prevalence of any form of IPV is higher among women who identify as bisexual (59.8%) and lesbian (46.3%) compared with those who identify as heterosexual (37.2%); rates are comparable among men who identify as heterosexual (31.9%), bisexual (35.3%), and gay (35.1%).3 Preliminary data suggest that IPV may have increased in frequency and severity during the COVID-19 pandemic, particularly in the context of mandated shelter-in-place and stay-at-home orders.4-6
IPV is associated with numerous negative health consequences. They include fear and concern for safety, mental health disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and physical health problems including physical injury, chronic pain, sleep disturbance, and frequent headaches.2 IPV is also associated with a greater number of missed days from school and work and increased utilization of legal, health care, and housing services.2,7 The overall annual cost of IPV against women is estimated at $5.8 billion, with health care costs accounting for approximately $4.1 billion.7 Family physicians can play an important role in curbing the devastating effects of IPV by screening patients and providing resources when needed.
Facilitate disclosure using screening tools and protocol
In Ms. T’s case, evidence of violence was clearly visible. However, not all instances of IPV leave physical marks. The US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends that all women of childbearing age be screened for IPV, whether or not they exhibit signs of violence.8 While the USPSTF has only published recommendations regarding screening women for IPV, there has been a recent push to screen all patients given that men also experience high rates of IPV.9
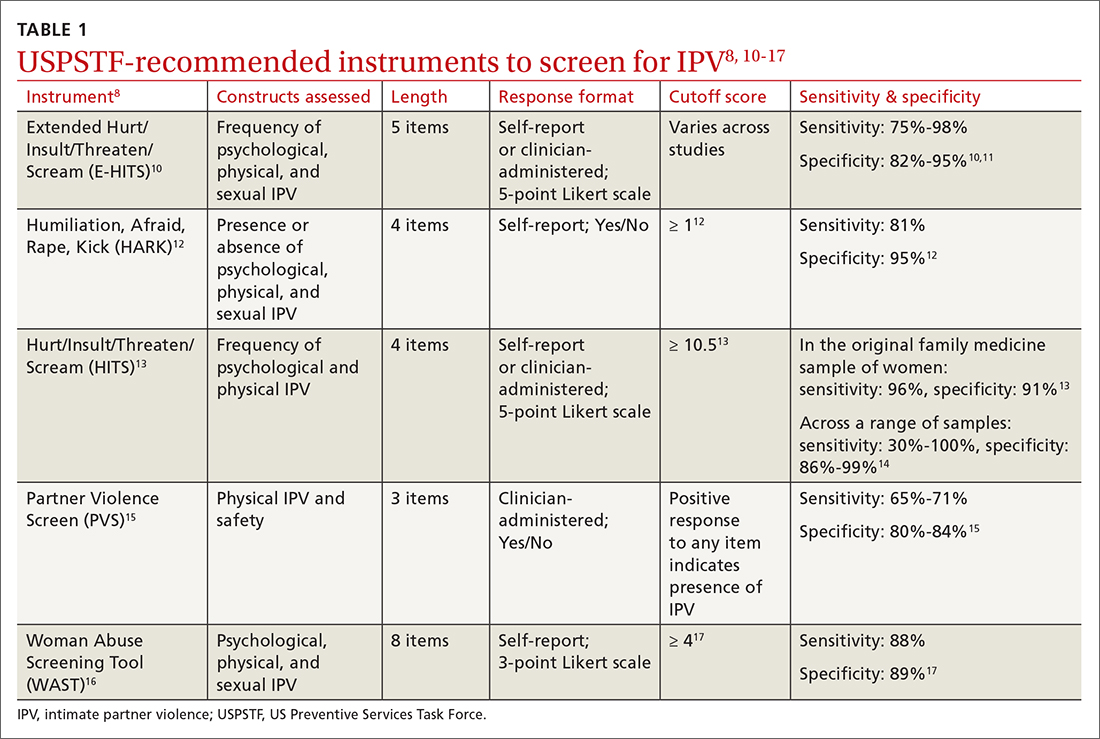
Utilize a brief screening tool. Directly ask patients about IPV; this can help reduce stigma, facilitate disclosure, and initiate the process of connecting patients to potentially lifesaving resources. The USPSTF lists several brief screening measures that can be used in primary care settings to assess exposure to IPV (TABLE 18,10-17). The brevity of these screening tools makes them well suited for busy physicians; cutoff scores facilitate the rapid identification of positive screens. While the USPSTF has not made specific recommendations regarding a screening interval, many studies examining the utility of these measures have reported on annual screenings.8 While there is limited evidence that brief screening alone leads to reductions in IPV,8 discussing IPV in a supportive and empathic manner and connecting patients to resources, such as supportive counseling, does have an important benefit: It can reduce symptoms of depression.18
Continue to: Screen patients in private; this protocol can help