DUBLIN – with high levels of visceral fat and overweight/obesity.
Three months of auricular acupuncture stimulation and dietary restriction led to a mean weight loss of nearly 9 kg plus a drop in waist circumference of more than 10 cm.
According to the researchers, acupuncture beads, used in Japan to augment weight loss for more than 30 years, are thought to stimulate nerves and organs that regulate appetite, satiety, hunger, and food cravings.
Findings of the observational study were presented by Takahiro Fujimoto, MD, PhD, Clinic F, Tokyo, at this year’s European Congress on Obesity.
Together with a prior study using the same intervention in women, Dr. Fujimoto and colleagues have now gathered data in more than 1,000 individuals, he said. “We wanted a method that was simple and noninvasive that would serve as a support to exercise and dietary therapy,” Dr. Fujimoto said in an interview.
“We believe there is an effect,” he asserted. “Acupuncture’s effect lies in stimulating the satiety center with benefits in helping individuals to control their food cravings and intake when reducing meals,” he said, pointing out that similar techniques have been used in patients undergoing withdrawal from drug addiction and in smoking cessation. He explained that acupuncture beads are believed to help individuals change their lifestyle habits, and added that “the relapse rate after 6 months is addressed in another paper, and it is very low.”
Professor Jason C.G. Halford, PhD, head of school at the University of Leeds, England, and president of the European Association for the Study of Obesity, commented on the findings. “There is no control group here receiving everything but the acupuncture,” he noted. “As such, it could be other elements of the intervention driving this [effect] including the act of keeping a food diary increasing awareness of one’s diet. A randomized controlled trial would be the next step.”
In women, the technique led to significantly more weight loss than in those who were untreated, and weight loss was maintained for 6 months after the end of treatment.
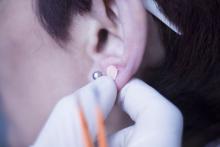
The researchers added that acupuncture stimulation with beads was a simpler method than traditional use of intradermal needles requiring expert acupuncturists. The stimulation is applied with 1.5-mm metal ear beads on 6 points of the outer ear (shen men, food pipe, upper stomach opening, stomach, lungs, and endocrine system) that correspond to meridian lines, and as such, restores the flow of qi by resolving any blockages or disruption. This may help with a variety of health conditions, according to the researchers. Placed on both ears, surgical tape was used to keep the beads in place to ensure participants continuously received uniform pressure on each of the six acupuncture points.
Dietary guidance was provided to participants to help reduce food intake by half, and nutritional supplements were given to compensate for any deficiencies. Participants attended twice-weekly clinic visits for bead sticking and diet progress monitoring. Body weight, body fat percentage, fat mass, lean mass, muscle mass, body mass index (BMI), and abdominal fat were assessed at the start and end of the study period.
“Since these tiny metal beads are attached to six points on the outer ear that stimulate nerves and organs which regulate appetite, satiety, and hunger, this type of acupuncture does not require complex knowledge or skill,” explained Dr. Fujimoto.
The results of the latest study, in men only, build on a prior study of more than 1,300 women who also received auricular acupuncture stimulation with beads as well as a halving of their food intake. In women, the weight loss program led to total body weight loss of 11.2% over 3 months.
At baseline, the 81 male participants, ages 21-78 years, had a mean BMI of 28.4 kg/m2 and mean waist circumference of 98.4 cm. Body fat percentage was 28.2%.
After 3 months, participants lost a mean of 8.6 kg (P < .001), decreased waist circumference by a mean of 10.4 cm (P < .001), and lost a mean of 4.0% of total body fat (P < .001). Visceral fat levels also fell by 2.2 points (P < .001), from 15.2 points at baseline to 13.0 points after 3 months. (A healthy visceral fat rating is between 1 and 12 points.) BMI decreased by almost 3 kg/m2 (from 28.4 at baseline to 25.5 at 3 months; P < .001).
Improvement in muscle-to-fat ratio was greater in men than women, whereas women had a greater decrease in percentage body fat than men.
“Whilst receiving ear acupuncture, the investigators asked participants to cut their food intake by half. It’s not unreasonable to expect that this major dietary change was the main reason participants lost weight,” remarked Graham Wheeler, PhD, statistical ambassador at the Royal Statistical Society, United Kingdom.
He also commented on the lack of a control group: “This study does not show us the impact of ear acupuncture on weight loss.”
Dr. Fujimoto and Dr. Halford have reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wheeler is a statistical ambassador for the Royal Statistical Society, is employed by GSK, and holds an honorary senior lecturer post at Imperial College London.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.