The Case for Potassium Supplementation
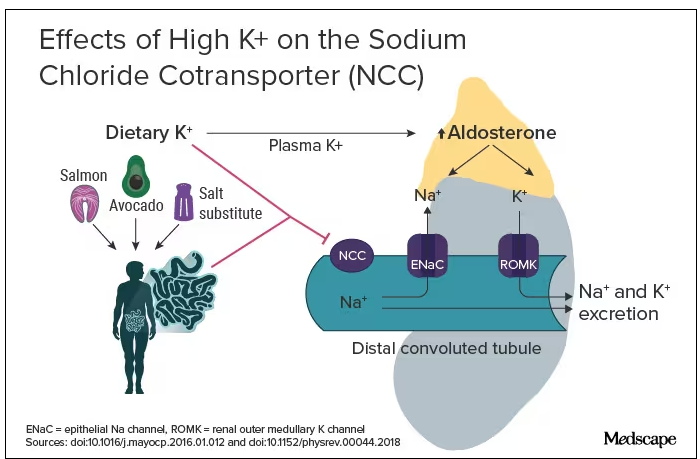
The evidence for salt restriction notwithstanding, Swapnil Hiremath, MD, MPH, from the University of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, argued in his editorial that potassium supplementation has gotten short shrift. Though he admits the studies for potassium supplementation have been smaller and sometimes rely on observational evidence, the evidence is there. In the distal convoluted tubule, the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC), aka the potassium switch, is turned on by low potassium levels and leads to sodium reabsorption by the kidney even in settings of high sodium intake (Figure). To nonnephrologists, renal physiology may be a black box. But if you quickly brush up on the mechanism of action of thiazide diuretics, the preceding descriptor will make more sense.
Dr. Hiremath points out that the DASH diet study also got patients to increase their potassium intake by eating more fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, the SSaSS study tested a salt substitute that was 25% potassium (and 75% sodium).
How much blood pressure lowering is due to sodium restriction vs potassium supplementation is a complex question because lowering sodium intake will invariably lead to more potassium intake. “It’s very hard to untangle the relationship,” Dr. Hiremath said in an interview. “It’s sort of synergistic but it’s not completely additive. It’s not as if you add four and four and get eight.” But he maintains there is more evidence regarding the benefit of potassium supplementation than many realize.
Realistic Diets and Taste Issues
“We know that increasing potassium, decreasing sodium is useful. The question is how do we do that?” says Dr. Hiremath. Should we encourage fruit and vegetable consumption in a healthy diet, give potassium supplements, or encourage the use of low-sodium salt substitutes?
Recommending a healthier diet with more fruits and vegetables is a no-brainer. But getting people to do it is hard. In a world where fruit is more expensive than junk food is, economic realities may drive food choice regardless of our best efforts. The 4700 mg of potassium in the DASH eating plan is the equivalent of eleven bananas daily; although not impossible, it would require a substantive shift in eating patterns for most people.
Given that we prescribe iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and vitamin D to patients who need them, why not potassium tablets to help with blood pressure? Granted, there are concerns about inducing hyperkalemia. Also, why not just prescribe a proven anti-hypertensive, such as ramipril, which has the added benefit of helping with renal protection or cardiac remodeling? Dr. Hiremath points out that patients are far less reluctant to take dietary supplements. Medication is something you take when sick. A supplement is seen as “natural” and “healthy” and might be more attractive to people resistant to prescription meds.
Another drawback of oral potassium supplementation is taste. In a Consumer Reports taste test, potassium chloride fared poorly. It was bitter and had a metallic aftertaste. At least one tester wouldn’t ever consume it again. Potassium citrate is slightly more palpable.
Salt substitutes, like the 75:25 ratio of sodium to potassium used in SSaSS, may be as high as you can go for potassium in any low-sodium salt alternative. If you go any higher than that, the taste will just turn people off, suggests Dr. Hiremath.
But SsaSS, which was done in China, may not be relevant to North America. In China, most sodium is added during cooking at home, and the consumption of processed foods is low. For the typical North American, roughly three quarters of the sodium eaten is added to their food by someone else; only about 15% is added during cooking at home or at the dinner table. If you aren’t someone who cooks, buying a salt substitute is probably not going to have much impact.
Given that reality, Dr. Juraschek thinks we need to target the sodium in processed foods. “There’s just so much sodium in so many products,” he says. “When you think about public policy, it’s most expeditious for there to be more regulation about how much is added to our food supply vs trying to get people to consume eight to 12 servings of fruit.”