- Use fishing line cut to different lengths (4 cm=10 g; 8 cm=1 g) as substitutes for monofilaments to assist in the diagnosis of diabetic neuropathy. This test is highly specific for neuropathy; using longer lengths of line increases sensitivity.
- Physicians and healthcare providers can use this quick, inexpensive tool for screening neuropathy. Patients can be empowered inexpensively to examine their own feet and reduce the likelihood of developing foot ulcers or amputations.
If there were a less expensive means of reliably performing a standard clinical test in diabetes care, would you want to know about it? If your answer is yes, then the results of this study should be of interest to you. What’s more, your patients can be given the same test to perform at home.
Patients with diabetes have a 15- to 40-times greater risk of leg amputations than those without diabetes, due to loss of protective sensation, ulceration, infection, and gangrene.1-6 Screening for loss of sensation helps prevent foot ulcerations and amputations.
According to the 1988 San Antonio ADA/AAN consensus,7 a diagnosis of diabetic neuropathy (revised in 1992)8 requires that 2 of 4 criteria be met: signs and symptoms, nerve conduction abnormalities, quantitative sensory test (QST) abnormalities, or autonomic test abnormalities. Monofilament testing, part of the QST, can detect loss of pressure sensation on the foot. The 10-g monofilament predicts foot ulcers,9-11 and the 1-g tests sensitivity.12 The reproducibility and predbictive value of monofilaments in identifying diabetes patients at risk for serious limb complications have led the International Diabetes Federation and the World Health Organization to recommend their use.13
Our aim was to demonstrate the utility of 10-g and 1-g monofilaments constructed from fishing line in screening for diabetes neuropathy compared with other QST modalities, including the entire set of monofilaments, in a forced-choice algorithm. We also wanted to show that physicians and patients alike can use this simple, disposable, single-use method for detecting neuropathy.
Methods
We studied 871 subjects (579 normal controls and 292 patients with diagnosed peripheral neuropathy). The study consisted of a 15-item questionnaire that surveyed age, height, weight, race, and diabetes-related issues. We measured random glucose levels with a glucometer to rule out undisclosed hypoglycemia among controls, and performed vibration detection thresholds (VDT) as another confirmatory neuropathy test (values >15 V).
Disposable monofilaments were constructed in our laboratory using commercially available 25-lb “South Bend” brand high-knot-strength fishing line No. M-1425 (South Bend, Inc, North Brook, Ill), which measured 0.020 inches (500 microns) in diameter. We cut the 10-g monofilament to 4 cm in length; the 1-g monofilament to 8 cm. Gripping 1 cm of each monofilament at one end, we used a standard laboratory balance to confirm the buckling force of these lengths. Different brands of fishing line would have to be tested separately for the length needed to create 1- and 10-g monofilaments.
We used a straightforward “yes-no” algorithm in which the subject was asked to identify the presence of sensation correctly on 4 out of 5 trials. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVAR) was used to evaluate interval variables, and likelihood ratio chi-square tests for nominal variables. Statistical significance for all comparisons was accepted at P<.05.
Results
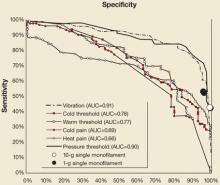
The demographic characteristics of the groups studied are shown in TABLE 1. The sensitivity of the single 10-g and 1-g monofilament was found to be 42.8% and 52.4%, and specificity for each was 99.3% and 96.3%, respectively. TABLE 2 shows the comparison of all of the sensory modalities studied regarding sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV). PPV and NPV were calculated for each modality, with an assumption of disease prevalence of 55% in the diabetic population.14 The 1-g and 10-g monofilaments have very high PPV due to their high specificity (98.7% and 94.6%), but relatively poor NPV (58.7% and 62.3%). The other sensory modalities had good PPV as well (ranging from 81.4% to 91.2%), but a wide range of NPV (53.3% to 75.7%). Lastly, receiver operating characteristic curves (FIGURE) were used to demonstrate the relative value of different sensory modalities, including the single-point values for the 1-g and 10-g monofilaments.
TABLE 1
Epidemiology and group characteristics of the cohort
| CONTROLS | DIABETIC NEUROPATHS | P VALUE | TEST | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 579 | 292 | ||
| Age (years±SE) | 38.5±0.7 | 61.4±0.8 | <.0001 | ANOVA |
| Gender (M : F) | 200:376 | 169:123 | <.0001 | χ2 |
| Race (n, % of group) | <.0001 | χ2 | ||
| White | 198 (38%) | 226 (87%) | ||
| Black | 274 (53%) | 27 (10%) | ||
| Asian/Pacific Area | 24 (5%) | 1 (<1%) | ||
| Hispanic | 14 (3%) | 2 (1%) | ||
| Native American | 10 (2%) | 0 | ||
| Other | 1 (<1%) | 3 (1%) | ||
| Height | 66.7±0.2 | 67.4±0.3 | .0837 | ANOVA |
| Weight | 168.8±1.9 | 200.8±4.2 | <.0001 | ANOVA |
| Body-mass index | 26.6±0.3 | 30.5±0.7 | <.0001 | ANOVA |
| Random glucose (finger stick) | 95.3±0.8 | 138.2±4.9 | <.0001 | ANOVA |
TABLE 2
Sensitivity and specificity of sensory modalities*
| DIAGNOSTIC CUTOFF LEVEL | SENSITIVITY | SPECIFICITY | PPV† | NPV† | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-g single monofilament | 10 g | 42.8% | 99.3% | 98.7% | 58.7% |
| 1-g single monofilament | 1 g | 52.4% | 96.3% | 94.6% | 62.3% |
| Pressure threshold (multiple monofilaments) | 0.98 g | 76.3% | 90.6% | 90.8% | 75.7% |
| Vibration threshold | 5.1 volts | 76.0% | 91.0% | 91.2% | 75.6% |
| Cold detection threshold | 1.6°C | 44.8% | 90.0% | 84.6% | 57.2% |
| Warm detection threshold | 1.6°C | 46.6% | 92.1% | 87.9% | 58.5% |
| Cold pain threshold | 0.0°C | 35.3% | 90.2% | 81.4% | 53.3% |
| Heat pain threshold | 17.8°C | 35.5% | 90.2% | 81.5% | 53.4% |
| * Includes pressure monofilaments (multiple monofilaments using a forced-choice algorithm), the 10-g and 1-g monofilament, and other sensory modalities. The diagnostic cutoff level for each sensory continuum was set at 90% specificity. | |||||
| † Positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) assume presence of diabetes and 55% disease prevalence of neuropathy in the diabetic population. | |||||
FIGURE
Evaluation of neuropathy: ROC curve analysis
Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) of all of the sensory modalities across their spectrum of measurement, expressed here as sensitivity and specificity (instead of the more customary 1–specificity used in signal detection theory) for clinical usefulness. AUC denotes area under the curve for each modality.