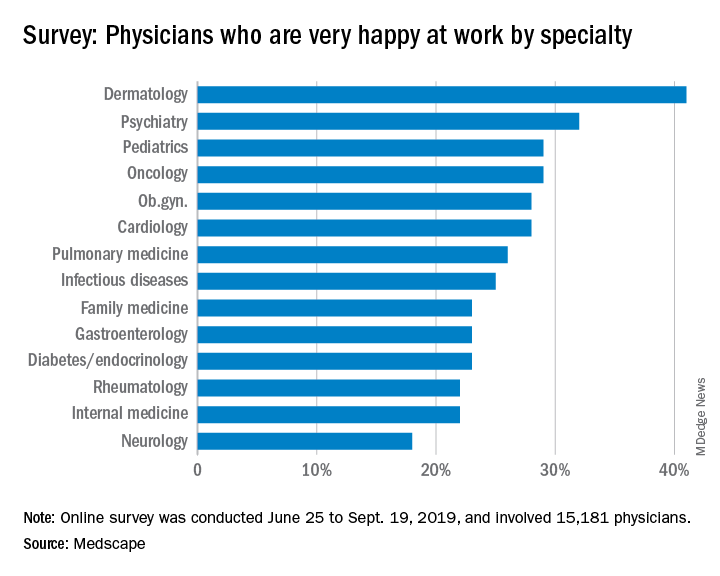
When it comes to physician happiness both in and outside the workplace, oncologists are about average, according to Medscape’s 2020 Lifestyle, Happiness, and Burnout Report.
Oncologists landed in the middle of the pack among all physicians surveyed for happiness. Rheumatologists were most likely to report being very or extremely happy outside of work (60%) and neurologists were least likely to do so (44%), but about half of oncologists (51%) reported being very/extremely happy outside of work. For happiness at work, dermatologists topped the list (41%), neurologists came in last (18%), and oncologists remained in the middle (29%).
Oncologists were average when it came to burnout as well, matching the rate of overall physicians. Specifically, 32% of oncologists were burned out, 4% were depressed, and 9% were both burned out and depressed.
The most commonly reported factors contributing to burnout among oncologists were an overabundance of bureaucratic tasks (74%), spending too many hours at work (42%), and a lack of respect from colleagues in the workplace (36%).
Exercise was the most commonly reported way oncologists dealt with burnout (51%), followed by talking with family and friends (49%), and isolating themselves from others (38%). In addition, 57% of oncologists took 3-4 weeks’ vacation, compared with 44% of physicians overall; 29% of oncologists took less than 3 weeks’ vacation.
About 18% of oncologists said they had contemplated suicide, and 1% said they’d attempted it; 72% said they’d never had thoughts of suicide. Just under one-quarter of oncologists said they were currently seeking professional help or were planning to seek help for symptoms of depression and/or burnout.
“The survey results are concerning on several levels,” Maurie Markman, MD, of Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Philadelphia, said in an interview.
“First, the data suggest a considerable number of oncologists are simply burned out from the day-to-day bureaucracy (paperwork, etc.) of medical practice, which has absolutely nothing to do with the actual care delivered. This likely impacts the willingness to continue in this role. Second, one must be concerned for the future recruitment of physicians to become clinical oncologists. And finally, one must wonder about the impact of these concerning figures on the quality of care being provided to cancer patients.”
This survey was conducted from June 25 to Sept. 19, 2019, and involved 15,181 physicians. Oncologists made up 1% of the survey pool.