How do patients fare clinically?
From their chart reviews and interviews with case clinicians, Dr. Oster said, “we started to learn quickly that this is really a different type of myocarditis.”
For example, its onset, typically within a few days of the potential immunologic cause, was more rapid than in viral myocarditis, and its symptoms resolved faster, the report notes. Clinical presentations tended to be less severe, treatments not as intensive, and outcomes not as serious, compared with “the kind of typical viral myocarditis that most of the providers were used to taking care of in the past,” he said. “The pattern for these cases was very consistent.”
The study covered VAERS reports of suspected myocarditis arising within a week of first dose of a mRNA-based vaccine from the United States launch of public vaccination in December 2020 to August 2021, the CDC-based group reported. By then, more than 192 million people in the country had received either the Pfizer-BioNTech (age 12 or older) or Moderna (age 18 or older) vaccines.
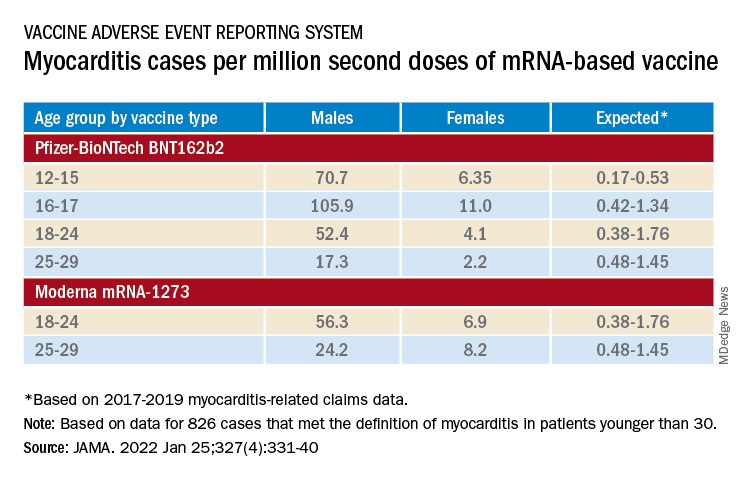
Of the 1,991 reports of myocarditis, including 391 also involving pericarditis, 1,626 met the study’s definition for myocarditis on adjudication; about 82% of the latter cases were in males.
Based on the investigators’ review of charts and clinician interviews connected with 826 cases that met their definition of myocarditis in patients younger than 30, 89% reported “chest pain, pressure, or discomfort” and 30% reported dyspnea or shortness of breath. Troponin levels were elevated in 98%, 72% of patients who underwent electrocardiography showed abnormalities, and 12% of those with echocardiography had left ventricular ejection fractions less than 50%.
About 96% were hospitalized, and presenting symptoms resolved by discharge in 87% of those with available data, the group noted. Among patients with data on in-hospital therapy, they wrote, NSAIDs were the most common therapy, in 87%.
‘Mild and self-limiting’
The case-control study from Hong Kong didn’t specifically examine patients’ treatment and clinical course, but it does portray their vaccine-associated myocarditis as contrasting with more familiar viral myocarditis.
Patients with “typical” myocarditis tend to be “overall much sicker than what we’re seeing with myocarditis following vaccination,” Dr. Truong agreed. None of the 20 patients with myocarditis after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in Hong Kong were admitted to the intensive care unit. That, she added, suggests none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or vasoactive support, often necessary in viral myocarditis. “And they had shorter hospital stays.”
In contrast, Dr. Wong noted, 14 of the study’s unvaccinated patients required ICU admission; 12 of them died during the follow-up period. None with vaccine-related carditis died during the study’s follow-up. “We also showed that cases following [Pfizer-BioNTech] vaccination were all mild and self-limiting.”
Dr. Truong largely agreed that SARS-CoV-2 vaccine myocarditis and most myocarditis seen before the pandemic can be viewed as distinct clinical entities, “at least in the short term. I think we do need to follow these patients to look at more long-term outcomes, because at this point I don’t think we know the long-term implications. But at least in the short term, it seems like these patients are different, are much less sick, and recover pretty quickly overall.”
Dr. Oster emphasized that the many and varied acute and long-term hazards from contracting COVID-19 far outweigh any risk for myocarditis from vaccination. But for individuals who were hit with myocarditis soon after their first mRNA vaccine dose, who have already established their susceptibility, he and his colleagues would recommend that they “consider alternatives and not get the vaccine again.”
Dr. Oster reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wong and colleagues did not report any relevant disclosures. Dr. Truong has previously disclosed serving as a consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.