SAN FRANCISCO – The hearts of 100 consecutive patients who underwent adjuvant radiotherapy for left-sided breast cancer in 2011 received an average of 2.9 Gray of radiation, considerably less than the mean cardiac exposure of 4.9-Gy reported in a recent review of 2,168 patients treated from 1958 to 2001 in Sweden and Denmark.
The findings confirm that three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) reduces cardiac exposure to radiation, Dr. Federico Lonardi and his associates reported at a breast cancer symposium sponsored by the American Society of Clinical Oncology. But certain areas of the heart still receive high doses when patients have adverse anatomic conditions that are not well suited to 3D-CRT. Because heart structures may differ in radiosensitivity, higher doses to small volumes of the heart, such as the coronary artery, might be associated with more risk, the researchers cautioned.
 Images courtesy Dr. Manuela Coeli
Images courtesy Dr. Manuela Coeli
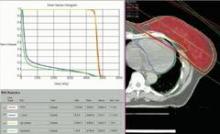
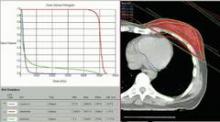
Fig. 1: 3-Dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT) of breast cancer in adjuvant setting may allow very low doses to the heart if anatomy is favorable. In this patient, the mean dose to the whole heart is 2.38 Gy. Less than 5% of the heart volume is exposed to 5Gy and less than 0.2% to 25Gy.
Most patients received a mean cardiac dose of 2-3 Gy (32%), 21% of patients were exposed to 1.15-1.99 Gy, and 1% got 0.8 Gy in a study of a consecutive series of breast cancer patients treated at Mater Salutis Hospital in Legnago, Italy. Only 17% of patients received a mean cardiac dose of more than 5 Gy, and 13% received 4.16-4.83 Gy.
The cardiac dose ranged from 0.8 to 13.05 Gy in Dr. Lonardi’s study, compared with a range of 0.03 to 27.72 Gy in the recently published Scandinavian study (N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;368:987-998). In the published study, the longitudinal risk for major cardiac events increased in a linear fashion, with a 7% increase for cardiac events with every 1 Gy increase in radiation to the heart.
In the Italian study, the median volumes of heart exposed to higher doses of radiation were "consistently low" with 4% of heart volumes exposed to 5 Gy or more, 3% exposed to 10Gy or more, 2% exposed to 15 Gy or more, and 0.7% exposed to 25 Gy or more Dr. Lonardi reported.
These patients received full-breast 3D-CRT with two to four customized tangential fields after mastectomy (10% of patients) or quadrantectomy (90%). The whole breast (or chest wall) received 50 Gy/25 fractions in 66 patients and 45 Gy/18 fractions in 34 patients. Boost to surgical bed (10 Gy/4-5 fractions) was delivered by photons in 10 patients. Median number of tangential fields was two (range, two to four). Patients were treated while supine on a breast board, without immobilization devices or instructions to hold their breath. They were freely breathing but were asked to minimize respiratory motion during the CT scan used to plan radiation delivery and the treatment itself. No dose constraints were specified for heart structures; a mean heart dose lower than 5 Gy was recommended at the time of treatment.
A preliminary assessment of radiation delivered to the left anterior descending coronary arteries in this series suggests that they received 9-25 Gy, Dr. Lonardi reported.
Based on estimates using previous models, the probability of death from cardiac causes within 15 years after standard fractionated radiotherapy may be less than 1% if less than 10% of the heart is exposed to 25Gy or more, he noted. "In this perspective, our results appear very favorable, though they confirm that the heart may receive high doses to limited volumes despite the use of standard 3D techniques. In such cases, high-conformal, intensity-modulated techniques are helpful" to further reduce the exposure of critical heart structures to radiation.
The symposium was cosponsored by the American Society of Breast Disease, the American Society of Breast Surgeons, the National Consortium of Breast Centers, the Society of Surgical Oncology, and the American Society for Radiation Oncology.
Dr. Lonardi reported having no financial disclosures.
On Twitter @sherryboschert