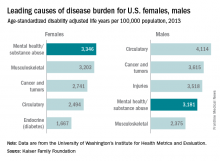
Mental health and substance abuse disorders are the leading cause of disease burden among U.S. females and the fourth-leading cause for males, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Mental health/substance abuse conditions caused 3,346 age-standardized disability adjusted life years (DALYs) per 100,000 population for females in 2013, putting those conditions ahead of musculoskeletal conditions (3,203 DALYs per 100,000), cancer and tumors (2,741 DALYs), circulatory conditions (2,494 DALYs), and diabetes and other endocrine conditions (1,667 DALYs), Kaiser reported.
Among males, the disease burden resulting from mental health/substance abuse – 3,181 DALYs per 100,000 population – was less than that from circulatory conditions (4,114 DALYs per 100,000), cancer and tumors (3,615 DALYs), and injuries (3,518 DALYs). Musculoskeletal disorders were fifth at 2,375 DALYs, according to data from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation’s Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.
The World Health Organization defines DALYs as “the sum of years of potential life lost due to premature mortality and the years of productive life lost due to disability.”