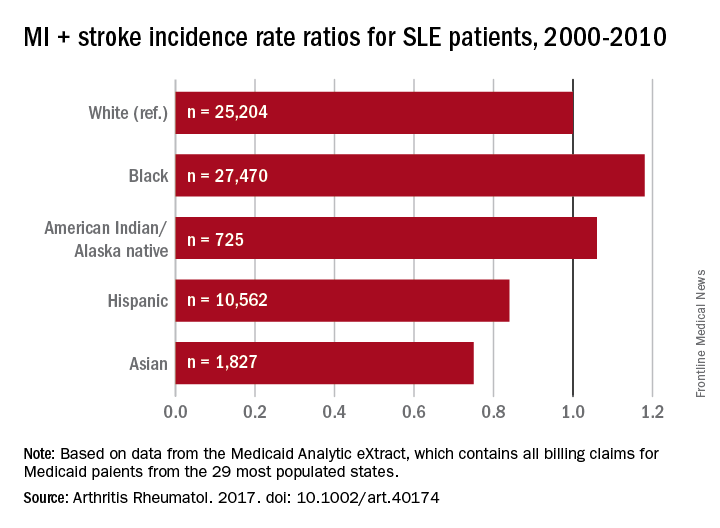
Black patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are more likely than whites to have a cardiovascular event, but Hispanics, Asians, and American Indians/Alaska natives with SLE are less likely than whites to experience a CV event, according to a study involving almost 66,000 Medicaid patients.
In a comparison of incidence rate ratios with whites as the reference group (IRR, 1.0), black patients with SLE had an IRR of 1.18 for cardiovascular events (defined as a first acute myocardial infarction or stroke), Hispanic patients had an IRR of 0.84, Asians had an IRR of 0.75, and American Indians/Alaska natives had an IRR of 1.06, reported Medha Barbhaiya, MD, MPH, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and her associates (Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. doi: 10.1002/art.40174).
The two components of the CV event rate did not always contribute equally, however. Blacks with SLE had a significantly higher risk of stroke, compared with whites, but the MI risk was almost equal. Hispanics also had a significantly higher stroke rate than did whites, but the MI risk for Hispanics was significantly lower. For Asian SLE patients, stroke and MI risks both were lower than for whites, but only the difference for MI was significant. The MI risk for American Indians/Alaska natives was lower, compared with whites, and the stroke risk was higher, but neither difference was significant, the investigators said.The substantial reduction in MI risk among Hispanics and Asians, compared with white SLE patients, suggests an “Hispanic and Asian paradox” since “SLE has been reported to be more prevalent, more severe, and to result in more end-organ damage in Hispanics and Asians compared to white patients,” Dr. Barbhaiya and her associates wrote.
The data for 65,788 cases of SLE from Jan. 1, 2000, to Dec. 31, 2010, were taken from the Medicaid Analytic eXtract, which contains all Medicaid billing claims from the 29 most populous states. Over a mean follow-up of 3.8 years, those SLE patients had 2,259 first-CV events, which works out to an overall incidence rate of 9.31 per 1,000 person-years.
The study was supported by awards from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. Dr. Barbhaiya and one of her associates are supported by awards from the Rheumatology Research Foundation. The investigators did not disclose any conflicts.