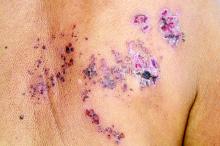
For patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), thiopurine exposure was associated with a significantly increased risk of herpes zoster, compared with 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) monotherapy, according to the results of two large retrospective cohort studies.
In the multivariable analysis, thiopurine monotherapy was linked to about a 47% increase in the risk of herpes zoster, compared with 5-ASA monotherapy (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.47; 95% confidence interval, 1.31-1.65; P less than .001). Combination therapy with thiopurines and tumor necrosis factor antagonists conferred about a 65% increase in zoster risk (aHR, 1.65; 95% CI, 1.22-2.23; P = .001). However, tumor necrosis factor–antagonist monotherapy did not appear to significantly increase the risk of zoster when compared with 5-ASA monotherapy, reported Nabeel Khan, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, and his associates.
“Compared to [patients without] IBD, ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD) each were associated with significantly increased risk of herpes zoster infection,” the researchers wrote online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “With the approval of a new and potentially safer vaccine for herpes zoster, the effects of immunization of patients with IBD should be investigated.”
Past studies have linked IBD with a 1.2- to 1.8-fold increase in the risk of zoster, but these studies date to the prebiologic era or excluded patients who were in their midsixties or older, the researchers wrote. “Additionally, these prior studies have not assessed the validity of the codes used to identify herpes zoster and also did not account for the impact of vaccination,” they added. “They also did not take into consideration the severity of the disease or degree of steroid exposure.”
Therefore, the researchers conducted two retrospective cohort studies of patients in the United States Department of Veterans Affairs between 2000 and 2016. The first cohort study compared the incidence of herpes zoster among patients with IBD who received 5-ASA alone with matched patients without IBD. The second cohort study measured the incidence of herpes zoster in patients with IBD who received various medications and combination regimen. “The VA has a predominantly older population, which makes it an ideal cohort to study herpes zoster incidence in a high-risk population,” the investigators noted. “Unlike insurance databases, the VA database can be validated internally and vaccination records are documented.”
After adjusting for age, race, sex, geographic region, disease flare, corticosteroid use, and baseline comorbidities, the estimated hazard of developing herpes zoster was 1.81 (95% confidence interval, 1.56-2.11) among patients with ulcerative colitis and 1.56 (95% CI, 1.28-1.91) among patients with Crohn’s disease, as compared with patients without IBD. Regardless of their age or the medications they were receiving, patients with IBD had a higher incidence of zoster than the oldest group of patients without IBD (older than 60 years), regardless of age or medication. “The highest risk of herpes zoster was observed in patients with IBD who were less than 60 years of age and on combination therapy,” the investigators wrote. “Patients with IBD younger than 50 years who were on combination therapy had higher risk of herpes zoster, compared with patients with IBD older than 60 years of age who were not on immunosuppressive therapy.” Based on the findings, they recommended studying the efficacy of widespread use of the new herpes zoster vaccine in patients with IBD.
Pfizer provided unrestricted research funding but was not otherwise involved in the study. One coinvestigator disclosed ties to Pfizer and several other pharmaceutical companies. The remaining investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Khan N et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jan 5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.12.052.