Among patients with the recently defined severe autoinflammatory syndrome VEXAS, those who are transfusion dependent or have a specific amino acid substitution are at highest risk for death, whereas those with ear chondritis are at significantly lower risk, a multinational team of investigators has found.
Their study of mortality and predictors of survival among patients with genetically confirmed VEXAS showed that patients with a VEXAS variant resulting in an amino acid substitution of a methionine for a valine had a 3.5-fold higher risk for death, compared with patients with either a methionine-to-threonine substitution or a methionine-to-leucine swap.
Transfusion dependence was an independent predictor of mortality. Patients who became dependent on transfusions after symptom onset had a nearly threefold higher risk for death, reported Marcela A. Ferrada, MD, a clinical fellow at the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases.
“These findings should inform risk assessment and clinical management in patients with VEXAS syndrome,” she said in an oral abstract presentation during the virtual annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology.
“These genetic findings have proven right now to be not only diagnostic, but we have shown that they’re also prognostic, and we hope that this is going to help us identify patients who could have more aggressive treatment,” Dr. Ferrada said.
She also discussed her findings in a media briefing held 2 days prior to her plenary presentation. At that briefing, this news organization asked participating clinicians whether they had patients who they suspected may have had undiagnosed VEXAS.
“My answer to that is interesting,” replied moderator Vaneet Sandhu, MD, from Loma Linda (Calif.) University and Riverside University Health System.
“In the last couple of days, I’ve been reading about VEXAS, and actually texted one of my colleagues yesterday and said, ‘Hey, you know these patients we’ve been seeing who have these strange rashes and chondritis and have maybe a diagnosis of leukocytoclastic vasculitis or something else – are we not diagnosing these patients?’ ” she said.
“I think we are looking at every patient with chondritis and reexamining their phenotype. We had dismissed certain symptoms because they didn’t fit the archetype for relapsing polychondritis, for example, but it could be VEXAS,” said Alfred Kim, MD, PhD, of Washington University in St. Louis, who also presented data during the briefing.
Three variants
VEXAS is caused by somatic mutations in UBA1, a gene that initiates cytoplasmic ubiquitylation, a process by which misfolded proteins are tagged for degradation.
The syndrome’s name is an acronym descriptive of the major features:
- Vacuoles in bone marrow cells.
- E-1 activating enzyme that UBA1 encodes for.
- X-linked.
- Autoinflammatory.
- Somatic mutation featuring hematologic mosaicism.
VEXAS results in rheumatologic, dermatologic, and hematologic symptoms that are often misdiagnosed as being caused by treatment-refractory relapsing polychondritis, polyarteritis nodosa, Sweet syndrome, giant cell arteritis, or myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
VEXAS was identified as a distinct syndrome within the past year by Dr. Ferrada and other investigators at NIAMS, the National Human Genome Research Institute, and other institutions.
In the study reported at ACR 2021, Dr. Ferrada and colleagues assessed 83 men who had been referred for genetic testing for VEXAS at the National Institutes of Health, in Bethesda, Md., and at Leeds (England) Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust.
All patients were confirmed to have VEXAS-defining genetic mutations in UBA1 by Sanger sequencing of peripheral blood samples. Only those patients with mutations at codon p.Met41 were included in the investigators’ analysis. Mutations at that site account for nearly all cases of VEXAS that have been identified to date.
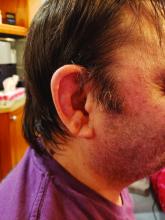
The most common clinical manifestation of VEXAS was skin involvement, which occurred in all but one of the 83 patients. Other common manifestations included arthritis (58 patients), pulmonary infiltrates (57 patients), and ear chondritis (54 patients).
Fifteen patients were found to have the leucine variant, 18 had the valine variant, and 50 had the threonine variant. The median age at disease onset was 66 years in the leucine and threonine variant groups and 65 in the valine variant group.
The clinical diagnosis differed according to genotype: 4 of 18 patients (22%) with the valine variant were diagnosed with relapsing polychondritis, compared with 8 of 15 (53%) with the leucine variant and 31 of 50 (62%) with the threonine variant (P = .01).
In contrast, 55% of patients with valine genotype were diagnosed with undifferentiated fever, compared with 6% of those with the leucine and 16% with the threonine genotypes (P = .001). More patients with the leucine variant (60%) were diagnosed with Sweet syndrome, compared with 11% and 14% of patients with the valine and threonine variants, respectively (P = .001).
There was no significant difference among the three genotypes in the percentage of patients diagnosed with MDS.
The follow-up period ranged from 1 to 18 years (median, 4.7 years). The median survival time from disease onset for all patients was 10 years.
Among patients with the valine variant, median survival was 9 years, which was significantly less than among patients with the other two variants (P = .01).
In univariable analysis, independent predictors of mortality were ear chondritis (hazard ratio, 0.26; P = .005), transfusion dependence, a time-dependent variable (HR, 2.59; P = .03), and the valine variant (HR, 3.5; P = .008).
The association between VEXAS genotype and phenotype could be explained by the finding that, among patients with the valine variant, there was significantly less translation of the catalytically proficient UBA1b isoform than in patients with the other two variants, Dr. Ferrada said.
Therapeutic options
Dr. Ferrada noted that to date no drugs have been shown to provide consistent therapeutic benefits for patients with VEXAS, but evidence as to the etiology of the syndrome points to possible treatment approaches.
“All of these findings I think are extremely important to help us guide management of these patients, as we know that the mutation is located in the stem cells in the bone marrow. So we suspect that doing a bone marrow transplant in these patients is going to be curative,” Dr. Ferrada said during the briefing.
Investigators are planning a phase 2 trial of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant for patients with VEXAS.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Ferrada, Dr. Sandhu, and Dr. Kim have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.