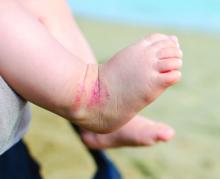
, while older adults tend to present with less flexural eczema and the fewest associated signs.
Those are key findings from a study conducted at a single academic medical center, which aimed to identify the age-related clinical phenotypes of AD.
“Previous studies have found differences in the clinical characteristics of AD depending on age of AD onset, ethnic background, and AD severity,” senior author Jonathan I. Silverberg, MD, PhD, MPH, director of clinical research in the department of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, and his coauthor wrote in the study, which was published online in JAAD International. “However, none have prospectively compared the clinical characteristics and associated signs by age group. Improved understanding of the clinical phenotypes of AD may help guide choice of treatment and improve health outcomes,” they added.
Along with coauthor Sheena Chatrath, a dermatology research fellow in the department, Dr. Silverberg prospectively reviewed self-reported questionnaires that were completed by 380 patients prior to their visit at GWU’s eczema clinic between 2013 and 2019. Questions included age of AD onset, sociodemographics, Visual Analog Scale (VAS) itch and sleep for Scoring AD, and Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) for skin pain and itch. The researchers used the Eczema Area Severity Index to assess AD severity and a dermatologist conducted full body skin exams, noting the distribution of AD involvement as well as associated signs.
Of the 380 patients, 6.1% were younger than aged 18 years, 46.3% were young adults aged 18-39 years, and 47.6% were older adults 40 years of age and older.
Compared with pediatric patients, both young and older adults were less likely to experience AD on the ankles (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.41 and 0.43, respectively), moderate to severe AD lesions on flexures (aOR, 0.47 and 0.30), pityriasis alba (aOR, 0.24 and 0.07), oozing lesions (aOR, 0.44 and 0.35), and moderate to severe excoriations (aOR, 0.49 and 0.44).
In children, severe itch was more common, reported in 47.1%, compared with 43.4% of the young adults and 38.6% of the older adults, and itch was less severe among the young and older adults. “Interestingly, despite increased itch in pediatric patients, we found no difference in the severity of skin pain across all age groups,” the researchers wrote. “Moreover, pediatric patients reported skin pain less often than adult patients. This may be due to age-related differences of pain perception.”
In other findings, compared with pediatric patients, young adults were more likely to experience AD around the eyes (aOR, 2.92), while older adults were less likely to experience AD on elbows (aOR, 0.34), nipples (aOR, 0.40), knees (aOR, 0.27), and less likely to have keratosis pilaris (aOR, 0.38), and lichenification (aOR, 0.47).
Dr. Silverberg and Ms. Chatrath used latent class analysis to identify four classes for distribution of AD lesions. In this model, class 1 had low probabilities of AD involvement at all sites examined and class 2 had low probabilities of scalp, face, and foot involvement, and intermediate probability of all other AD sites. Class 3 had low probabilities of hand and foot involvement, high probability of facial erythema, and intermediate probability of all other AD signs, while class 4 had intermediate probability of postauricular and foot involvement, and high probability of all other AD sites examined.
“Pediatric patients were most commonly in class 4 (33.3%), followed by class 1 and 2 (26.7%), and least commonly in class 3 (13.3%),” the authors wrote. “In young adults, class 4 and 1 were most common (32.4% and 29.4%), followed by class 2 (27.9%), and least commonly class 3 (10.3%). In older adults, class 1 was most common (40.3%), followed by class 4 (23.6%), and least commonly classes 2 and 3 (18.1%).”
The researchers also used latent class analysis to identify four classes for the signs and symptoms of AD. In this model, class 1 had zero-low probability of all AD signs and class 2 had low probability of all AD signs. Class 3 had high probability of oozing lesions and low probability of all other signs, while class 4 had high probability of xerosis, intermediate probability of ichthyosis and palmar hyperlinearity, and low probability of all other AD signs.
In all three groups, the most common class was class 1 (85.6% of older adults, 81.8% of younger adults, and 82.6% of pediatric patients). Among the pediatric patients, they wrote, “class 3 was the second most common (8.7%), followed by class 2 and 4 (4.4%).” Among the young adults, 9.7% were in class 2, 5.7% were in class 4, and 2.8% were in class 3; and among the older adults, 8.3% were in class 4, 4.4% were in class 2, and 1.67% were in class 3.
Zelma Chiesa Fuxench, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who was asked to comment on the study, said that while AD is traditionally largely thought of as a disease of children primarily involving the flexural areas, “this study provides additional evidence to support that AD is more than just a disease of childhood with a fixed clinical presentation, but is a heterogeneous disease whose clinical presentation varies across different population groups.”
While the study provides insight into the clinical differences that may be observed across AD groups, “care must be taken when interpreting these results as the study was done in a single center with observations collected during one single visit,” she added. “AD is not a ‘static’ disease; its presentation can stay the same in one patient but can vary even in another patient throughout their lifetime. Therefore, studies of a more prospective nature that evaluate the change in clinical presentation using multiple measures throughout time in these individuals would be a step forward to better understand if these phenotypic differences truly exist and, as such, what implications could they have for treatment selection.”
This study was supported by grants from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and the Dermatology Foundation. The researchers reported having no disclosures. Dr. Chiesa Fuxench disclosed serving as a consultant for the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America, National Eczema Association, Pfizer, AbbVie, and Incyte, for which she has received honoraria for AD-related work. She is the recipient of research grants through Regeneron, Sanofi, Tioga, Vanda, Menlo Therapeutics, Leo Pharma, and Eli Lilly for work related to AD as well as honoraria for continuing medical education work related to AD sponsored through educational grants from Regeneron/Sanofi and Pfizer.