As dermatologists, public health officials, and infectious disease specialists scramble to raise awareness about prevention and treatment, challenges ranging from a dearth of testing facilities and data to payer pushback over longer therapeutic courses remain.
Dermatophyte Discourse Changing
“Trichophyton indotineae is changing the way we talk about dermatophyte infections,” Avrom S. Caplan, MD, assistant professor in the Department of Dermatology at New York University, New York City, said in an interview. Called T mentagrophytes VIII (TMVIII) before a 2020 report in the journal Mycopathologia proposed the name T indotineae, this species requires clinicians to expand their conception of how tinea looks, acts, and responds to treatment.
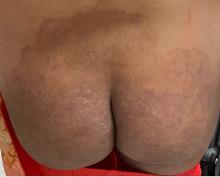
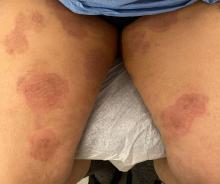
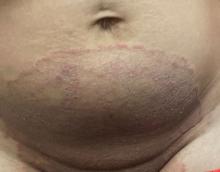
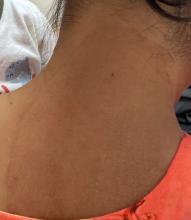
Boni E. Elewski, MD, professor and chair of dermatology, at The University of Alabama at Birmingham, saw her first case of probable T indotineae in a patient in early 2020. “He was covered with fine scale, and he itched all over. I thought he had atopic dermatitis. This didn’t look like any tinea. His face, arms, back, and legs were scaly.”
Nevertheless, KOH and biopsy confirmed dermatophytosis. Culture (performed at the Center for Medical Mycology [CMM] in Cleveland) identified T mentagrophytes. Back then, Elewski told this news organization, labs did not routinely go beyond genus and species. But based on the patient’s symptoms, history of unresponsiveness to terbinafine, borderline sensitivity to fluconazole, and travel to India and Spain, Elewski strongly suspected T indotineae.
The patient refused itraconazole, to which the fungus was sensitive, and did not respond to fluconazole 400 mg daily. Ultimately, he was lost to follow-up. “Last I saw him,” said Elewski, “he was not cured.”
Tracking Cases
Because T indotineae does not require reporting to public health agencies, said Jeremy Gold, MD, MS, a medical officer with the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Mycotic Diseases Branch in Atlanta, “there is no official public health surveillance keeping track of exactly how many cases have occurred.”
The same is true for TMVII and terbinafine-resistant T rubrum, which are also on the rise. Regarding T indotineae, authors from the University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio retrospectively reported 21 terbinafine-resistant isolates from North America in the July 2023 Journal of Clinical Microbiology .
Caplan has seen approximately 12 T indotineae cases to date, including the first two confirmed US cases, which he and co-authors, including Gold, reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report in May 2023. T indotineae is likely underreported, he said, because it eludes standard culture-based techniques, and identifying it requires molecular testing, which is available at only a handful of labs nationally.
To help educate providers, in July, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the International League of Dermatological Societies unveiled an Emerging Diseases Resource Center, which includes resources for providers and a registry for reporting confirmed and suspected resistant dermatophytes.
“Our goal is to provide easy-to-access and easy-to-understand resources to healthcare providers,” Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, told this news organization. She is director of Global Health Dermatology at Massachusetts General Hospital, associate professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, and chair of the AAD’s Emerging Diseases Task Force.
“Our resources include an algorithm for when to suspect a drug-resistant case and how to think through treatment options. We cover issues related to diagnosis and treatment, as well as linking to our case registry reporting system,” said Freeman.
The new registry resides within the AAD’s existing COVID-19, Mpox, and Emerging Infections Registry. “Our registry efforts have already captured 2500 COVID-19 and mpox cases from 72 different countries,” Freeman said. For all these infections, she added, “we hope that real-time data analysis of cases worldwide will provide information that helps physicians recognize and treat cases.”
Consistent with the registry’s approach, said Caplan and Gold, there is no silver bullet for battling dermatophyte resistance. What is needed, said Gold, is a coordinated approach involving public health officials, dermatologists, primary care providers, infectious disease specialists, pharmacists, and patients. “It’s going to be a team effort to address the challenge of emerging complex dermatophytosis,” he said.