Sticks and stones may break my bones, but clots will never hurt me
You’ve probably seen “Ghostbusters” or at least heard the theme song. Maybe you even know about the Discovery Channel’s “Mythbusters.” But now there’s a new buster in town, and it eats platitudes for breakfast: Meet Cliche-busters, LOTME’s new recurring feature.
This week, Cliche-busters takes on “Two wrongs don’t make a right.” Yum.
We start with blood clots, which are bad. Doctors go to a lot of trouble to get rid of the things because they are dangerous. A blood clot, then, is a bodily function gone wrong.
Tornadoes are also bad. Out there in the world, these violently rotating columns of air can destroy buildings, toss large objects long distances, and inspire mediocre action movies. They are examples of nature gone wrong.
Seemingly, these two wrongs – blood clots and tornadoes – are not about to make a right. Has Cliche-busters bitten off more than it can chew?
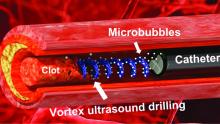
Not according to Xiaoning Jiang of North Carolina State University, Raleigh, and his team of researchers. They’ve figured out a way to use a tiny ultrasonic tornado to break down clots in the brain. “Our new work uses vortex ultrasound, where the ultrasound waves have a helical wavefront. In other words, the ultrasound is swirling as it moves forward,” he said in a statement from the university.
Their new tool’s single transducer is small enough to fit in a catheter, and its “vortex ultrasound-induced shear force has the potential to break down clots safely and improve the efficacy of thrombolysis,” they explained in the open-access journal Research.
The investigators used cow blood in a 3D-printed model of the cerebral venous sinus for the proof-of-concept study and were able to dissolve an acute blood clot in less than 30 minutes, compared with the 15-30 hours needed with a pharmaceutical intervention, according to the written statement.
Can you hear the sound of two wrongs making a right? We can, and that closes the curtain on this cliche.
With age does not come wisdom
We’ve all met this person before. The sort of person who takes a 10-minute IQ test on a shifty-looking website and then proceeds to brag about a 180 IQ until the heat death of the universe. The one who worships at the altar of Mensa. Yeah, that guy. They’re never as smart as they think they are, but they’ll never, ever admit it.
It’s not exactly a secret that IQ as a measurement of intelligence is highly overrated. A lot of scientists doubt we should bother measuring it at all. That said, a higher IQ is associated with greater success in academic and financial endeavors, so it’s not absolutely worthless. And if we’re stuck with it, we may as well study it.
That brings us neatly to new research published in Brain and Behavior. Most studies into IQ and self-estimated intelligence have focused on younger adults, and the author of this study was curious if the stereotype of young men inflating their IQ, a stereotype backed up by research, persisted into older adulthood. So she conducted a survey of 159 younger adults and 152 older adults to find out.
The results in younger adults were not surprising: Younger men overestimated their actual IQ by 5-15 points, which tracks with previous research. We’re in for a bit of a surprise with the older adults, though, because the older men were more humble about their intelligence, with their estimation falling in line with their actual IQ. Older women, however, not so much. In fact, they overestimated their intelligence just as much as the younger men.
In addition, older women who perceived themselves as more attractive reported the highest self-estimated intelligence of all. That isn’t how intelligence works, but honestly, if Grandma’s out and about thinking she looks good and has the brains to go and win “Jeopardy!” do you really have the heart to tell her otherwise?