For people with diabetes, disease management can become a part-time job that affects their actual jobs, their sleep, their relationships, and their recreational activities, according to a new survey by prescription manager UpWell Health.
The time spent on activities that come with diabetes management – blood glucose monitoring, diet planning, medical appointments – can add up to several hours a week. Among the 5,255 respondents to the online survey, 18% said that such tasks took up 5-10 hours each week, 7% said it was 10-15 hours, and 9% said they spent 15 or more hours a week on diabetes-related tasks, UpWell reported.
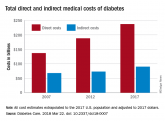
The survey, conducted in March 2017, examined other negative effects of diabetes on patients’ lives: 37% said that it had harmed relationships with loved ones, friends, or coworkers; 38% gave up hobbies, activities, or other interests; 55% had missed work in the past year because of their diabetes; and 62% had their sleep interrupted every week by diabetes complications, with 8% reporting 10 or more interruptions a week, UpWell said.Since medical expenses aren’t always fully covered by insurance, 43% of respondents paid up to $1,000 a year out of pocket to treat diabetes complications, 16% paid $1,000 to $2,000 a year, and 4% paid more than $5,000. Five percent also paid over $5,000 a year out of pocket for diabetes care from a physician and 45% said that they had sometimes gone without diabetes care because they couldn’t afford it, the survey data showed.
“Most people with diabetes are able to manage it successfully and live active, satisfying lives. But doing so requires constant planning, vigilance, and care. They eagerly seek trustworthy resources to help them reduce the burden of living with diabetes,” UpWell said.
rfranki@mdedge.com