EVIDENCE SUMMARY
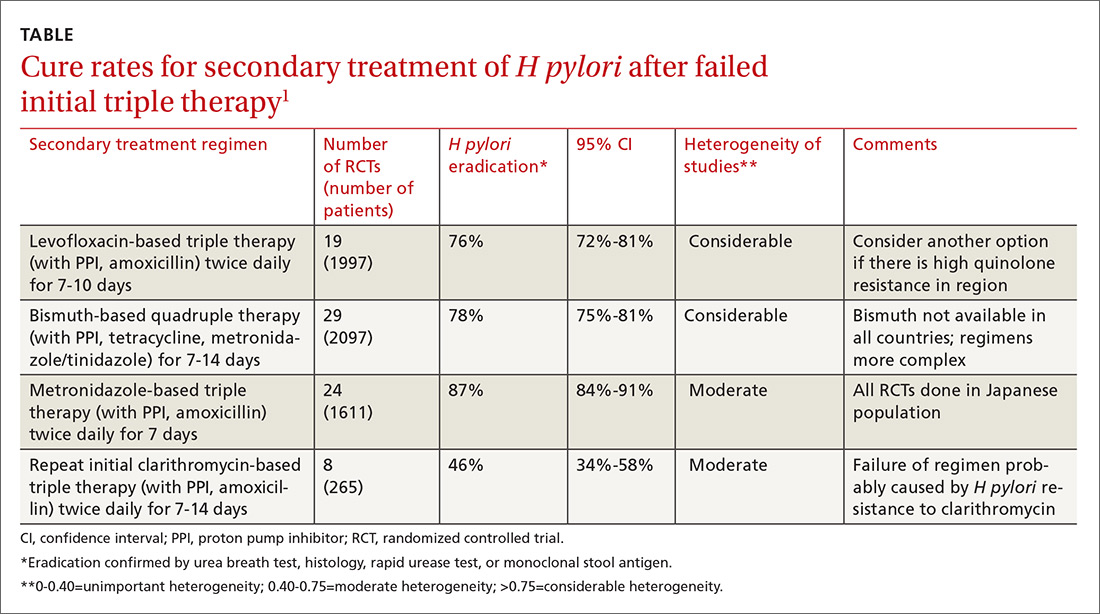
A meta-analysis of RCTs evaluating levofloxacin-based triple therapy as a secondary treatment regimen for patients with H pylori infection who had failed initial clarithromycin-based triple therapy found cure rates averaging 76% (TABLE).1 Most of the regimens comprised levofloxacin (500 mg), amoxicillin (1 g), and a PPI (40 mg), all twice daily for 7 to 10 days. Ten-day regimens produced better cure rates than 7-day regimens (84% vs 69%; comparison statistic not supplied).
The meta-analysis also included RCTs evaluating bismuth-based quadruple therapy as secondary treatment, which found cure rates averaging 78%.1 The regimens varied, comprising bismuth salts (120-600 mg, 2-4 times daily), metronidazole (250-500 mg, 2-4 times daily), tetracycline (250-500 mg, 2-4 times daily), and a PPI (40 mg twice daily). Longer duration of therapy produced higher cure rates (7 days=76%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.72-0.80 in 29 RCTs with 2097 patients; 10 days=77%; 95% CI, 0.60-0.93 in 2 RCTs with 142 patients; 14 days=82%; 95% CI, 0.76-0.88 in 12 RCTs with 831 patients).
Repeating the original clarithromycin-based triple therapy (8 RCTs, 265 patients) produced low cure rates (46%).1
Metronidazole-based therapy has high cure rate in a homogeneous population
A meta-analysis of 24 RCTs (1611 patients) that evaluated metronidazole-based triple therapy (mostly composed of amoxicillin 750 mg, metronidazole 250 mg, and any of a number of PPIs, all dosed at 40 mg) twice daily for 7 days found cure rates averaging 87% in an exclusively Japanese study population.1
Comparable cure rates for levofloxacin- and bismuth-based therapy
Six RCTs with a total of 1057 patients compared cure rates for levofloxacin-based triple therapy with bismuth-based quadruple therapy and found no difference.1
Two earlier meta-analyses not included in the previously described study, comprising 8 RCTs with a total of 613 patients, produced conflicting results. The larger study (15 RCTs, 1462 patients) found no difference in cure rates.2 The smaller study (7 RCTs, 787 patients) favored quadruple therapy.3
Continue to: Two secondary antibiotic regimens show similar cure rates