The cosmetic industry improves techniques for tightening faces, hands, necks, and decolletes; meanwhile, sagging elbows and knees, once ignored, also are a visible sign of aging. Modifying techniques commonly used for the face and neck can yield significant improvements in the elbows and knees. The elbows and knees naturally have looser skin to allow for joint movement; over time, the skin over these joints is exposed to sun damage, friction, and recurrent extension and flexion, which cause skin laxity and aging.
A combination approach addressing skin texture, collagen damage, rhytides, and fat deposition is the most effective method for knee and elbow rejuvenation.
For knees and elbows with loose skin and rhytides, in-office noninvasive and minimally invasive radio-frequency and light energy treatments are helpful in increasing collagen production and tissue tightening. Similarly, microfocused ultrasound has been shown to be a safe and effective skin tightening treatment for the knees. In comparison to the face, however, the skin around the elbows and knees can be thinner and has fewer sebaceous glands. Caution should be used particularly with minimally invasive radio-frequency techniques in order to protect the epidermal skin. Often, treatments have to be repeated to give optimal results, which are not apparent until 3-6 months after the initial procedure.
For knee skin with severe laxity, a comprehensive approach using polydioxanone (PDO) or poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA) threads in both the upper thighs and circumferentially around the knees provides collagen production and tightening of the loose skin. Treatment of the upper thighs is essential in providing a vector that lifts the skin of the knees. Treatments can be repeated, with results seen after 90 days. Thread lifts of the knees and thighs are highly effective, noninvasive procedures with little to no downtime and can be used for severe skin laxity, wrinkling, and thinning of the knee skin.
Loose, roughened knee and elbow skin can also be treated with nonablative factional resurfacing, radio-frequency microneedling, or a series of monthly treatments with PLLA and hyaluronic acid fillers injected in the superficial to mid-dermis. Both fractional resurfacing and dermal filler injections help stimulate collagen production and improve both fine rhytides and dermatoheliosis.
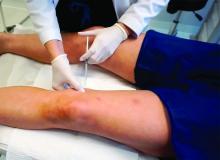
Adipose tissue around the knees can be treated with monthly deoxycholic acid injections (for a video of this procedure, go to https://drive.google.com/file/d/1rhw-nESy15AoDhKUrc25DDjKEun7RL4i/view). The volume of injection, however, is significantly higher than that recommended in the submental area. Two to four times the volume is needed per knee over a series of 3-6 treatments, depending on the amount of fat in the knees.
Cryolipolysis is also an effective option for fat pockets around the knees; however, in my experience, it can be difficult to fit the applicators onto the area of concern appropriately unless smaller applicators are applied.
With the increasing demand for body rejuvenation techniques, providers are adapting techniques used for the face and neck to lift, tighten, thin, and sculpt the knees and elbows. A combination approach using lasers, ultrasound, fillers, threads, and cryolipolysis can be effective for these areas. Results are obtainable when repeat treatments are performed; however, one must be patient because results are not seen for 6 months or more.
Dr. Lily Talakoub and Dr. Naissan Wesley are cocontributors to this column. Dr. Talakoub is in private practice in McLean, Va. Dr. Wesley practices dermatology in Beverly Hills, Calif. This month’s column is by Dr. Talakoub. Write to them at dermnews@mdedge.com. They had no relevant disclosures.
References
Macedo O. et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70(Suppl 1), Abstract P800, page AB193.