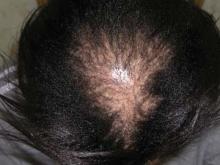
Despite being the most common pattern of scarring hair loss among African American women, central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia is still poorly understood, according to a report published online April 11 in Archives of Dermatology.
The etiology of and risk factors for the disorder have not been established. And although African American women commonly present with the condition, the exact prevalence remains unknown, said Dr. Angela Kyei and her associates at the Cleveland Clinic Institute of Dermatology and Plastic Surgery.
Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia (CCCA) – previously known as hot comb alopecia or follicular degeneration syndrome – is a scarring hair loss centered on the vertex of the scalp and spreading peripherally, which is described almost exclusively in African American women. In the late 1960s it was linked to the use of hot combs, but since then almost every method of hair grooming in this population has been associated, albeit weakly, with the disorder. Few studies have examined other possible etiologies, such as immunologic, dermatologic, or genetic factors.
"Given the lack of epidemiologic data, the main goal of [our] study was to elucidate environmental as well as medical risk factors that may be associated with CCCA," the researchers wrote.
They administered questionnaires to 326 African American women attending two churches and a health fair in the Cleveland area. Sixteen of the women ended up being excluded from the analysis.
The questionnaires asked detailed information about family history of male- and female-pattern hair loss; personal medical history, including bacterial and fungal skin infections, autoimmune conditions, and hormonal dysregulation; and hair grooming methods used. The study subjects also underwent a scalp examination that included the grading of hair loss.
A total of 86 of the 310 women (28%) were judged to have central hair loss. Of these, 52 women – 17% of the total study population – had CCCA.
It appeared that hair grooming practices that cause traction, such as weaves and braids, may contribute to the development of CCCA, as women with the most severe central hair loss used these styles more frequently than did those without hair loss. "This has some clinical bearing because traction can clinically produce folliculitis of the scalp, which can cause scarring if this inflammation is prolonged," noted Dr. Kyei and her colleagues (Arch. Dermatol. 2011 April 11 [doi:10.1001/archdermatol.2011.66]).
After paying hundreds of dollars for such hair styling, women often maintain weaves and braids for weeks to months, so any reactive inflammation usually is prolonged, the investigators added.
However, "the relationship between chemical relaxer use and the development of CCCA continues to be murky," they noted. These products clearly weaken the hair shaft, which can cause breakage, but that does not necessarily lead to CCCA. "The fact that most African Americans use chemical relaxers in combination with braiding and other hair grooming practices makes it even more difficult to tease out a relationship," Dr. Kyei and her associates added.
It is difficult to find subjects who do not use chemical relaxers for comparison, since most African Americans begin the practice in childhood. In this study, 91% of the women reported using chemical relaxers, and began doing so at an average age of 10 years.
Nevertheless, "we feel that it is not unreasonable to assume that the scalp may absorb some of the caustic chemicals found in relaxers, which in time leads to damage of the scalp in the form of scarring," they wrote.
Although the prevalence of bacterial skin infections in these study subjects was only 11%, there was a significant elevation among women with CCCA, compared with women who did not have CCCA. The rate of acne also was elevated in affected subjects, but not to a significant degree. Thus, the researchers said that their study "demonstrates that inflammation in the form of bacterial infection and acne may also be contributing to the development of CCCA, a finding consistent with the histopathologic characteristics of this disease," which show a lymphocytic perifollicular infiltrate in its early stages.
In contrast, there was no such association with fungal infections of the scalp, ringworm, or vaginal yeast infections, which was "surprising given how prone this population is to fungal infection," they added.
"One of the most surprising findings ... was the overrepresentation of type 2 [diabetes mellitus] in those with CCCA," the authors noted. Again, the prevalence of type 2 diabetes was low, at 8%, but it was significantly elevated in women with CCCA, compared with those without CCCA.