From the Editor

Start offering aspirin to pregnant women at high risk for preeclampsia
Aspirin 81 mg daily, initiated at 12 weeks of pregnancy, modestly reduces preeclampsia risk for women with multifetal gestation, chronic...

Fetal hydrops was the end result of a serious problem in utero that could not have developed during the hours of labor and delivery; it most likely arose days to weeks before delivery. Nothing that occurred during labor and delivery caused hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy.
Verdict: An Illinois defense verdict was returned.
Child has permanent shoulder injury: $1M verdict
A mother was admitted to a hospital in full-term labor. During delivery, anterior shoulder dystocia was encountered.
The child received a diagnosis of a left brachial plexus injury and extracranial and intracranial bleeding. She underwent 3 surgeries to reattach nerve roots and move muscles and tendons in her shoulder and forearm in an effort to improve function in her left arm, wrist, and hand. She has undergone extensive physical and occupational therapy. Her left arm is smaller than her right arm and she has minimal strength, dexterity, and only 20% functionality of her left arm.
Parent's claim: The ObGyn exerted excessive traction when delivering the child. Alternate methods should have been used to manage shoulder dystocia. The hospital nurses should not have used fundal pressure.
Defendants' defense: The suit was brought against the ObGyn, his practice, and the hospital. The ObGyn claimed that he used several maneuvers to manage shoulder dystocia. The child’s injuries were a result of the maternal forces of labor and were not caused by negligence on the part of the ObGyn or nurses. The nurses denied using fundal pressure; they were trained to use suprapubic pressure.
Verdict: A $1,012,00 Illinois verdict was returned, finding the ObGyn’s practice 100% liable.
Parvovirus exposure: Fetal death
When a woman first saw an ObGyn, ultrasonography (US) indicated that her fetus was at 8 to 9 weeks’ gestation. One month later, she told the same ObGyn that she had been exposed to Fifth disease. Because blood work was positive for parvovirus B19, the ObGyn ordered the patient to undergo US every 2 weeks for the next 10 weeks. Two weeks later, the patient saw a second ObGyn at the same clinic. Although the first ObGyn had ordered US, none was performed; the patient’s next appointment was scheduled in 4 weeks. At that time, the patient saw a third ObGyn, who ordered US. He noted in her chart that the fetus had a nuchal fold, indicating Down syndrome. He told the patient to return in 2 weeks for a follow-up US. The results of that US showed that the fetus had died. Fetal cord blood tested positive for parvovirus B19.
Parent's claim: All 3 ObGyns failed to react properly to indications of parvovirus infection. Regular US should have been performed, as suggested by the first ObGyn. The mother should have been referred to a perinatologist or other maternal-fetal specialist when blood work was positive for parvovirus B19. A specialist could have provided treatment for the virus.
Physician's defense: The ObGyns denied any breach in the standard of care. They claimed that results would have been the same if they had referred the patient to a specialist.
Verdict: An Alabama defense verdict was returned.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.

Aspirin 81 mg daily, initiated at 12 weeks of pregnancy, modestly reduces preeclampsia risk for women with multifetal gestation, chronic...
By arming yourself with knowledge of the most common complications—and their causes—and employing well-chosen surgical strategies, you can lower...
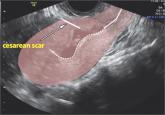
Treatment of cesarean scar ectopic pregnancy

An overview of surgical techniques illustrated by a case of laparoscopic cornual resection

My preferred posterior axilla maneuver is the Menticoglou maneuver. Here, a look at your options and steps to delivery.
