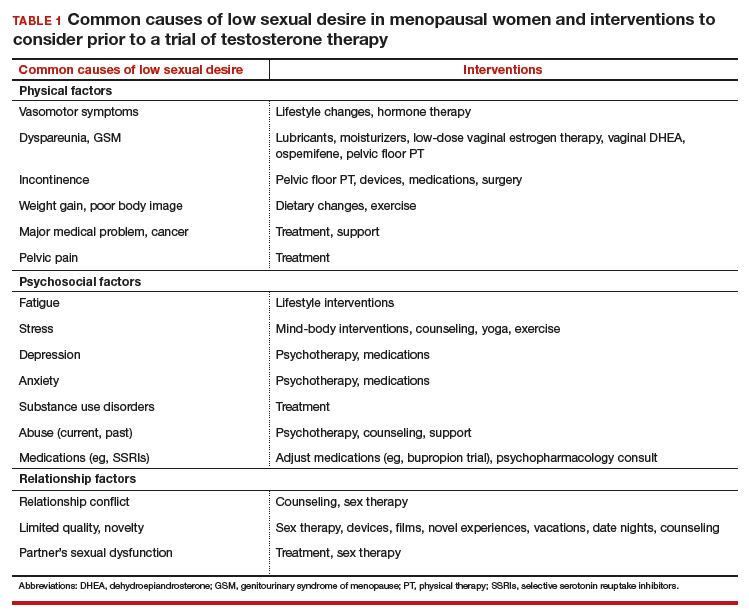
There are many effective therapies for low sexual desire to consider prior to initiating a trial of testosterone, which should be considered for HSDD only if the disorder persists after addressing all other possible contributing factors (TABLE 1).
Sex therapy, for example, provides information on sexual functioning and helps improve communication and mutual pleasure and satisfaction. Strongly encourage—if not require—a consultation with a sex therapist before prescribing testosterone for low libido. Any testosterone-derived improvement in sexual functioning will be enhanced by improved communication and additional strategies to achieve mutual pleasure.
Hormone therapy. Vasomotor symptoms, with their associated sleep disruption, fatigue, and reduced quality of life (QOL), often adversely impact sexual desire. Estrogen therapy does not appear to improve libido in otherwise asymptomatic women; however, in women with bothersome vasomotor symptoms treated with estrogen, sexual interest may increase as a result of improved sleep, fatigue, and overall QOL. The benefits of systemic hormone therapy generally outweigh its risks for most healthy women younger than age 60 who have bothersome hot flashes and night sweats.1
Nonhormonal and other therapies. GSM with dyspareunia is a principal cause of sexual dysfunction in older women.2 Many safe and effective treatments are available, including low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy, nonhormonal moisturizers and lubricants, ospemifene, vaginal dehydroepiandrosterone, and pelvic floor physical therapy.3 Urinary incontinence commonly occurs in midlife women and contributes to low libido.4
Lifestyle approaches. Address fatigue and stress by having the patient adjust her work and sleep schedules, obtain help with housework and meals, and engage in mind-body interventions, counseling, or yoga. Sexual function may benefit from yoga practice, likely as a result of the patient experiencing reduced stress and enhanced body image. Improving overall health and body image with regular exercise, optimal diet, and weight management may contribute to a more satisfying sex life after the onset of menopause.
Relationship refresh. Women’s sexual interest often declines with relationship duration, and both men and women who are in new relationships generally have increased libido, affirming the importance of novelty over the long term. Couples will benefit from “date nights,” weekends away from home, and trying novel positions, locations, and times for sex. Couple’s counseling may address relationship conflict.
Expert referral. Depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders are prevalent in menopausal women and contribute to sexual dysfunction. Effective therapy is available, although some pharmacologic treatments (including SSRIs) may be an additional cause of sexual dysfunction. In addition to recommending appropriate counseling and support, referring the patient to a psychopharmacologist with expertise in managing sexual adverse effects of medications may optimize care.
Continue to: Sexual function improves, but patient still wants to try testosterone