Anterior compartment repairs
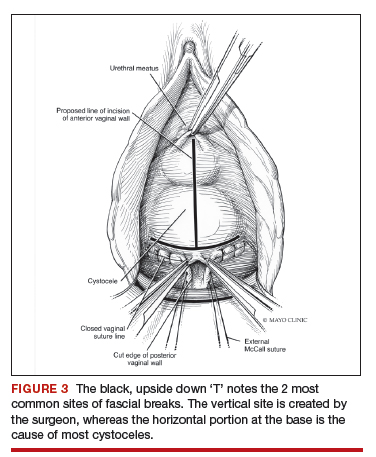
The anterior compartment seems the most susceptible to forces within the pelvis and is a common site of prolapse. Many theories exist as to what causes a cystocele—distension, displacement, detachment, etc. While paravaginal defects exist, I believe that most cystoceles arise horizontally at the base of the bladder as the anterior endopelvic fascia detaches from the apex or cervix. The tissue then attenuates as the hernia progresses.
For surgical success: Make certain your repair addresses re-establishing continuity of the anterior endopelvic fascia with the fascia and ligaments at the vaginal apex; it will increase your success in treating anterior compartment prolapse.
We prefer to mobilize the epithelium in the midline from the vaginal apex to the mid‑urethra (if performing a midurethral sling, we stop short of the bladder neck and perform a separate suburethral incision). When incising the epithelium in the midline, the underlying fascia is also split in the midline, creating a midline defect. Once the epithelium is split and mobilized laterally off the underlying fascia, we can begin reconstruction.
The midline fascial defect that was just created is closed with a running 2-0 polyglactin from just beneath the bladder neck down to and including the fascia and uterosacral ligaments at the apex. This is accomplished in an upside down ‘T’ orientation (FIGURE 3). It is critical that the fascia is reunited at the base or you will leave the patient with a hernia.
For surgical success: To check intraoperatively that the fascia is reunited at the base, try to place an index finger between the base of the cystocele repair and the apex. If you can insert your finger, that is where the hernia still exists. If you meet resistance with your finger, you are palpating reunification of the anterior and apical fascia.
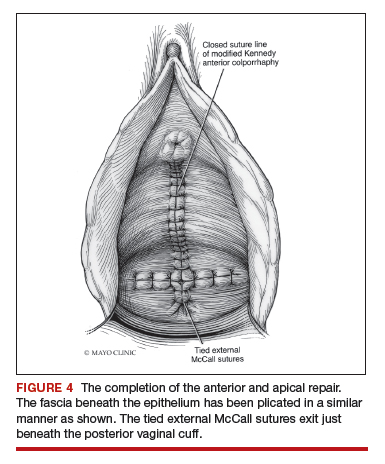
Technique for Kelly-Kennedy bladder neck plication. If the patient has mild incontinence that does not require a sling procedure, we now complete the second portion of the anterior repair starting with a Kelly-Kennedy bladder neck plication. Utilizing interrupted 1-0 polyglactin suture, vertical bites are taken periurethrally, starting at the midurethra and then the bladder neck. This nicely supports the urethra and proximal bladder neck and is very helpful for mild incontinence or for prophylactic benefit. Then starting beneath the bladder neck, the fascia is plicated again in the midline, reinforcing the suture line of the inverse ‘T’ with 2-0 polyglactin. The redundant epithelium is trimmed and reapproximated with interrupted 2-0 polyglactin (FIGURE 4). We tend to be more aggressive by adding the Kelly-Kennedy plication, which can lead to temporary voiding delay. We offer placement of a suprapubic catheter at the time of surgery or self-intermittent catherization.
Lastly, given that we have just dissected and then plicated the tissues beneath the bladder, I like to perform cystoscopy to be certain the bladder has not been violated. It is also important not to over-plicate the anterior fascia so that the sutures shear through the fascia and weaken the support or narrow the vaginal lumen.
Continue to: Posterior compartment repairs...