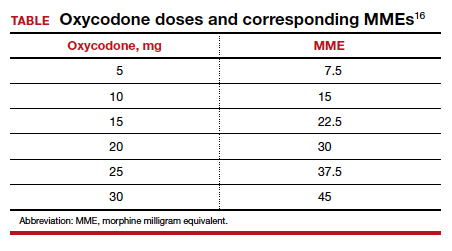
Among 4,689 and 4,624 patients who underwent CD before and after the intervention, the daily morphine milligram equivalents (MME) consumed in the hospital decreased from 10.7 to 5.4. The percentage of women who required no opioids while in the hospital increased from 8.3% to 21.4% after ERAS implementation, while the percentage of time that patients reported acceptable pain scores increased from 82.1% to 86.4%. The average number of opioid tablets prescribed at discharge also decreased, from 37 to 26 MME.12 (The TABLE shows oxycodone doses converted to MMEs.)
A similar initiative at a network of 5 hospitals in Texas showed that implementation of a “multimodal pain power plan” (which incorporated postpartum activity goals with standardized order sets) decreased opioid use after both vaginal delivery and CD.14
Strategy 2: Order set change to eliminate routine use of opioids
A tertiary care center in Boston, Massachusetts, implemented a quality improvement project aimed at eliminating the routine use of opioid medication after CD through an order set change.11 The intervention consisted of the following:
- intrathecal morphine
- multimodal postoperative pain management including scheduled oral acetaminophen for 72 hours followed by as-needed oral acetaminophen, scheduled NSAIDs for 72 hours followed by as-needed NSAIDs
- no postoperative order for opioids unless the patient had a contraindication to acetaminophen or NSAIDs, had a history of opioid dependence, or underwent complex surgery
- counseling patients that opioids were available for breakthrough pain if needed. In this case, nursing staff would page the responding clinician, who would order oxycodone 5 mg every 6 hours for 6 doses.
- specific criteria for discharge quantities of opioids: if the patient required no opioids in the hospital, she received no opioids at discharge; if the patient required opioids in the hospital but none at the time of discharge, she received no more than 10 tablets of oxycodone 5 mg; if the patient required opioids at the time of discharge, she received a maximum of 20 tablets of oxycodone 5 mg.
Among 191 and 181 women undergoing CD before and after the intervention, the percentage of patients who received any opioids in the hospital decreased from 68.1% to 45.3%.11 Similarly, the percentage of patients receiving a discharge prescription for opioids decreased from 90.6% to 40.3%, while patient pain scores and satisfaction with pain control remained unchanged.
Strategy 3: Shared decision-making tool
Another tertiary care center in Boston evaluated the effects of a shared decision-making tool on opioid discharge prescribing after CD.15 The intervention consisted of a 10-minute clinician-facilitated session incorporating:
- education around anticipated patterns of postoperative pain
- expected outpatient opioid use after CD
- risks and benefits of opioids and nonopioids
- education around opioid disposal and access to refills.
Among the 50 women enrolled in the study, the number of oxycodone 5-mg tablets prescribed at discharge decreased from the institutional standard of 40 to 20. Ninety percent of women reported being satisfied or very satisfied with their pain control, while only 4 of 50 women required an opioid refill. A follow-up quality improvement project, which implemented the shared decision-making model along with a standardized multimodal pain management protocol, demonstrated a similar decrease in the quantity of opioids prescribed at discharge.13
Continue to: Change is here to stay: A new culture of postpartum analgesia...