Morcellation and patient counseling
Uteri up to 12 weeks’ gestational size usually can be extracted transvaginally, and most uteri regardless of size can be morcellated and extracted through the vagina, providing that the vaginal fornix is accessible from below. In some cases, such as when the apex is too high, a minilaparotomic incision is needed to extract the uterus, or when available, power morcellation can be performed.
A major challenge, given our growing ability to laparoscopically remove very larger uteri, is that uteri heavier than about 2.5 kg in weight cannot be morcellated inside a morcellation bag. The risk of upstaging a known or suspected uterine malignancy, or of spreading an unknown malignant sarcoma (presumed benign myoma), should be incorporated in each patient’s decision making.
Thorough counseling about surgical options and on the risks of morcellating a very large uterus without containment in a bag is essential. Each patient must understand the risks and decide whether the benefits of minimally invasive surgery outweigh these risks. While MRI can sometimes provide increased suspicion of a leiomyosarcoma, malignancy can never be completed excluded preoperatively.
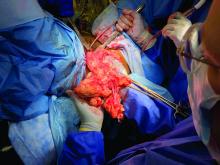
Removal of a 7.4-kg uterus
Our patient was a 44-year-old with a markedly enlarged fibroid uterus. Having been told by other providers that she was not a candidate for minimally invasive hysterectomy, she had delayed surgical management for a number of years, allowing for such a generous uterine size to develop.
The patient was knowledgeable about her condition and, given her comorbid obesity, she requested a minimally invasive approach. Preoperative imaging included an ultrasound, which had to be completed abdominally because of the size of her uterus, and an additional MRI was needed to further characterize the extent and nature of her uterus. A very detailed discussion regarding risk of leiomyosarcoma, operative complications, and conversion to laparotomy ensued.
Intraoperatively, we placed the first 5 mm port in the left upper quadrant initially to survey the anatomy for feasibility of laparoscopic hysterectomy. The left utero-ovarian pedicle was easily viewed by airplaning the bed alone. While the right utero-ovarian pedicle was much more skewed and enlarged, the right IP was easily accessible and the ureter well visualized.
The decision was made to place additional ports and proceed with laparoscopic hysterectomy. The 5-mm assistant ports were placed lateral and directly above the upper vascular pedicles. Operative time was 4 hours and 12 minutes, and blood loss was only 700 cc. Her preoperative hemoglobin was optimized at 13.3 g/dL and dropped to 11.3 g/dL postoperatively. The patient was discharged home the next morning and had a normal recovery with no complications.
Dr. Pasic is professor of obstetrics, gynecology & women’s health; director of the section of advanced gynecologic endoscopy; and codirector of the AAGL fellowship in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery at the University of Louisville (Ky.). Dr. Pasic is the current president of the International Society of Gynecologic Endoscopy. He is also a past president of the AAGL (2009). Dr. Cesta is Dr. Pasic’s current fellow in minimally invasive gynecologic surgery as well as an instructor in obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Louisville. Dr. Pasic disclosed he is a consultant for Ethicon Endo, Medtronic, and Olympus and is a speaker for Cooper Surgical, which manufactures some of the instruments mentioned in this article. Dr. Cesta had no relevant financial disclosures.